Xuanyu Shi
An automated approach to extracting positive and negative clinical research results
Dec 07, 2022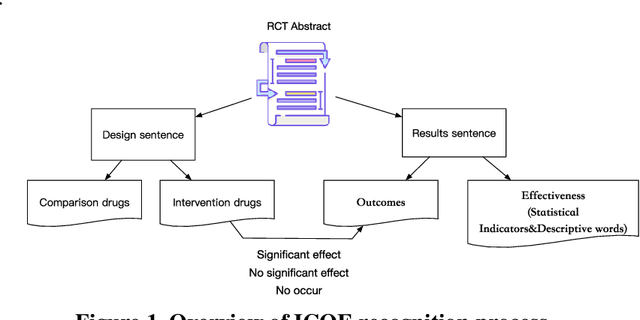
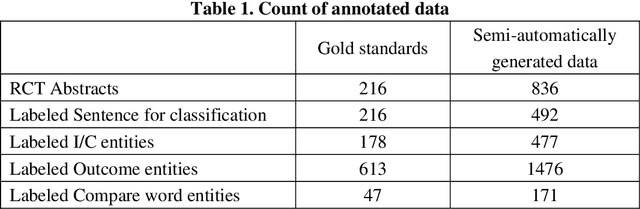
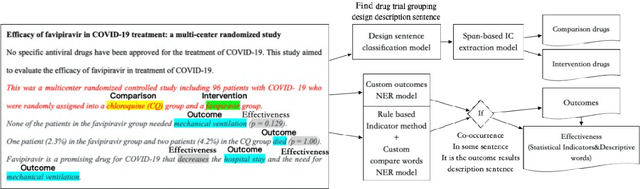
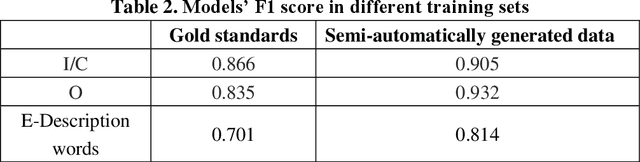
Abstract:Failure is common in clinical trials since the successful failures presented in negative results always indicate the ways that should not be taken. In this paper, we proposed an automated approach to extracting positive and negative clinical research results by introducing a PICOE (Population, Intervention, Comparation, Outcome, and Effect) framework to represent randomized controlled trials (RCT) reports, where E indicates the effect between a specific I and O. We developed a pipeline to extract and assign the corresponding statistical effect to a specific I-O pair from natural language RCT reports. The extraction models achieved a high degree of accuracy for ICO and E descriptive words extraction through two rounds of training. By defining a threshold of p-value, we find in all Covid-19 related intervention-outcomes pairs with statistical tests, negative results account for nearly 40%. We believe that this observation is noteworthy since they are extracted from the published literature, in which there is an inherent risk of reporting bias, preferring to report positive results rather than negative results. We provided a tool to systematically understand the current level of clinical evidence by distinguishing negative results from the positive results.
Distinguishing Transformative from Incremental Clinical Evidence: A Classifier of Clinical Research using Textual features from Abstracts and Citing Sentences
Dec 24, 2021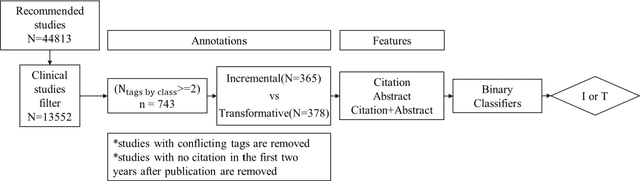
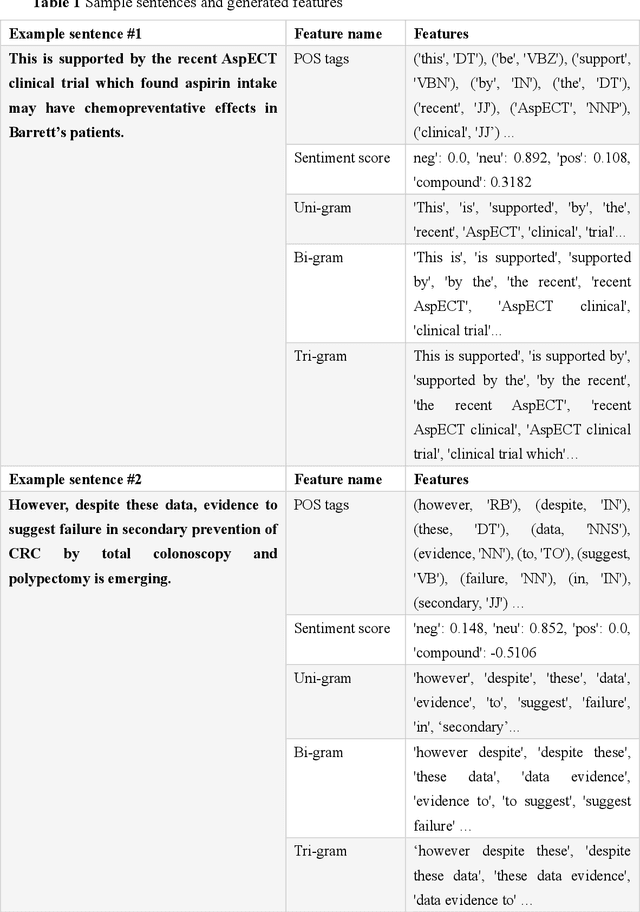
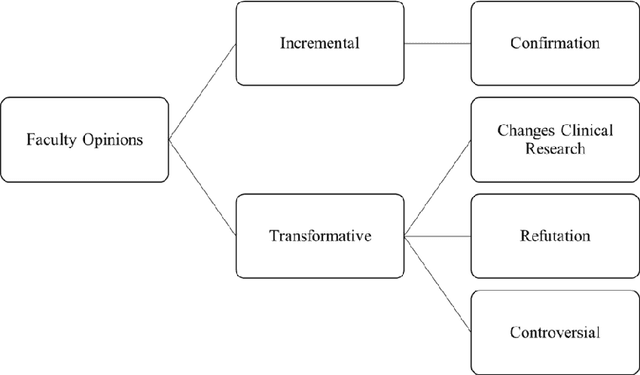
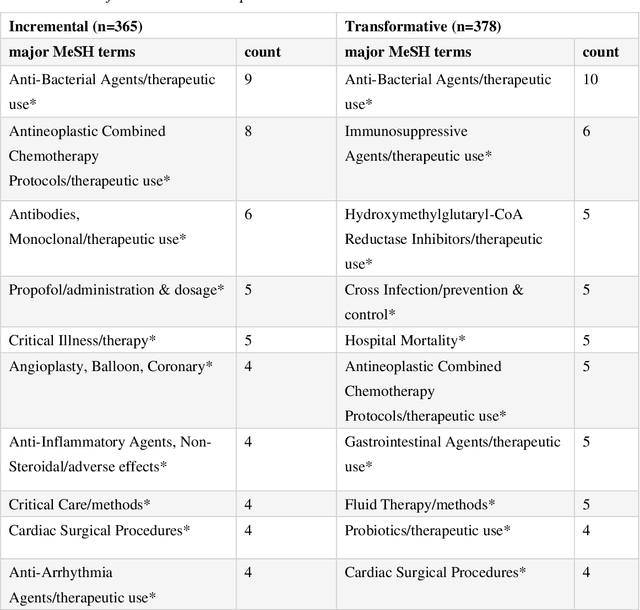
Abstract:In clinical research and clinical decision-making, it is important to know if a study changes or only supports the current standards of care for specific disease management. We define such a change as transformative and a support as incremental research. It usually requires a huge amount of domain expertise and time for humans to finish such tasks. Faculty Opinions provides us with a well-annotated corpus on whether a research challenges or only confirms established research. In this study, a machine learning approach is proposed to distinguishing transformative from incremental clinical evidence. The texts from both abstract and a 2-year window of citing sentences are collected for a training set of clinical studies recommended and labeled by Faculty Opinions experts. We achieve the best performance with an average AUC of 0.755 (0.705-0.875) using Random Forest as the classifier and citing sentences as the feature. The results showed that transformative research has typical language patterns in citing sentences unlike abstract sentences. We provide an efficient tool for identifying those clinical evidence challenging or only confirming established claims for clinicians and researchers.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge