Wolf-Tilo Balke
A Conceptual Model for Attributions in Event-Centric Knowledge Graphs
Mar 05, 2025Abstract:The use of narratives as a means of fusing information from knowledge graphs (KGs) into a coherent line of argumentation has been the subject of recent investigation. Narratives are especially useful in event-centric knowledge graphs in that they provide a means to connect different real-world events and categorize them by well-known narrations. However, specifically for controversial events, a problem in information fusion arises, namely, multiple viewpoints regarding the validity of certain event aspects, e.g., regarding the role a participant takes in an event, may exist. Expressing those viewpoints in KGs is challenging because disputed information provided by different viewpoints may introduce inconsistencies. Hence, most KGs only feature a single view on the contained information, hampering the effectiveness of narrative information access. This paper is an extension of our original work and introduces attributions, i.e., parameterized predicates that allow for the representation of facts that are only valid in a specific viewpoint. For this, we develop a conceptual model that allows for the representation of viewpoint-dependent information. As an extension, we enhance the model by a conception of viewpoint-compatibility. Based on this, we deepen our original deliberations on the model's effects on information fusion and provide additional grounding in the literature.
Lost in Recursion: Mining Rich Event Semantics in Knowledge Graphs
Apr 25, 2024Abstract:Our world is shaped by events of various complexity. This includes both small-scale local events like local farmer markets and large complex events like political and military conflicts. The latter are typically not observed directly but through the lenses of intermediaries like newspapers or social media. In other words, we do not witness the unfolding of such events directly but are confronted with narratives surrounding them. Such narratives capture different aspects of a complex event and may also differ with respect to the narrator. Thus, they provide a rich semantics concerning real-world events. In this paper, we show how narratives concerning complex events can be constructed and utilized. We provide a formal representation of narratives based on recursive nodes to represent multiple levels of detail and discuss how narratives can be bound to event-centric knowledge graphs. Additionally, we provide an algorithm based on incremental prompting techniques that mines such narratives from texts to account for different perspectives on complex events. Finally, we show the effectiveness and future research directions in a proof of concept.
On Dimensions of Plausibility for Narrative Information Access to Digital Libraries
Aug 22, 2022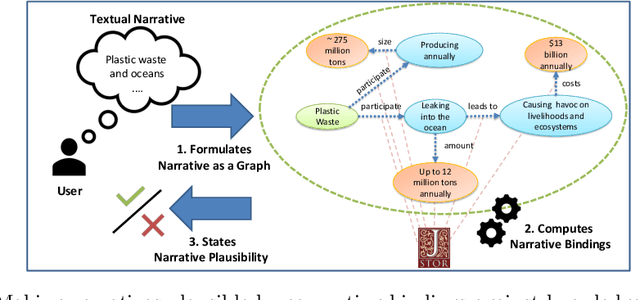
Abstract:Designing keyword-based access paths is a common practice in digital libraries. They are easy to use and accepted by users and come with moderate costs for content providers. However, users usually have to break down the search into pieces if they search for stories of interest that are more complex than searching for a few keywords. After searching for every piece one by one, information must then be reassembled manually. In previous work we recommended narrative information access, i.e., users can precisely state their information needs as graph patterns called narratives. Then a system takes a narrative and searches for evidence for each of its parts. If the whole query, i.e., every part, can be bound against data, the narrative is considered plausible and, thus, the query is answered. But is it as easy as that? In this work we perform case studies to analyze the process of making a given narrative plausible. Therefore, we summarize conceptual problems and challenges to face. Moreover, we contribute a set of dimensions that must be considered when realizing narrative information access in digital libraries.
It's the Same Old Story! Enriching Event-Centric Knowledge Graphs by Narrative Aspects
May 08, 2022
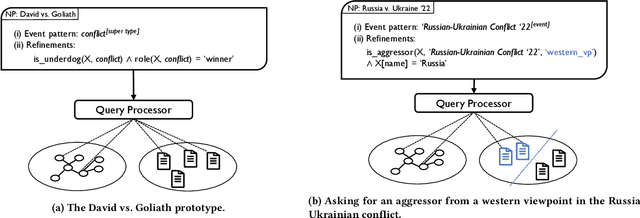
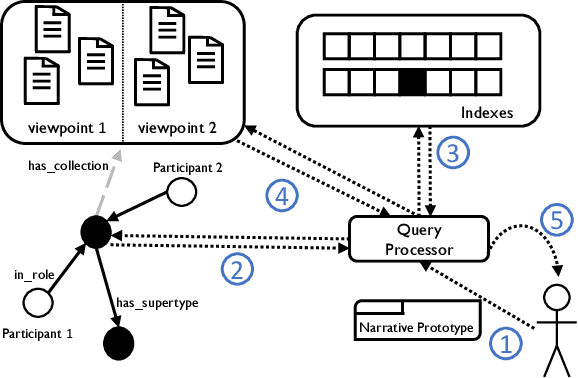

Abstract:Our lives are ruled by events of varying importance ranging from simple everyday occurrences to incidents of societal dimension. And a lot of effort is taken to exchange information and discuss about such events: generally speaking, stringent narratives are formed to reduce complexity. But when considering complex events like the current conflict between Russia and Ukraine it is easy to see that those events cannot be grasped by objective facts alone, like the start of the conflict or respective troop sizes. There are different viewpoints and assessments to consider, a different understanding of the roles taken by individual participants, etc. So how can such subjective and viewpoint-dependent information be effectively represented together with all objective information? Recently event-centric knowledge graphs have been proposed for objective event representation in the otherwise primarily entity-centric domain of knowledge graphs. In this paper we introduce a novel and lightweight structure for event-centric knowledge graphs, which for the first time allows for queries incorporating viewpoint-dependent and narrative aspects. Our experiments prove the effective incorporation of subjective attributions for event participants and show the benefits of specifically tailored indexes for narrative query processing.
A Library Perspective on Nearly-Unsupervised Information Extraction Workflows in Digital Libraries
May 02, 2022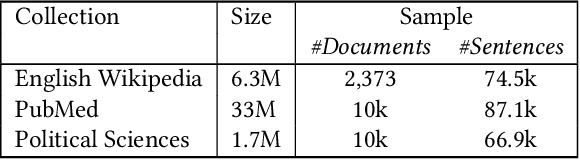
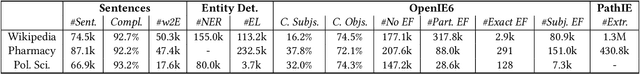


Abstract:Information extraction can support novel and effective access paths for digital libraries. Nevertheless, designing reliable extraction workflows can be cost-intensive in practice. On the one hand, suitable extraction methods rely on domain-specific training data. On the other hand, unsupervised and open extraction methods usually produce not-canonicalized extraction results. This paper tackles the question how digital libraries can handle such extractions and if their quality is sufficient in practice. We focus on unsupervised extraction workflows by analyzing them in case studies in the domains of encyclopedias (Wikipedia), pharmacy and political sciences. We report on opportunities and limitations. Finally we discuss best practices for unsupervised extraction workflows.
Extracting Features from Ratings: The Role of Factor Models
Jan 12, 2011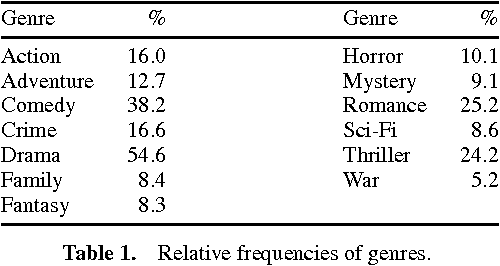
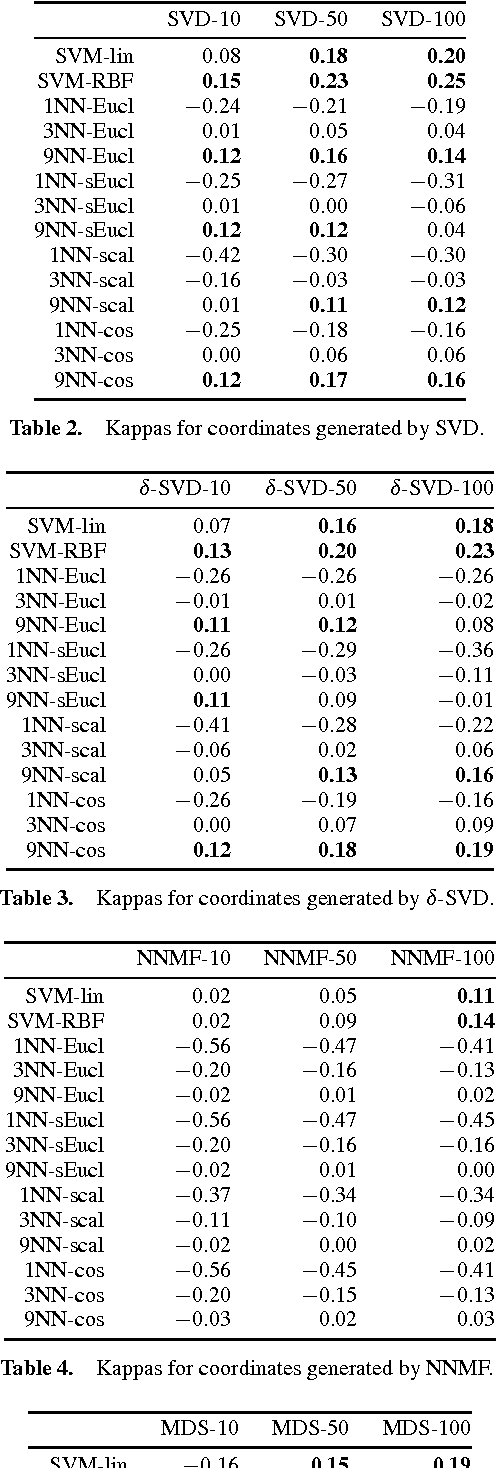
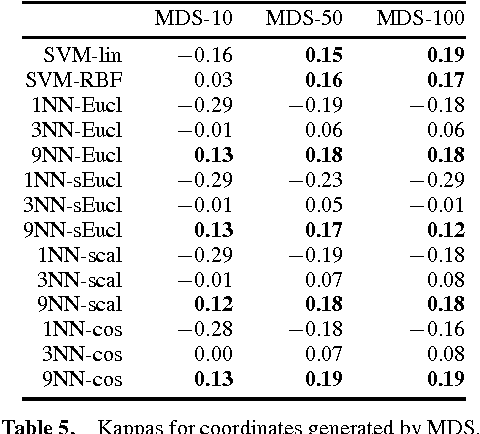
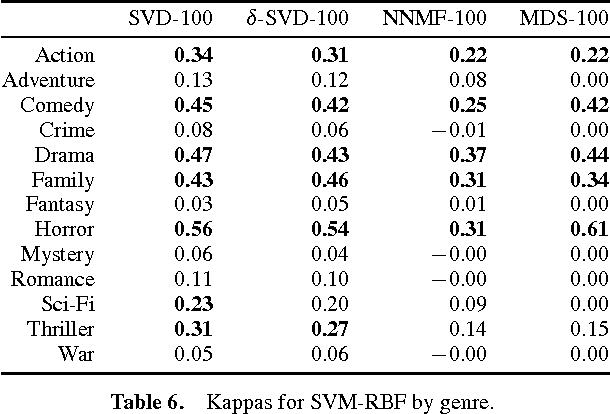
Abstract:Performing effective preference-based data retrieval requires detailed and preferentially meaningful structurized information about the current user as well as the items under consideration. A common problem is that representations of items often only consist of mere technical attributes, which do not resemble human perception. This is particularly true for integral items such as movies or songs. It is often claimed that meaningful item features could be extracted from collaborative rating data, which is becoming available through social networking services. However, there is only anecdotal evidence supporting this claim; but if it is true, the extracted information could very valuable for preference-based data retrieval. In this paper, we propose a methodology to systematically check this common claim. We performed a preliminary investigation on a large collection of movie ratings and present initial evidence.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge