Weijun Zhu
An approach for auxiliary diagnosing and screening coronary disease based on machine learning
Jul 24, 2020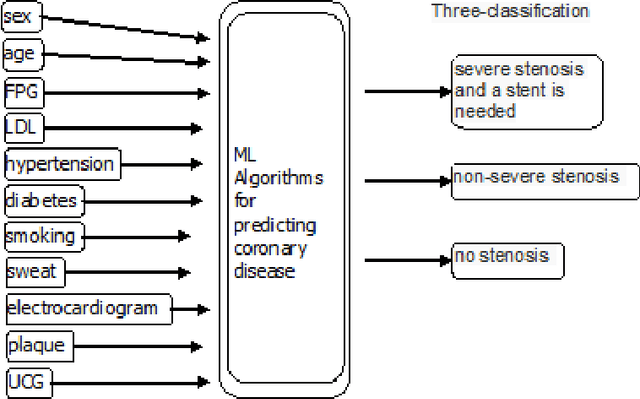
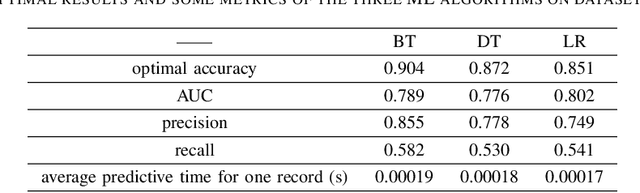
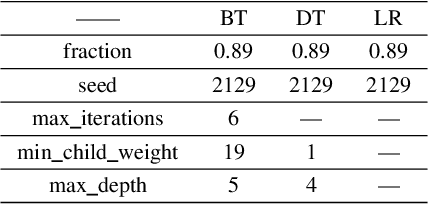
Abstract:How to accurately classify and predict whether an individual has Coronary Artery Disease (CAD) and the degree of coronary stenosis without using invasive examination? This problem has not been solved satisfactorily. To this end, the three kinds of machine learning (ML)algorithms, i.e., Boost Tree (BT), Decision Tree (DT), Logistic Regression (LR), are employed in this paper. First, 11 features including basic information of an individual, symptoms and results of routine physical examination are selected, and one label is specified, indicating whether an individual suffers from CAD or different severity of coronary artery stenosis. On the basis of it, a sample set is constructed. Second, each of these three ML algorithms learns from the sample set to obtain the corresponding optimal predictive results, respectively. The experimental results show that: BT predicts whether an individual has CAD with an accuracy of 94%, and this algorithm predicts the degree of an individuals coronary artery stenosis with an accuracy of 90%.
Predicting the Results of LTL Model Checking using Multiple Machine Learning Algorithms
Jan 23, 2019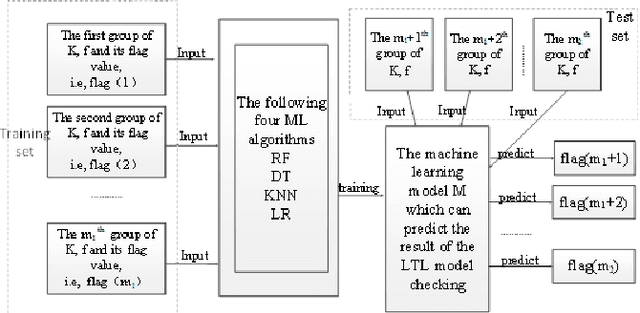
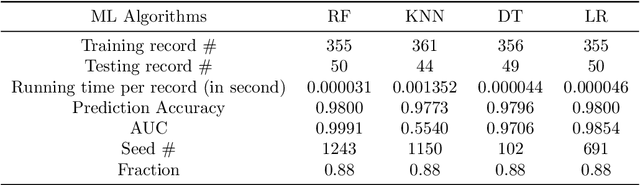
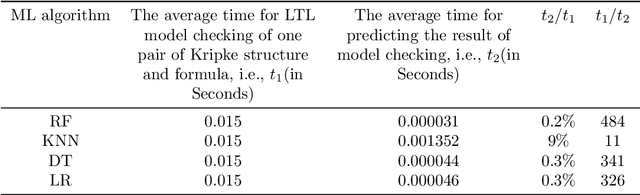
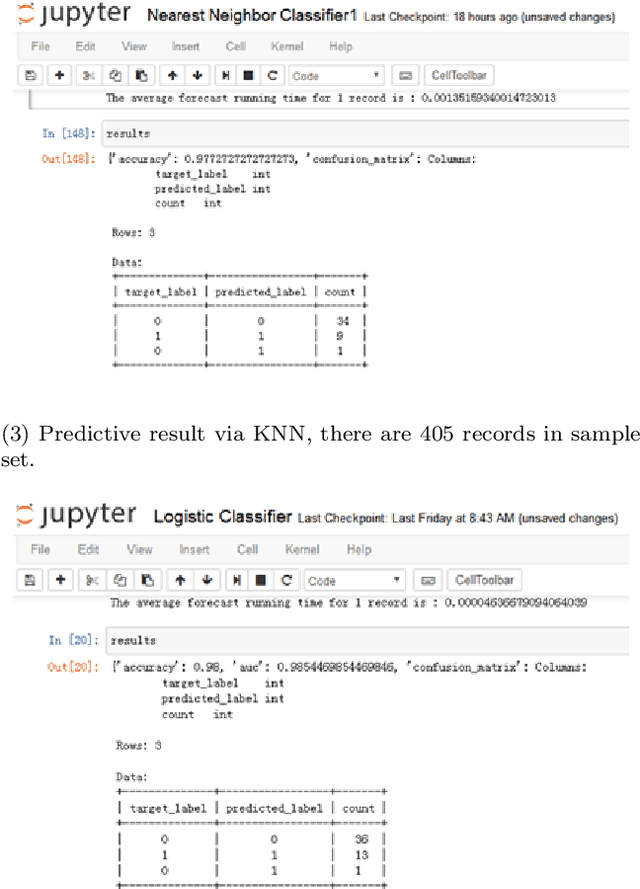
Abstract:In this paper, we study how to predict the results of LTL model checking using some machine learning algorithms. Some Kripke structures and LTL formulas and their model checking results are made up data set. The approaches based on the Random Forest (RF), K-Nearest Neighbors (KNN), Decision tree (DT), and Logistic Regression (LR) are used to training and prediction. The experiment results show that the average computation efficiencies of the RF, LR, DT, and KNN-based approaches are 2066181, 2525333, 1894000 and 294 times than that of the existing approach, respectively.
Analyzing DNA Hybridization via machine learning
Jul 02, 2018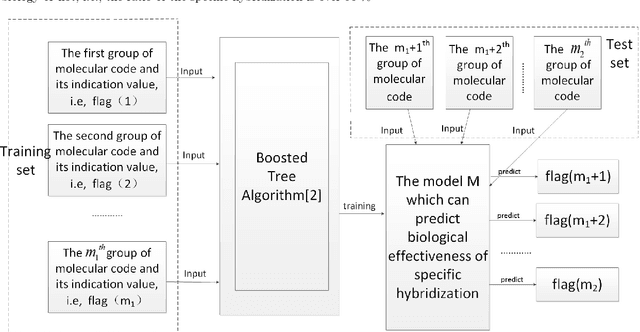
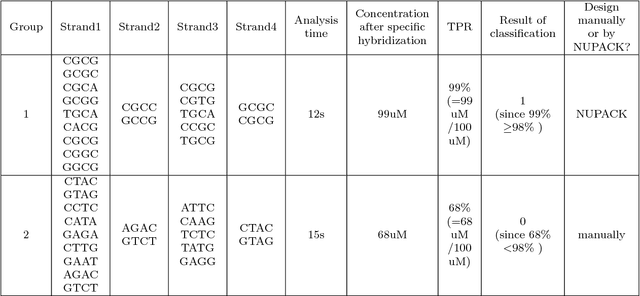
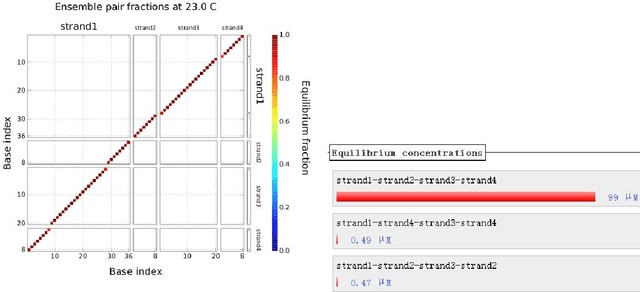
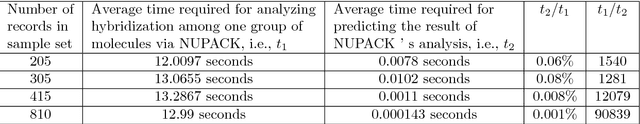
Abstract:In DNA computing, it is impossible to decide whether a specific hybridization among complex DNA molecules is effective or not within acceptable time. In order to address this common problem, we introduce a new method based on the machine learning technique. First, a sample set is employed to train the Boosted Tree (BT) algorithm, and the corresponding model is obtained. Second, this model is used to predict classification results of molecular hybridizations. The experiments show that the average accuracy of the new method is over 94.2%, and its average efficiency is over 90839 times higher than that of the existing method. These results indicate that the new method can quickly and accurately determine the biological effectiveness of molecular hybridization for a given DNA design.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge