Xinhong Dai
Energy-Efficient UAV-Mounted RIS Assisted Mobile Edge Computing
Mar 24, 2022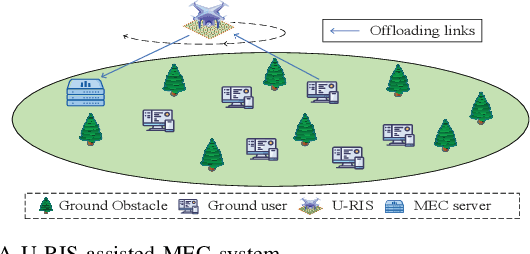
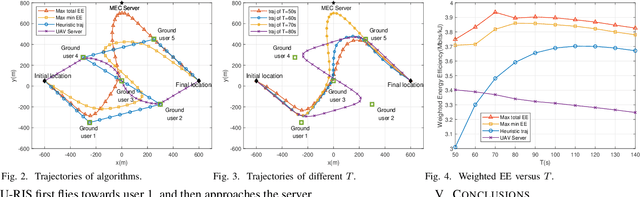
Abstract:Unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) and reconfigurable intelligent surface (RIS) have been recently applied in the field of mobile edge computing (MEC) to improve the data exchange environment by proactively changing the wireless channels through maneuverable location deployment and intelligent signals reflection, respectively. Nevertheless, they may suffer from inherent limitations in practical scenarios. UAV-mounted RIS (U-RIS), as a promising integrated approach, can combine the advantages of UAV and RIS to break the limit. Inspired by this, we consider a novel U-RIS assisted MEC system, where a U-RIS is deployed to assist the communication between the ground users and an MEC server. The joint UAV trajectory, RIS passive beamforming and MEC resource allocation design is developed to maximize the energy efficiency (EE) of the system. To tackle the intractable non-convex problem, we divide it into two subproblems and solve them iteratively based on successive convex approximation (SCA) and the Dinkelbach method. Finally we obtain a high-performance suboptimal solution. Simulation results show that the proposed algorithm significantly improves the energy efficiency of the MEC system.
Energy-Efficient UAV Communications: A Generalised Propulsion Energy Consumption Model
Feb 17, 2022

Abstract:This paper proposes a generalised propulsion energy consumption model (PECM) for rotary-wing ummanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) under the consideration of the practical thrust-to-weight ratio (TWR) with respect to the velocity, acceleration and direction change of the UAVs. To verify the effectiveness of the proposed PECM, we consider a UAV-enabled communication system, where a rotary-wing UAV serves multiple ground users as an aerial base station. We aim to maximize the energy efficiency (EE) of the UAV by jointly optimizing the user scheduling and UAV trajectory variables. However, the formulated problem is a non-convex fractional integer programming problem, which is challenging to obtain its optimal solution. To tackle this, we propose an efficient iterative algorithm by decomposing the original problem into two sub-problems to obtain a suboptimal solution based on the successive convex approximation technique. Simulation results show that the optimized UAV trajectory by applying the proposed PECM are smoother and the corresponding EE has significant improvement as compared to other benchmark schemes.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge