Xingchen Zhang
SSVIF: Self-Supervised Segmentation-Oriented Visible and Infrared Image Fusion
Sep 26, 2025Abstract:Visible and infrared image fusion (VIF) has gained significant attention in recent years due to its wide application in tasks such as scene segmentation and object detection. VIF methods can be broadly classified into traditional VIF methods and application-oriented VIF methods. Traditional methods focus solely on improving the quality of fused images, while application-oriented VIF methods additionally consider the performance of downstream tasks on fused images by introducing task-specific loss terms during training. However, compared to traditional methods, application-oriented VIF methods require datasets labeled for downstream tasks (e.g., semantic segmentation or object detection), making data acquisition labor-intensive and time-consuming. To address this issue, we propose a self-supervised training framework for segmentation-oriented VIF methods (SSVIF). Leveraging the consistency between feature-level fusion-based segmentation and pixel-level fusion-based segmentation, we introduce a novel self-supervised task-cross-segmentation consistency-that enables the fusion model to learn high-level semantic features without the supervision of segmentation labels. Additionally, we design a two-stage training strategy and a dynamic weight adjustment method for effective joint learning within our self-supervised framework. Extensive experiments on public datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed SSVIF. Remarkably, although trained only on unlabeled visible-infrared image pairs, our SSVIF outperforms traditional VIF methods and rivals supervised segmentation-oriented ones. Our code will be released upon acceptance.
FusionCounting: Robust visible-infrared image fusion guided by crowd counting via multi-task learning
Aug 28, 2025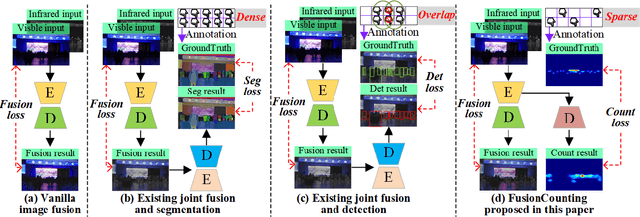

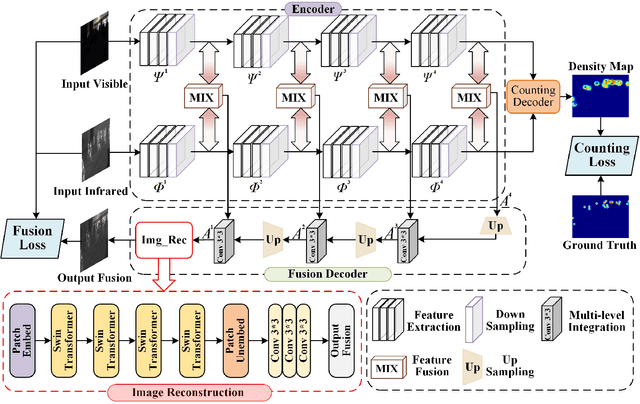
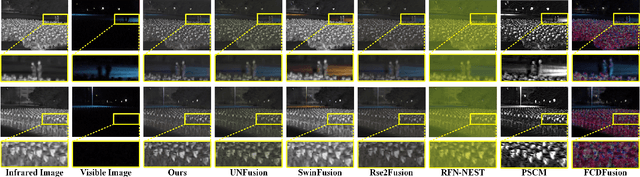
Abstract:Most visible and infrared image fusion (VIF) methods focus primarily on optimizing fused image quality. Recent studies have begun incorporating downstream tasks, such as semantic segmentation and object detection, to provide semantic guidance for VIF. However, semantic segmentation requires extensive annotations, while object detection, despite reducing annotation efforts compared with segmentation, faces challenges in highly crowded scenes due to overlapping bounding boxes and occlusion. Moreover, although RGB-T crowd counting has gained increasing attention in recent years, no studies have integrated VIF and crowd counting into a unified framework. To address these challenges, we propose FusionCounting, a novel multi-task learning framework that integrates crowd counting into the VIF process. Crowd counting provides a direct quantitative measure of population density with minimal annotation, making it particularly suitable for dense scenes. Our framework leverages both input images and population density information in a mutually beneficial multi-task design. To accelerate convergence and balance tasks contributions, we introduce a dynamic loss function weighting strategy. Furthermore, we incorporate adversarial training to enhance the robustness of both VIF and crowd counting, improving the model's stability and resilience to adversarial attacks. Experimental results on public datasets demonstrate that FusionCounting not only enhances image fusion quality but also achieves superior crowd counting performance.
MultiTaskVIF: Segmentation-oriented visible and infrared image fusion via multi-task learning
May 10, 2025Abstract:Visible and infrared image fusion (VIF) has attracted significant attention in recent years. Traditional VIF methods primarily focus on generating fused images with high visual quality, while recent advancements increasingly emphasize incorporating semantic information into the fusion model during training. However, most existing segmentation-oriented VIF methods adopt a cascade structure comprising separate fusion and segmentation models, leading to increased network complexity and redundancy. This raises a critical question: can we design a more concise and efficient structure to integrate semantic information directly into the fusion model during training-Inspired by multi-task learning, we propose a concise and universal training framework, MultiTaskVIF, for segmentation-oriented VIF models. In this framework, we introduce a multi-task head decoder (MTH) to simultaneously output both the fused image and the segmentation result during training. Unlike previous cascade training frameworks that necessitate joint training with a complete segmentation model, MultiTaskVIF enables the fusion model to learn semantic features by simply replacing its decoder with MTH. Extensive experimental evaluations validate the effectiveness of the proposed method. Our code will be released upon acceptance.
Self-Supervised RGB-T Tracking with Cross-Input Consistency
Jan 26, 2023



Abstract:In this paper, we propose a self-supervised RGB-T tracking method. Different from existing deep RGB-T trackers that use a large number of annotated RGB-T image pairs for training, our RGB-T tracker is trained using unlabeled RGB-T video pairs in a self-supervised manner. We propose a novel cross-input consistency-based self-supervised training strategy based on the idea that tracking can be performed using different inputs. Specifically, we construct two distinct inputs using unlabeled RGB-T video pairs. We then track objects using these two inputs to generate results, based on which we construct our cross-input consistency loss. Meanwhile, we propose a reweighting strategy to make our loss function robust to low-quality training samples. We build our tracker on a Siamese correlation filter network. To the best of our knowledge, our tracker is the first self-supervised RGB-T tracker. Extensive experiments on two public RGB-T tracking benchmarks demonstrate that the proposed training strategy is effective. Remarkably, despite training only with a corpus of unlabeled RGB-T video pairs, our tracker outperforms seven supervised RGB-T trackers on the GTOT dataset.
Benchmarking and Comparing Multi-exposure Image Fusion Algorithms
Jul 30, 2020



Abstract:Multi-exposure image fusion (MEF) is an important area in computer vision and has attracted increasing interests in recent years. Apart from conventional algorithms, deep learning techniques have also been applied to multi-exposure image fusion. However, although much efforts have been made on developing MEF algorithms, the lack of benchmark makes it difficult to perform fair and comprehensive performance comparison among MEF algorithms, thus significantly hindering the development of this field. In this paper, we fill this gap by proposing a benchmark for multi-exposure image fusion (MEFB) which consists of a test set of 100 image pairs, a code library of 16 algorithms, 20 evaluation metrics, 1600 fused images and a software toolkit. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first benchmark in the field of multi-exposure image fusion. Extensive experiments have been conducted using MEFB for comprehensive performance evaluation and for identifying effective algorithms. We expect that MEFB will serve as an effective platform for researchers to compare performances and investigate MEF algorithms.
Multi-focus Image Fusion: A Benchmark
May 03, 2020



Abstract:Multi-focus image fusion (MFIF) has attracted considerable interests due to its numerous applications. While much progress has been made in recent years with efforts on developing various MFIF algorithms, some issues significantly hinder the fair and comprehensive performance comparison of MFIF methods, such as the lack of large-scale test set and the random choices of objective evaluation metrics in the literature. To solve these issues, this paper presents a multi-focus image fusion benchmark (MFIFB) which consists a test set of 105 image pairs, a code library of 30 MFIF algorithms, and 20 evaluation metrics. MFIFB is the first benchmark in the field of MFIF and provides the community a platform to compare MFIF algorithms fairly and comprehensively. Extensive experiments have been conducted using the proposed MFIFB to understand the performance of these algorithms. By analyzing the experimental results, effective MFIF algorithms are identified. More importantly, some observations on the status of the MFIF field are given, which can help to understand this field better.
VIFB: A Visible and Infrared Image Fusion Benchmark
Feb 09, 2020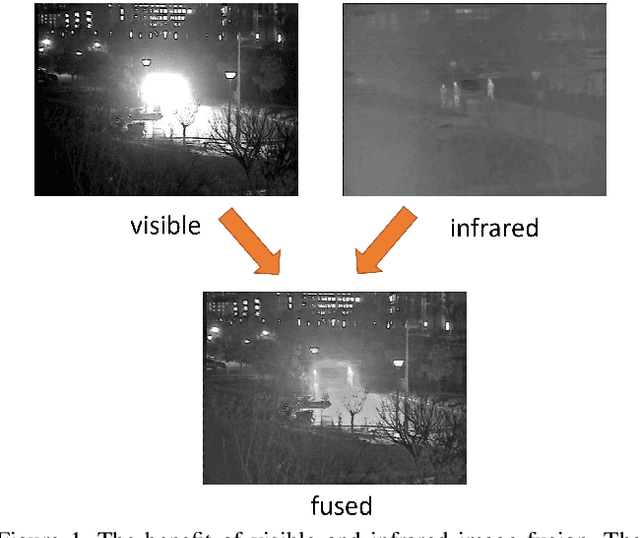


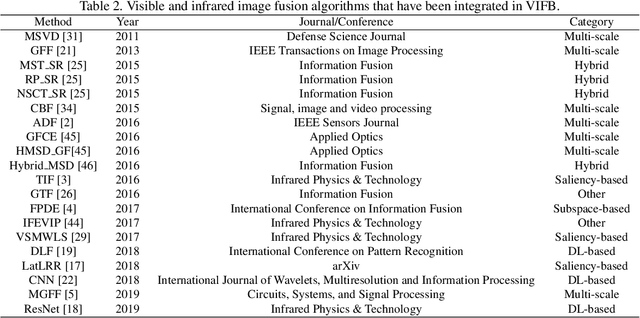
Abstract:Visible and infrared image fusion is one of the most important areas in image processing due to its numerous applications. While much progress has been made in recent years with efforts on developing fusion algorithms, there is a lack of code library and benchmark which can gauge the state-of-the-art. In this paper, after briefly reviewing recent advances of visible and infrared image fusion, we present a visible and infrared image fusion benchmark (VIFB) which consists of 21 image pairs, a code library of 20 fusion algorithms and 13 evaluation metrics. We also carry out large scale experiments within the benchmark to understand the performance of these algorithms. By analyzing qualitative and quantitative results, we identify effective algorithms for robust image fusion and give some observations on the status and future prospects of this field. The benchmark, including dataset, code library, evaluation metrics, and results is available upon request.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge