Wei Ren Tan
Improved ArtGAN for Conditional Synthesis of Natural Image and Artwork
Aug 23, 2018

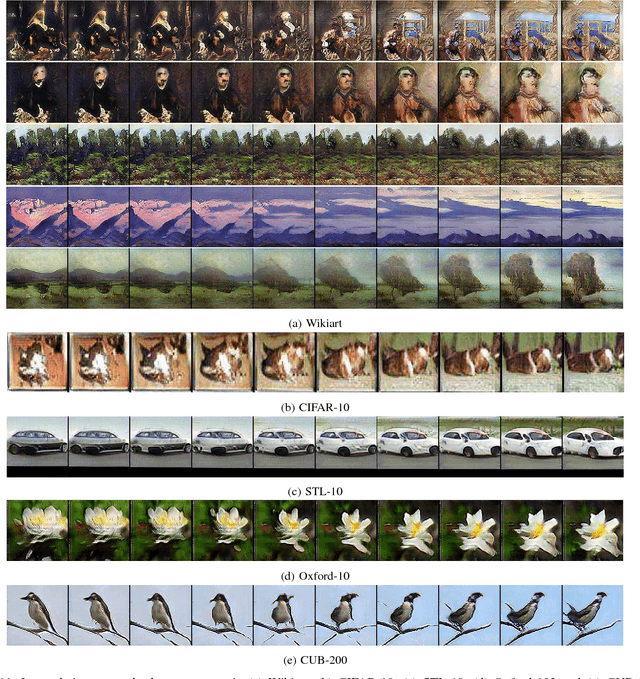

Abstract:This paper proposes a series of new approaches to improve Generative Adversarial Network (GAN) for conditional image synthesis and we name the proposed model as ArtGAN. One of the key innovation of ArtGAN is that, the gradient of the loss function w.r.t. the label (randomly assigned to each generated image) is back-propagated from the categorical discriminator to the generator. With the feedback from the label information, the generator is able to learn more efficiently and generate image with better quality. Inspired by recent works, an autoencoder is incorporated into the categorical discriminator for additional complementary information. Last but not least, we introduce a novel strategy to improve the image quality. In the experiments, we evaluate ArtGAN on CIFAR-10 and STL-10 via ablation studies. The empirical results showed that our proposed model outperforms the state-of-the-art results on CIFAR-10 in terms of Inception score. Qualitatively, we demonstrate that ArtGAN is able to generate plausible-looking images on Oxford-102 and CUB-200, as well as able to draw realistic artworks based on style, artist, and genre. The source code and models are available at: https://github.com/cs-chan/ArtGAN
A Fusion Approach for Efficient Human Skin Detection
Oct 14, 2014



Abstract:A reliable human skin detection method that is adaptable to different human skin colours and illu- mination conditions is essential for better human skin segmentation. Even though different human skin colour detection solutions have been successfully applied, they are prone to false skin detection and are not able to cope with the variety of human skin colours across different ethnic. Moreover, existing methods require high computational cost. In this paper, we propose a novel human skin de- tection approach that combines a smoothed 2D histogram and Gaussian model, for automatic human skin detection in colour image(s). In our approach an eye detector is used to refine the skin model for a specific person. The proposed approach reduces computational costs as no training is required; and it improves the accuracy of skin detection despite wide variation in ethnicity and illumination. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first method to employ fusion strategy for this purpose. Qualitative and quantitative results on three standard public datasets and a comparison with state-of-the-art methods have shown the effectiveness and robustness of the proposed approach.
* Accepted in IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, vol. 8(1), pp. 138-147, new skin detection + ground truth (Pratheepan) dataset
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge