Wen-ling Huang
Department of Mathematics & Computer Science, University of Bremen, Germany
A Stochastic Approach to Classification Error Estimates in Convolutional Neural Networks
Dec 21, 2023Abstract:This technical report presents research results achieved in the field of verification of trained Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) used for image classification in safety-critical applications. As running example, we use the obstacle detection function needed in future autonomous freight trains with Grade of Automation (GoA) 4. It is shown that systems like GoA 4 freight trains are indeed certifiable today with new standards like ANSI/UL 4600 and ISO 21448 used in addition to the long-existing standards EN 50128 and EN 50129. Moreover, we present a quantitative analysis of the system-level hazard rate to be expected from an obstacle detection function. It is shown that using sensor/perceptor fusion, the fused detection system can meet the tolerable hazard rate deemed to be acceptable for the safety integrity level to be applied (SIL-3). A mathematical analysis of CNN models is performed which results in the identification of classification clusters and equivalence classes partitioning the image input space of the CNN. These clusters and classes are used to introduce a novel statistical testing method for determining the residual error probability of a trained CNN and an associated upper confidence limit. We argue that this greybox approach to CNN verification, taking into account the CNN model's internal structure, is essential for justifying that the statistical tests have covered the trained CNN with its neurons and inter-layer mappings in a comprehensive way.
Complete Agent-driven Model-based System Testing for Autonomous Systems
Oct 25, 2021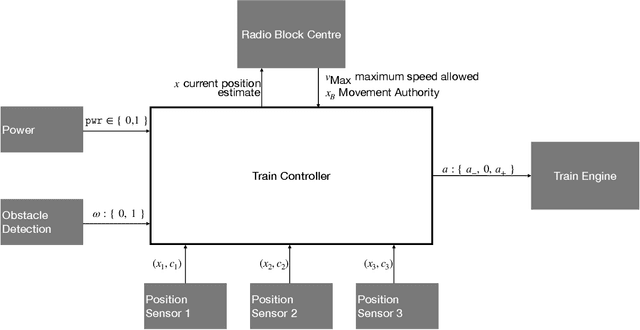
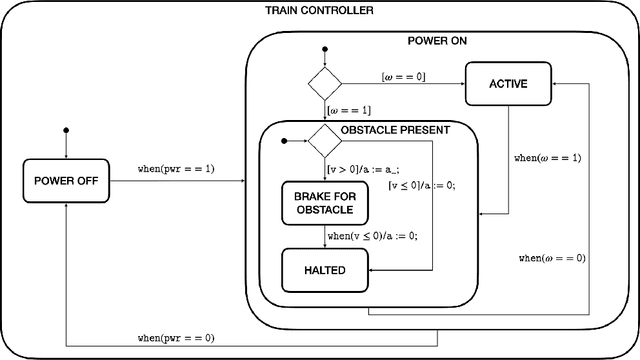
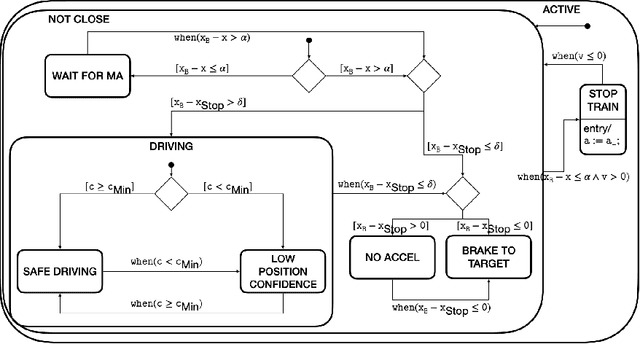
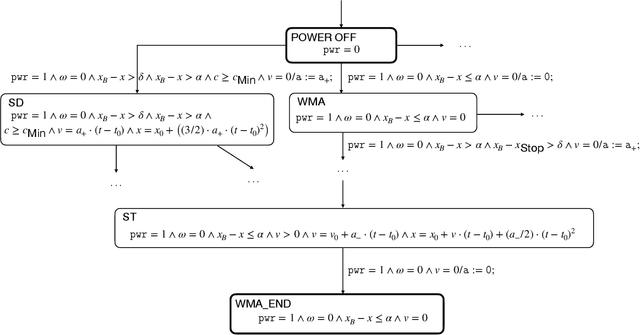
Abstract:In this position paper, a novel approach to testing complex autonomous transportation systems (ATS) in the automotive, avionic, and railway domains is described. It is intended to mitigate some of the most critical problems regarding verification and validation (V&V) effort for ATS. V&V is known to become infeasible for complex ATS, when using conventional methods only. The approach advocated here uses complete testing methods on the module level, because these establish formal proofs for the logical correctness of the software. Having established logical correctness, system-level tests are performed in simulated cloud environments and on the target system. To give evidence that 'sufficiently many' system tests have been performed with the target system, a formally justified coverage criterion is introduced. To optimise the execution of very large system test suites, we advocate an online testing approach where multiple tests are executed in parallel, and test steps are identified on-the-fly. The coordination and optimisation of these executions is achieved by an agent-based approach. Each aspect of the testing approach advocated here is shown to either be consistent with existing standards for development and V&V of safety-critical transportation systems, or it is justified why it should become acceptable in future revisions of the applicable standards.
* In Proceedings FMAS 2021, arXiv:2110.11527
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge