Xin-yu Dai
Generating Diverse Translation by Manipulating Multi-Head Attention
Nov 21, 2019



Abstract:Transformer model has been widely used on machine translation tasks and obtained state-of-the-art results. In this paper, we report an interesting phenomenon in its encoder-decoder multi-head attention: different attention heads of the final decoder layer align to different word translation candidates. We empirically verify this discovery and propose a method to generate diverse translations by manipulating heads. Furthermore, we make use of these diverse translations with the back-translation technique for better data augmentation. Experiment results show that our method generates diverse translations without severe drop in translation quality. Experiments also show that back-translation with these diverse translations could bring significant improvement on performance on translation tasks. An auxiliary experiment of conversation response generation task proves the effect of diversity as well.
Pre-train and Learn: Preserve Global Information for Graph Neural Networks
Oct 27, 2019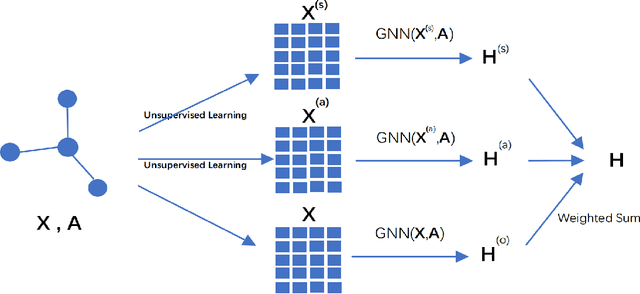
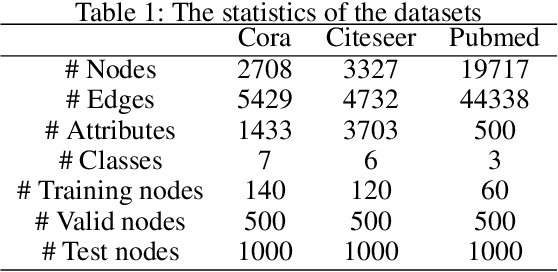
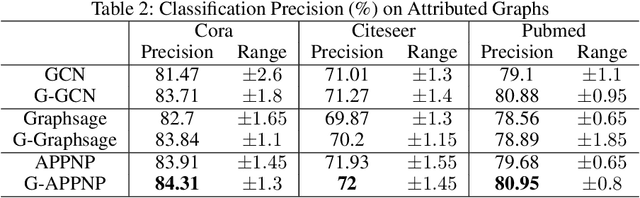
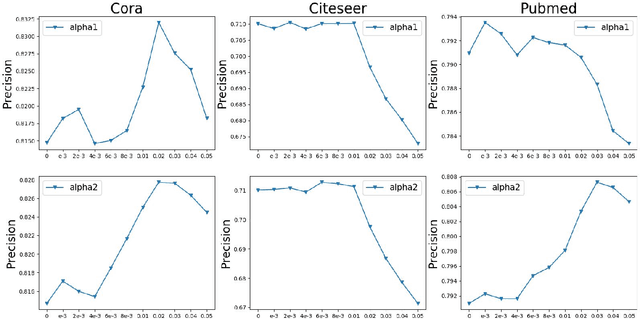
Abstract:Graph neural networks (GNNs) have shown great power in learning on attributed graphs. However, it is still a challenge for GNNs to utilize information faraway from the source node. Moreover, general GNNs require graph attributes as input, so they cannot be appled to plain graphs. In the paper, we propose new models named G-GNNs (Global information for GNNs) to address the above limitations. First, the global structure and attribute features for each node are obtained via unsupervised pre-training, which preserve the global information associated to the node. Then, using the global features and the raw network attributes, we propose a parallel framework of GNNs to learn different aspects from these features. The proposed learning methods can be applied to both plain graphs and attributed graphs. Extensive experiments have shown that G-GNNs can outperform other state-of-the-art models on three standard evaluation graphs. Specially, our methods establish new benchmark records on Cora (84.31\%) and Pubmed (80.95\%) when learning on attributed graphs.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge