Xunlian Luo
STG4Traffic: A Survey and Benchmark of Spatial-Temporal Graph Neural Networks for Traffic Prediction
Jul 02, 2023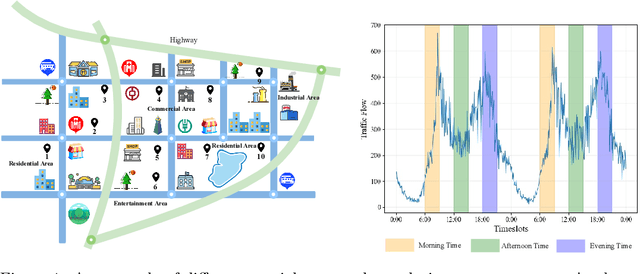
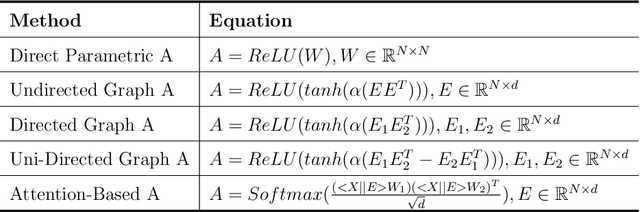
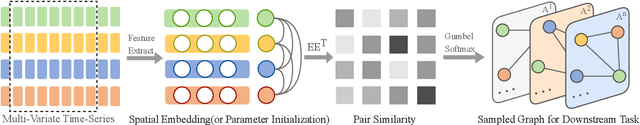
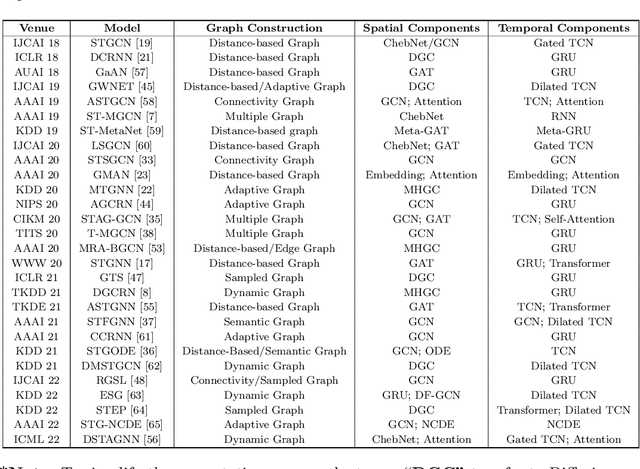
Abstract:Traffic prediction has been an active research topic in the domain of spatial-temporal data mining. Accurate real-time traffic prediction is essential to improve the safety, stability, and versatility of smart city systems, i.e., traffic control and optimal routing. The complex and highly dynamic spatial-temporal dependencies make effective predictions still face many challenges. Recent studies have shown that spatial-temporal graph neural networks exhibit great potential applied to traffic prediction, which combines sequential models with graph convolutional networks to jointly model temporal and spatial correlations. However, a survey study of graph learning, spatial-temporal graph models for traffic, as well as a fair comparison of baseline models are pending and unavoidable issues. In this paper, we first provide a systematic review of graph learning strategies and commonly used graph convolution algorithms. Then we conduct a comprehensive analysis of the strengths and weaknesses of recently proposed spatial-temporal graph network models. Furthermore, we build a study called STG4Traffic using the deep learning framework PyTorch to establish a standardized and scalable benchmark on two types of traffic datasets. We can evaluate their performance by personalizing the model settings with uniform metrics. Finally, we point out some problems in the current study and discuss future directions. Source codes are available at https://github.com/trainingl/STG4Traffic.
Dynamic Graph Convolution Network with Spatio-Temporal Attention Fusion for Traffic Flow Prediction
Feb 24, 2023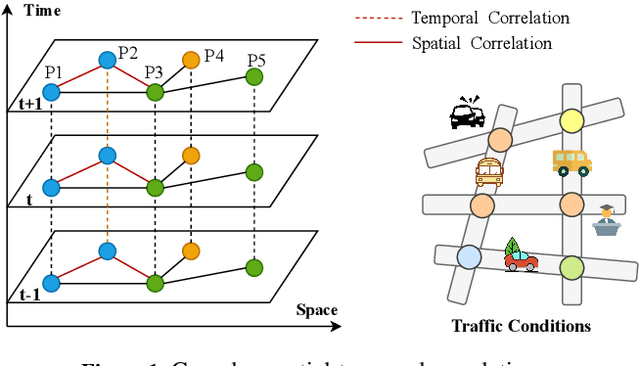
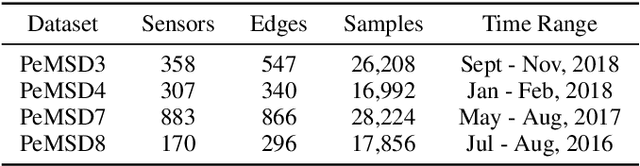
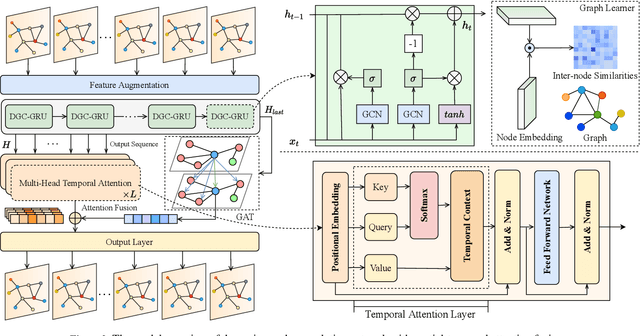
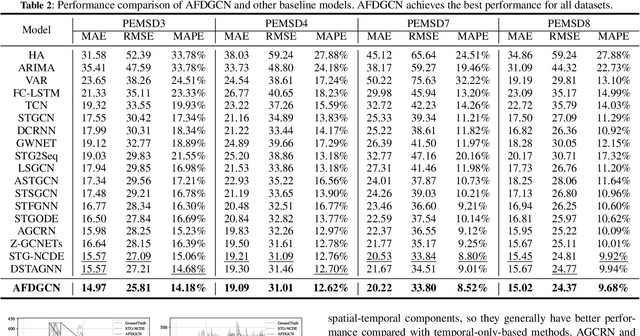
Abstract:Accurate and real-time traffic state prediction is of great practical importance for urban traffic control and web mapping services (e.g. Google Maps). With the support of massive data, deep learning methods have shown their powerful capability in capturing the complex spatio-temporal patterns of road networks. However, existing approaches use independent components to model temporal and spatial dependencies and thus ignore the heterogeneous characteristics of traffic flow that vary with time and space. In this paper, we propose a novel dynamic graph convolution network with spatio-temporal attention fusion. The method not only captures local spatio-temporal information that changes over time, but also comprehensively models long-distance and multi-scale spatio-temporal patterns based on the fusion mechanism of temporal and spatial attention. This design idea can greatly improve the spatio-temporal perception of the model. We conduct extensive experiments in 4 real-world datasets to demonstrate that our model achieves state-of-the-art performance compared to 22 baseline models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge