Weronika Borek-Marciniec
Employing Sentence Space Embedding for Classification of Data Stream from Fake News Domain
Jul 15, 2024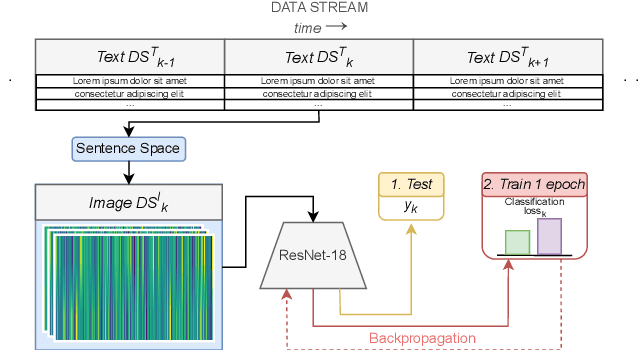
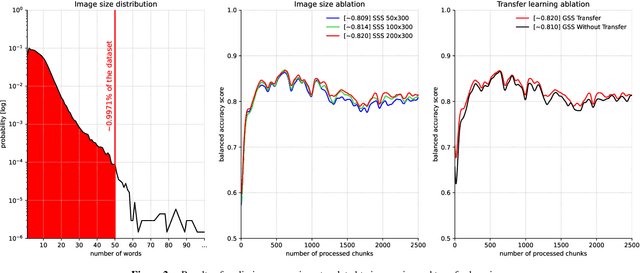
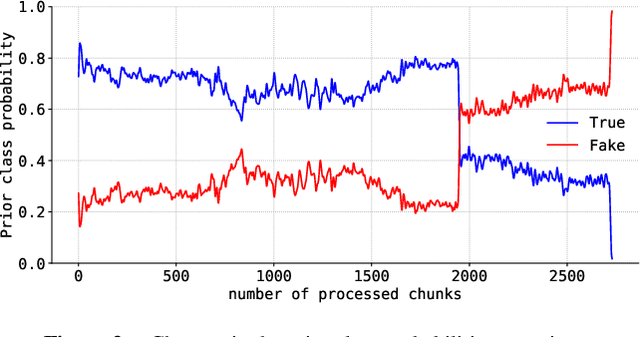
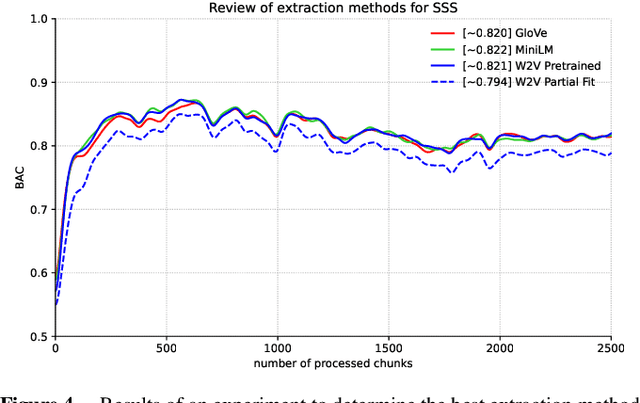
Abstract:Tabular data is considered the last unconquered castle of deep learning, yet the task of data stream classification is stated to be an equally important and demanding research area. Due to the temporal constraints, it is assumed that deep learning methods are not the optimal solution for application in this field. However, excluding the entire -- and prevalent -- group of methods seems rather rash given the progress that has been made in recent years in its development. For this reason, the following paper is the first to present an approach to natural language data stream classification using the sentence space method, which allows for encoding text into the form of a discrete digital signal. This allows the use of convolutional deep networks dedicated to image classification to solve the task of recognizing fake news based on text data. Based on the real-life Fakeddit dataset, the proposed approach was compared with state-of-the-art algorithms for data stream classification based on generalization ability and time complexity.
WarCov -- Large multilabel and multimodal dataset from social platform
Jun 10, 2024



Abstract:In the classification tasks, from raw data acquisition to the curation of a dataset suitable for use in evaluating machine learning models, a series of steps - often associated with high costs - are necessary. In the case of Natural Language Processing, initial cleaning and conversion can be performed automatically, but obtaining labels still requires the rationalized input of human experts. As a result, even though many articles often state that "the world is filled with data", data scientists suffer from its shortage. It is crucial in the case of natural language applications, which is constantly evolving and must adapt to new concepts or events. For example, the topic of the COVID-19 pandemic and the vocabulary related to it would have been mostly unrecognizable before 2019. For this reason, creating new datasets, also in languages other than English, is still essential. This work presents a collection of 3~187~105 posts in Polish about the pandemic and the war in Ukraine published on popular social media platforms in 2022. The collection includes not only preprocessed texts but also images so it can be used also for multimodal recognition tasks. The labels define posts' topics and were created using hashtags accompanying the posts. The work presents the process of curating a dataset from acquisition to sample pattern recognition experiments.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge