Wenxiang Deng
Unsupervised anomaly localization using VAE and beta-VAE
May 19, 2020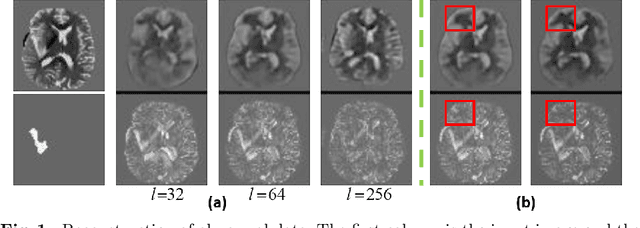
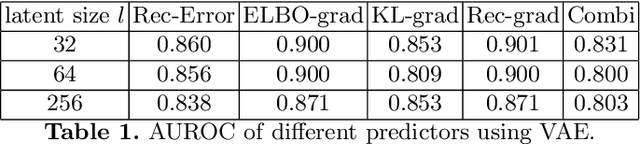
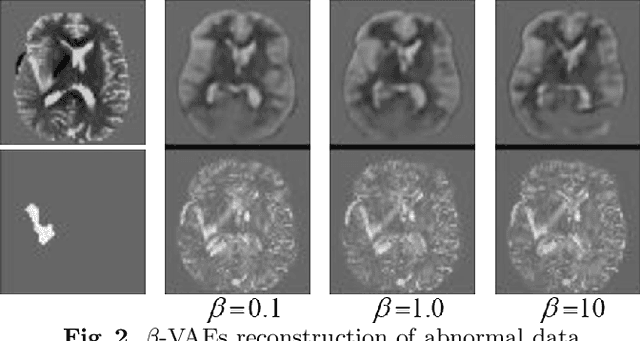
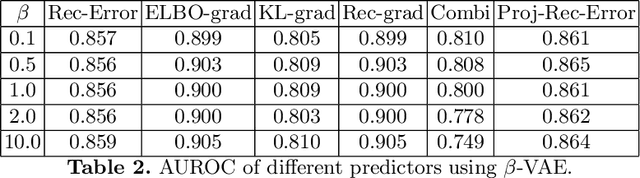
Abstract:Variational Auto-Encoders (VAEs) have shown great potential in the unsupervised learning of data distributions. An VAE trained on normal images is expected to only be able to reconstruct normal images, allowing the localization of anomalous pixels in an image via manipulating information within the VAE ELBO loss. The ELBO consists of KL divergence loss (image-wise) and reconstruction loss (pixel-wise). It is natural and straightforward to use the later as the predictor. However, usually local anomaly added to a normal image can deteriorate the whole reconstructed image, causing segmentation using only naive pixel errors not accurate. Energy based projection was proposed to increase the reconstruction accuracy of normal regions/pixels, which achieved the state-of-the-art localization accuracy on simple natural images. Another possible predictors are ELBO and its components gradients with respect to each pixels. Previous work claimed that KL gradient is a robust predictor. In this paper, we argue that the energy based projection in medical imaging is not as useful as on natural images. Moreover, we observe that the robustness of KL gradient predictor totally depends on the setting of the VAE and dataset. We also explored the effect of the weight of KL loss within beta-VAE and predictor ensemble in anomaly localization.
Robust Image Segmentation Quality Assessment without Ground Truth
Mar 20, 2019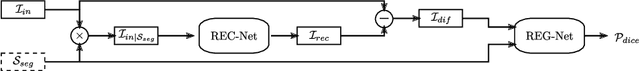
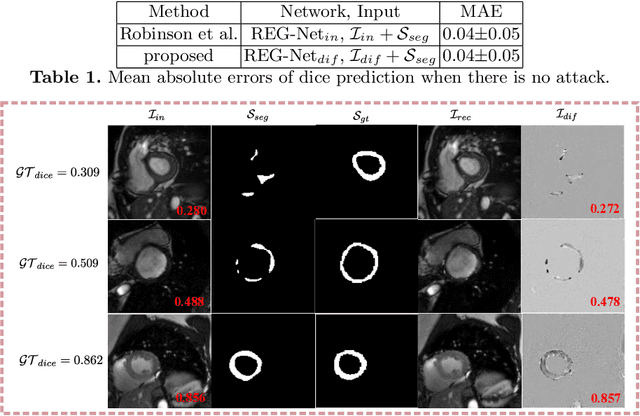

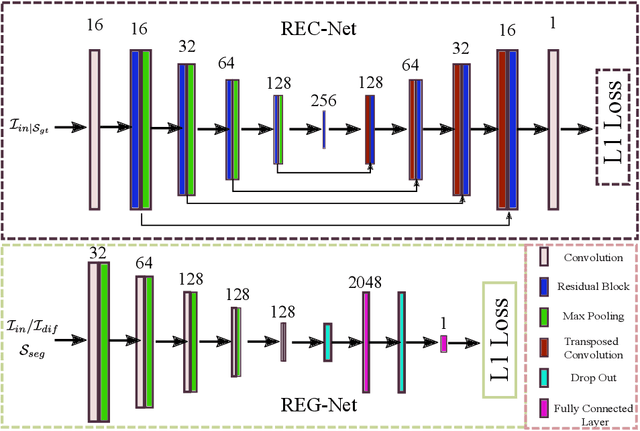
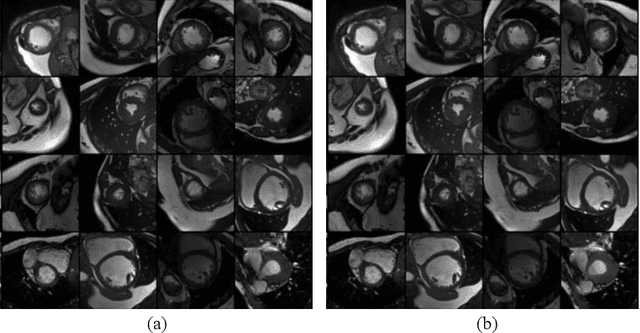
Abstract:Deep learning based image segmentation methods have achieved great success, even having human-level accuracy in some applications. However, due to the black box nature of deep learning, the best method may fail in some situations. Thus predicting segmentation quality without ground truth would be very crucial especially in clinical practice. Recently, people proposed to train neural networks to estimate the quality score by regression. Although it can achieve promising prediction accuracy, the network suffers robustness problem, e.g. it is vulnerable to adversarial attacks. In this paper, we propose to alleviate this problem by utilizing the difference between the input image and the reconstructed image, which is reconstructed from the segmentation to be assessed. The deep learning based reconstruction network (REC-Net) is trained with the input image masked by the ground truth segmentation against the original input image as the target. The rationale behind is that the trained REC-Net can best reconstruct the input image masked by accurate segmentation. The quality score regression network (REG-Net) is then trained with difference images and the corresponding segmentations as input. In this way, the regression network may have lower chance to overfit to the undesired image features from the original input image, and thus is more robust. Results on ACDC17 dataset demonstrated our method is promising.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge