MAPN: Enhancing Heterogeneous Sparse Graph Representation by Mamba-based Asynchronous Aggregation
Paper and Code
Feb 23, 2025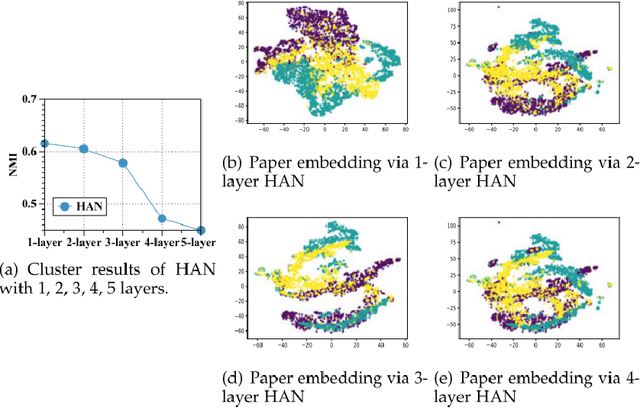
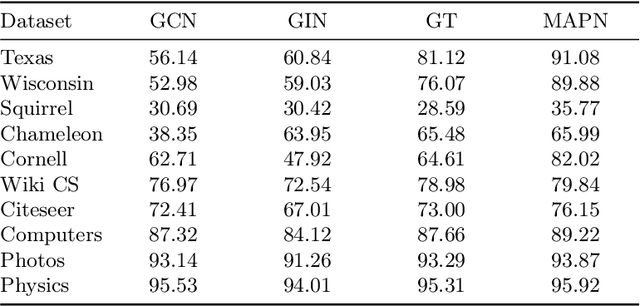
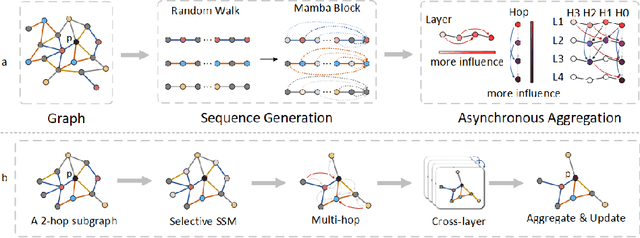
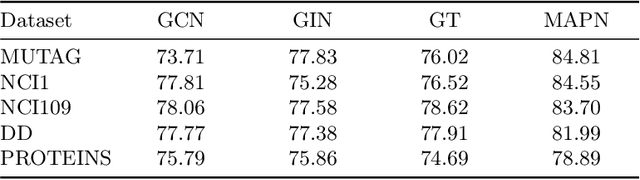
Graph neural networks (GNNs) have become the state of the art for various graph-related tasks and are particularly prominent in heterogeneous graphs (HetGs). However, several issues plague this paradigm: first, the difficulty in fully utilizing long-range information, known as over-squashing; second, the tendency for excessive message-passing layers to produce indistinguishable representations, referred to as over-smoothing; and finally, the inadequacy of conventional MPNNs to train effectively on large sparse graphs. To address these challenges in deep neural networks for large-scale heterogeneous graphs, this paper introduces the Mamba-based Asynchronous Propagation Network (MAPN), which enhances the representation of heterogeneous sparse graphs. MAPN consists of two primary components: node sequence generation and semantic information aggregation. Node sequences are initially generated based on meta-paths through random walks, which serve as the foundation for a spatial state model that extracts essential information from nodes at various distances. It then asynchronously aggregates semantic information across multiple hops and layers, effectively preserving unique node characteristics and mitigating issues related to deep network degradation. Extensive experiments across diverse datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of MAPN in graph embeddings for various downstream tasks underscoring its substantial benefits for graph representation in large sparse heterogeneous graphs.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge