Xi-Zhi Niu
Uncovering the Mechanism of Hepatotoxiciy of PFAS Targeting L-FABP Using GCN and Computational Modeling
Sep 16, 2024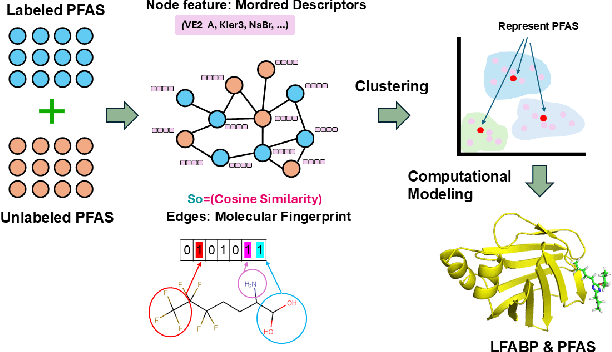
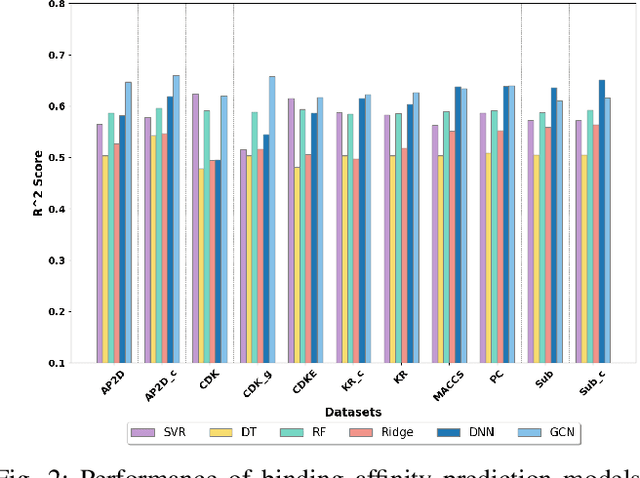
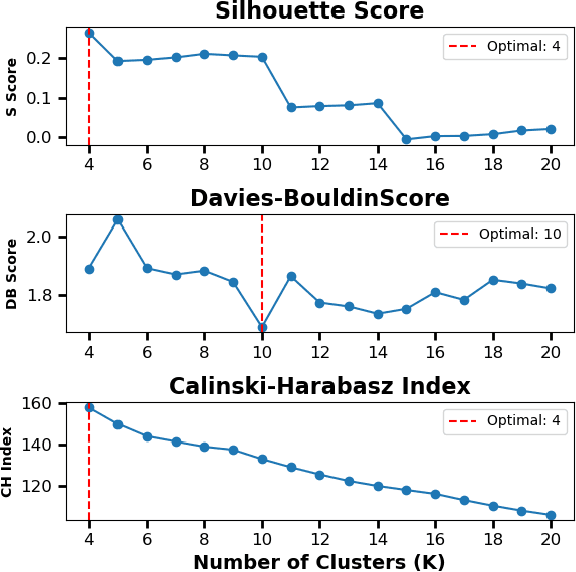
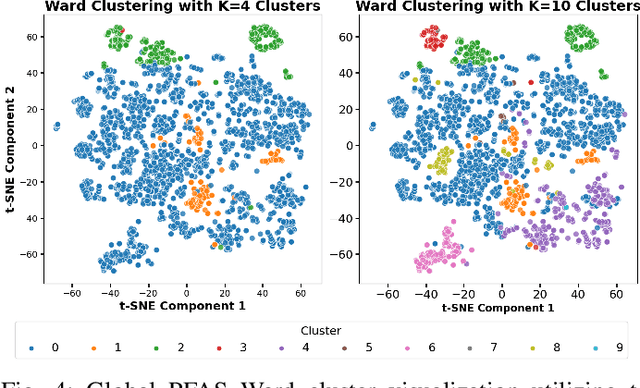
Abstract:Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) are persistent environmental pollutants with known toxicity and bioaccumulation issues. Their widespread industrial use and resistance to degradation have led to global environmental contamination and significant health concerns. While a minority of PFAS have been extensively studied, the toxicity of many PFAS remains poorly understood due to limited direct toxicological data. This study advances the predictive modeling of PFAS toxicity by combining semi-supervised graph convolutional networks (GCNs) with molecular descriptors and fingerprints. We propose a novel approach to enhance the prediction of PFAS binding affinities by isolating molecular fingerprints to construct graphs where then descriptors are set as the node features. This approach specifically captures the structural, physicochemical, and topological features of PFAS without overfitting due to an abundance of features. Unsupervised clustering then identifies representative compounds for detailed binding studies. Our results provide a more accurate ability to estimate PFAS hepatotoxicity to provide guidance in chemical discovery of new PFAS and the development of new safety regulations.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge