Xavier Lorca
Bounds of MIN_NCC and MAX_NCC and filtering scheme for graph domain variables
May 03, 2021Abstract:Graph domain variables and constraints are an extension of constraint programming introduced by Dooms et al. This approach had been further investigated by Fages in its PhD thesis. On the other hand, Beldiceanu et al. presented a generic filtering scheme for global constraints based on graph properties. This scheme strongly relies on the computation of graph properties' bounds and can be used in the context of graph domain variables and constraints with a few adjustments. Bounds of MIN_NCC and MAX_NCC had been defined for the graph-based representation of global constraint for the path_with_loops graph class. In this note, we generalize those bounds for graph domain variables and for any graph class. We also provide a filtering scheme for any graph class and arbitrary bounds.
Event Selection Rules to Compute Explanations
Aug 29, 2016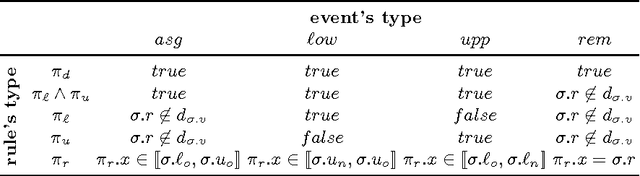
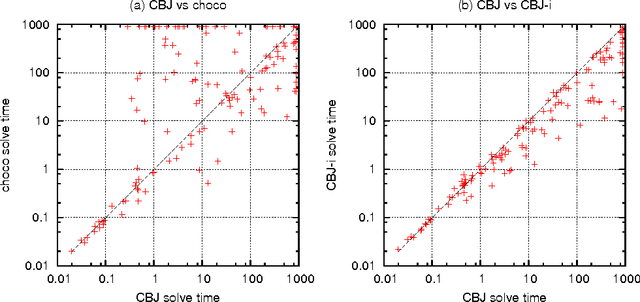
Abstract:Explanations have been introduced in the previous century. Their interest in reducing the search space is no longer questioned. Yet, their efficient implementation into CSP solver is still a challenge. In this paper, we introduce ESeR, an Event Selection Rules algorithm that filters events generated during propagation. This dynamic selection enables an efficient computation of explanations for intelligent backtracking al- gorithms. We show the effectiveness of our approach on the instances of the last three MiniZinc challenges
A Probabilistic-Based Model for Binary CSP
Jun 13, 2016

Abstract:This work introduces a probabilistic-based model for binary CSP that provides a fine grained analysis of its internal structure. Assuming that a domain modification could occur in the CSP, it shows how to express, in a predictive way, the probability that a domain value becomes inconsistent, then it express the expectation of the number of arc-inconsistent values in each domain of the constraint network. Thus, it express the expectation of the number of arc-inconsistent values for the whole constraint network. Next, it provides bounds for each of these three probabilistic indicators. Finally, a polytime algorithm, which propagates the probabilistic information, is presented.
Improving the Asymmetric TSP by Considering Graph Structure
Jun 15, 2012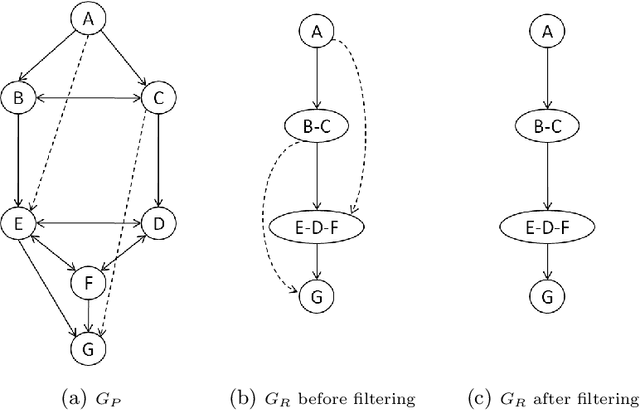
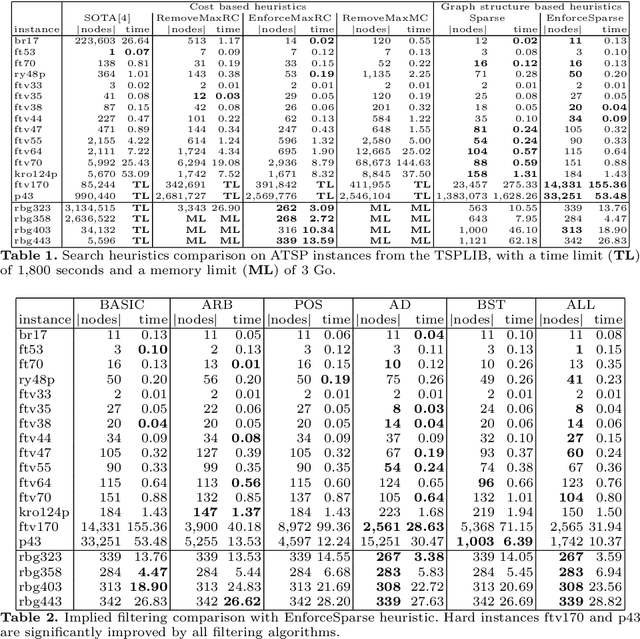
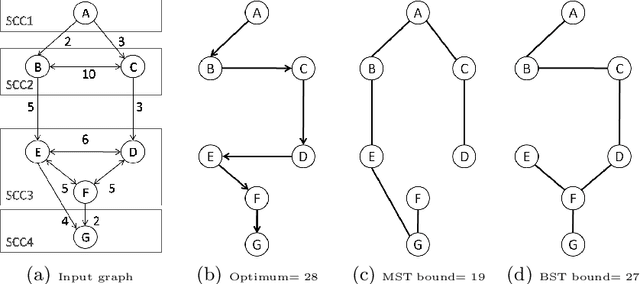
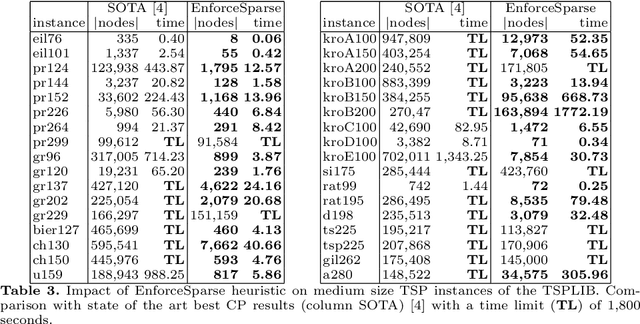
Abstract:Recent works on cost based relaxations have improved Constraint Programming (CP) models for the Traveling Salesman Problem (TSP). We provide a short survey over solving asymmetric TSP with CP. Then, we suggest new implied propagators based on general graph properties. We experimentally show that such implied propagators bring robustness to pathological instances and highlight the fact that graph structure can significantly improve search heuristics behavior. Finally, we show that our approach outperforms current state of the art results.
A Generalized Arc-Consistency Algorithm for a Class of Counting Constraints: Revised Edition that Incorporates One Correction
Oct 21, 2011Abstract:This paper introduces the SEQ BIN meta-constraint with a polytime algorithm achieving general- ized arc-consistency according to some properties. SEQ BIN can be used for encoding counting con- straints such as CHANGE, SMOOTH or INCREAS- ING NVALUE. For some of these constraints and some of their variants GAC can be enforced with a time and space complexity linear in the sum of domain sizes, which improves or equals the best known results of the literature.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge