Xiaobo Yang
STEP3-VL-10B Technical Report
Jan 15, 2026Abstract:We present STEP3-VL-10B, a lightweight open-source foundation model designed to redefine the trade-off between compact efficiency and frontier-level multimodal intelligence. STEP3-VL-10B is realized through two strategic shifts: first, a unified, fully unfrozen pre-training strategy on 1.2T multimodal tokens that integrates a language-aligned Perception Encoder with a Qwen3-8B decoder to establish intrinsic vision-language synergy; and second, a scaled post-training pipeline featuring over 1k iterations of reinforcement learning. Crucially, we implement Parallel Coordinated Reasoning (PaCoRe) to scale test-time compute, allocating resources to scalable perceptual reasoning that explores and synthesizes diverse visual hypotheses. Consequently, despite its compact 10B footprint, STEP3-VL-10B rivals or surpasses models 10$\times$-20$\times$ larger (e.g., GLM-4.6V-106B, Qwen3-VL-235B) and top-tier proprietary flagships like Gemini 2.5 Pro and Seed-1.5-VL. Delivering best-in-class performance, it records 92.2% on MMBench and 80.11% on MMMU, while excelling in complex reasoning with 94.43% on AIME2025 and 75.95% on MathVision. We release the full model suite to provide the community with a powerful, efficient, and reproducible baseline.
PaCoRe: Learning to Scale Test-Time Compute with Parallel Coordinated Reasoning
Jan 09, 2026Abstract:We introduce Parallel Coordinated Reasoning (PaCoRe), a training-and-inference framework designed to overcome a central limitation of contemporary language models: their inability to scale test-time compute (TTC) far beyond sequential reasoning under a fixed context window. PaCoRe departs from the traditional sequential paradigm by driving TTC through massive parallel exploration coordinated via a message-passing architecture in multiple rounds. Each round launches many parallel reasoning trajectories, compacts their findings into context-bounded messages, and synthesizes these messages to guide the next round and ultimately produce the final answer. Trained end-to-end with large-scale, outcome-based reinforcement learning, the model masters the synthesis abilities required by PaCoRe and scales to multi-million-token effective TTC without exceeding context limits. The approach yields strong improvements across diverse domains, and notably pushes reasoning beyond frontier systems in mathematics: an 8B model reaches 94.5% on HMMT 2025, surpassing GPT-5's 93.2% by scaling effective TTC to roughly two million tokens. We open-source model checkpoints, training data, and the full inference pipeline to accelerate follow-up work.
VidFormer: A novel end-to-end framework fused by 3DCNN and Transformer for Video-based Remote Physiological Measurement
Jan 07, 2025



Abstract:Remote physiological signal measurement based on facial videos, also known as remote photoplethysmography (rPPG), involves predicting changes in facial vascular blood flow from facial videos. While most deep learning-based methods have achieved good results, they often struggle to balance performance across small and large-scale datasets due to the inherent limitations of convolutional neural networks (CNNs) and Transformer. In this paper, we introduce VidFormer, a novel end-to-end framework that integrates 3-Dimension Convolutional Neural Network (3DCNN) and Transformer models for rPPG tasks. Initially, we conduct an analysis of the traditional skin reflection model and subsequently introduce an enhanced model for the reconstruction of rPPG signals. Based on this improved model, VidFormer utilizes 3DCNN and Transformer to extract local and global features from input data, respectively. To enhance the spatiotemporal feature extraction capabilities of VidFormer, we incorporate temporal-spatial attention mechanisms tailored for both 3DCNN and Transformer. Additionally, we design a module to facilitate information exchange and fusion between the 3DCNN and Transformer. Our evaluation on five publicly available datasets demonstrates that VidFormer outperforms current state-of-the-art (SOTA) methods. Finally, we discuss the essential roles of each VidFormer module and examine the effects of ethnicity, makeup, and exercise on its performance.
Tuning-free Universally-Supervised Semantic Segmentation
May 23, 2024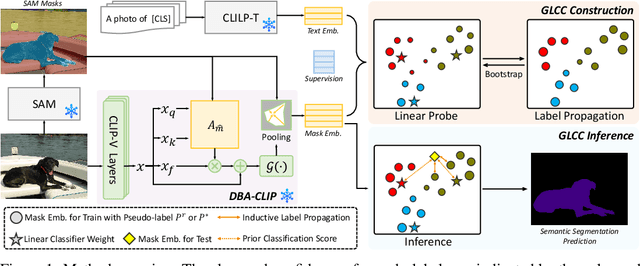
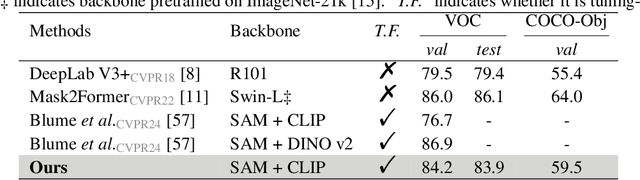
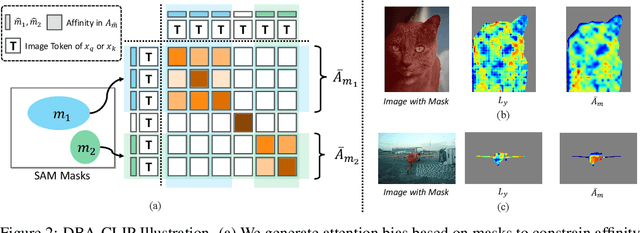
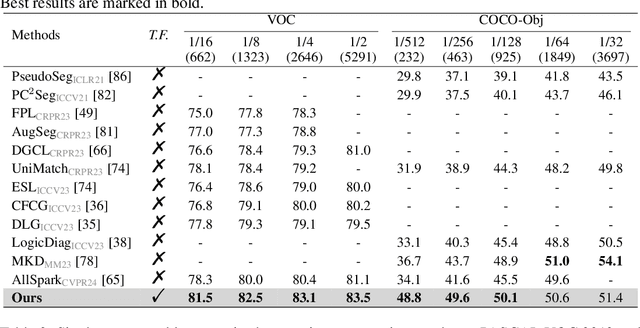
Abstract:This work presents a tuning-free semantic segmentation framework based on classifying SAM masks by CLIP, which is universally applicable to various types of supervision. Initially, we utilize CLIP's zero-shot classification ability to generate pseudo-labels or perform open-vocabulary segmentation. However, the misalignment between mask and CLIP text embeddings leads to suboptimal results. To address this issue, we propose discrimination-bias aligned CLIP to closely align mask and text embedding, offering an overhead-free performance gain. We then construct a global-local consistent classifier to classify SAM masks, which reveals the intrinsic structure of high-quality embeddings produced by DBA-CLIP and demonstrates robustness against noisy pseudo-labels. Extensive experiments validate the efficiency and effectiveness of our method, and we achieve state-of-the-art (SOTA) or competitive performance across various datasets and supervision types.
Foundation Model Assisted Weakly Supervised Semantic Segmentation
Dec 10, 2023Abstract:This work aims to leverage pre-trained foundation models, such as contrastive language-image pre-training (CLIP) and segment anything model (SAM), to address weakly supervised semantic segmentation (WSSS) using image-level labels. To this end, we propose a coarse-to-fine framework based on CLIP and SAM for generating high-quality segmentation seeds. Specifically, we construct an image classification task and a seed segmentation task, which are jointly performed by CLIP with frozen weights and two sets of learnable task-specific prompts. A SAM-based seeding (SAMS) module is designed and applied to each task to produce either coarse or fine seed maps. Moreover, we design a multi-label contrastive loss supervised by image-level labels and a CAM activation loss supervised by the generated coarse seed map. These losses are used to learn the prompts, which are the only parts need to be learned in our framework. Once the prompts are learned, we input each image along with the learned segmentation-specific prompts into CLIP and the SAMS module to produce high-quality segmentation seeds. These seeds serve as pseudo labels to train an off-the-shelf segmentation network like other two-stage WSSS methods. Experiments show that our method achieves the state-of-the-art performance on PASCAL VOC 2012 and competitive results on MS COCO 2014. Code is available at https://github.com/HAL-42/FMA-WSSS.git.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge