Woochan Hwang
Integrating Reinforcement Learning to Self Training for Pulmonary Nodule Segmentation in Chest X-rays
Nov 21, 2018

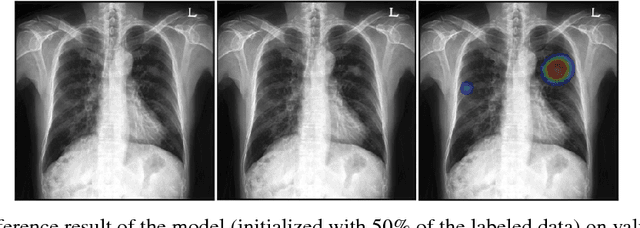
Abstract:Machine learning applications in medical imaging are frequently limited by the lack of quality labeled data. In this paper, we explore the self training method, a form of semi-supervised learning, to address the labeling burden. By integrating reinforcement learning, we were able to expand the application of self training to complex segmentation networks without any further human annotation. The proposed approach, reinforced self training (ReST), fine tunes a semantic segmentation networks by introducing a policy network that learns to generate pseudolabels. We incorporate an expert demonstration network, based on inverse reinforcement learning, to enhance clinical validity and convergence of the policy network. The model was tested on a pulmonary nodule segmentation task in chest X-rays and achieved the performance of a standard U-Net while using only 50% of the labeled data, by exploiting unlabeled data. When the same number of labeled data was used, a moderate to significant cross validation accuracy improvement was achieved depending on the absolute number of labels used.
False Positive Reduction by Actively Mining Negative Samples for Pulmonary Nodule Detection in Chest Radiographs
Jul 26, 2018


Abstract:Generating large quantities of quality labeled data in medical imaging is very time consuming and expensive. The performance of supervised algorithms for various tasks on imaging has improved drastically over the years, however the availability of data to train these algorithms have become one of the main bottlenecks for implementation. To address this, we propose a semi-supervised learning method where pseudo-negative labels from unlabeled data are used to further refine the performance of a pulmonary nodule detection network in chest radiographs. After training with the proposed network, the false positive rate was reduced to 0.1266 from 0.4864 while maintaining sensitivity at 0.89.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge