Weihao Hu
Model-Free Voltage Regulation of Unbalanced Distribution Network Based on Surrogate Model and Deep Reinforcement Learning
Jun 24, 2020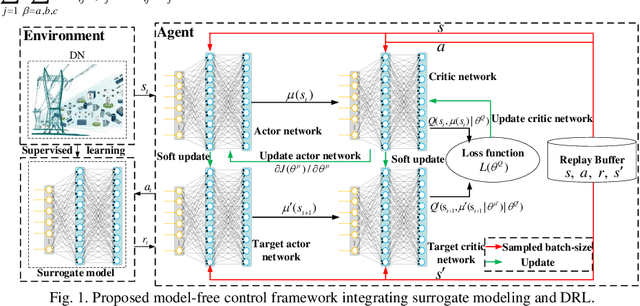

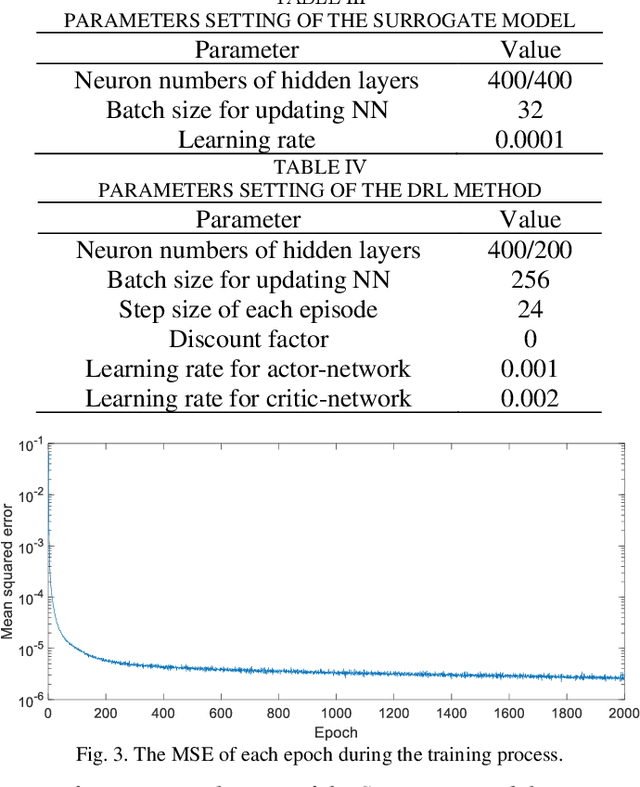
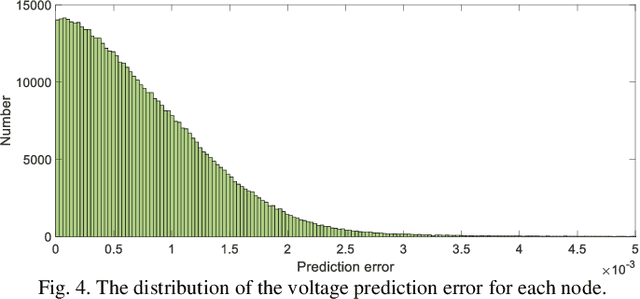
Abstract:Accurate knowledge of the distribution system topology and parameters is required to achieve good voltage controls, but this is difficult to obtain in practice. This paper develops a model-free approach based on the surrogate model and deep reinforcement learning (DRL). We have also extended it to deal with unbalanced three-phase scenarios. The key idea is to learn a surrogate model to capture the relationship between the power injections and voltage fluctuation of each node from historical data instead of using the original inaccurate model affected by errors and uncertainties. This allows us to integrate the DRL with the learned surrogate model. In particular, DRL is applied to learn the optimal control strategy from the experiences obtained by continuous interactions with the surrogate model. The integrated framework contains training three networks, i.e., surrogate model, actor, and critic networks, which fully leverage the strong nonlinear fitting ability of deep learning and DRL for online decision making. Several single-phase approaches have also been extended to deal with three-phase unbalance scenarios and the simulation results on the IEEE 123-bus system show that our proposed method can achieve similar performance as those that use accurate physical models.
Distributed Voltage Regulation of Active Distribution System Based on Enhanced Multi-agent Deep Reinforcement Learning
May 31, 2020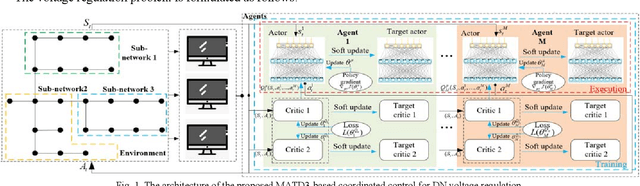

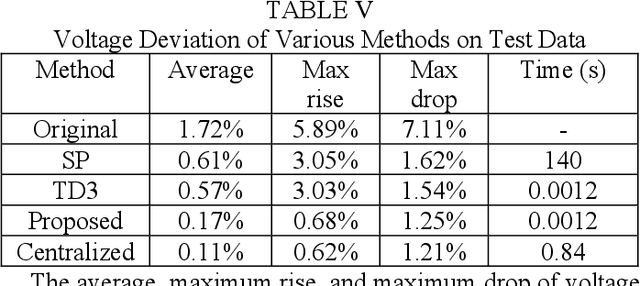
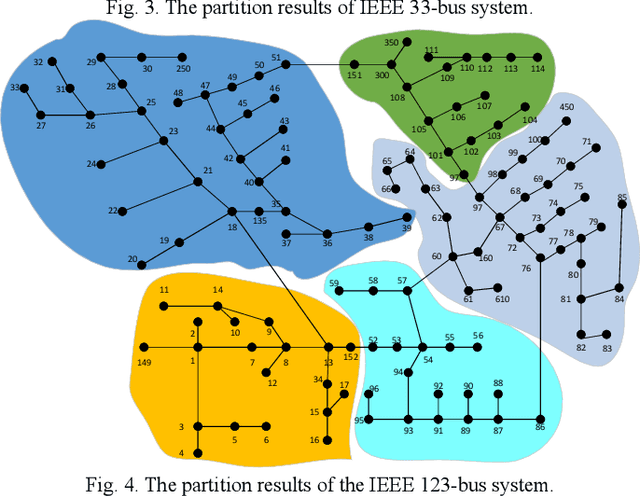
Abstract:This paper proposes a data-driven distributed voltage control approach based on the spectrum clustering and the enhanced multi-agent deep reinforcement learning (MADRL) algorithm. Via the unsupervised clustering, the whole distribution system can be decomposed into several sub-networks according to the voltage and reactive power sensitivity. Then, the distributed control problem of each sub-network is modeled as Markov games and solved by the enhanced MADRL algorithm, where each sub-network is modeled as an adaptive agent. Deep neural networks are used in each agent to approximate the policy function and the action value function. All agents are centrally trained to learn the optimal coordinated voltage regulation strategy while executed in a distributed manner to make decisions based on only local information. The proposed method can significantly reduce the requirements of communications and knowledge of system parameters. It also effectively deals with uncertainties and can provide online coordinated control based on the latest local information. Comparison results with other existing model-based and data-driven methods on IEEE 33-bus and 123-bus systems demonstrate the effectiveness and benefits of the proposed approach.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge