On Dimensions of Plausibility for Narrative Information Access to Digital Libraries
Paper and Code
Aug 22, 2022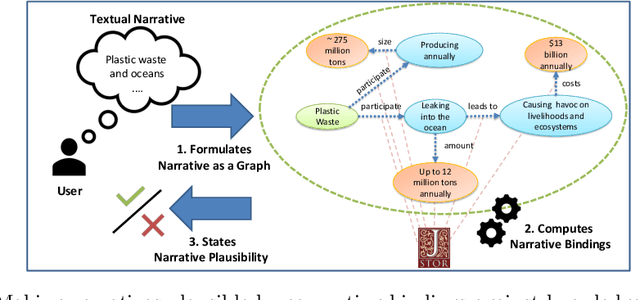
Designing keyword-based access paths is a common practice in digital libraries. They are easy to use and accepted by users and come with moderate costs for content providers. However, users usually have to break down the search into pieces if they search for stories of interest that are more complex than searching for a few keywords. After searching for every piece one by one, information must then be reassembled manually. In previous work we recommended narrative information access, i.e., users can precisely state their information needs as graph patterns called narratives. Then a system takes a narrative and searches for evidence for each of its parts. If the whole query, i.e., every part, can be bound against data, the narrative is considered plausible and, thus, the query is answered. But is it as easy as that? In this work we perform case studies to analyze the process of making a given narrative plausible. Therefore, we summarize conceptual problems and challenges to face. Moreover, we contribute a set of dimensions that must be considered when realizing narrative information access in digital libraries.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge