Wanling Cai
Exploring the Design of Generative AI in Supporting Music-based Reminiscence for Older Adults
Mar 03, 2024Abstract:Music-based reminiscence has the potential to positively impact the psychological well-being of older adults. However, the aging process and physiological changes, such as memory decline and limited verbal communication, may impede the ability of older adults to recall their memories and life experiences. Given the advanced capabilities of generative artificial intelligence (AI) systems, such as generated conversations and images, and their potential to facilitate the reminiscing process, this study aims to explore the design of generative AI to support music-based reminiscence in older adults. This study follows a user-centered design approach incorporating various stages, including detailed interviews with two social workers and two design workshops (involving ten older adults). Our work contributes to an in-depth understanding of older adults' attitudes toward utilizing generative AI for supporting music-based reminiscence and identifies concrete design considerations for the future design of generative AI to enhance the reminiscence experience of older adults.
A Survey on Conversational Recommender Systems
Apr 01, 2020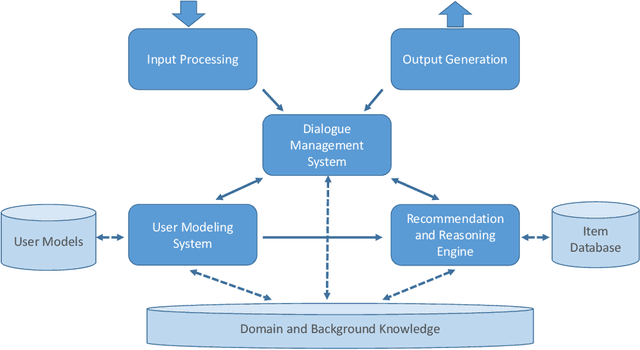

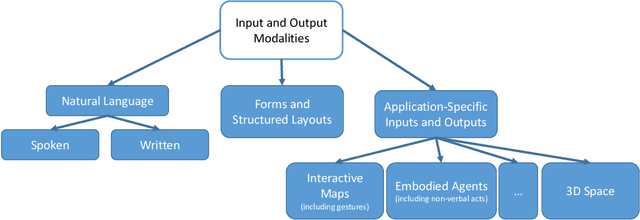

Abstract:Recommender systems are software applications that help users to find items of interest in situations of information overload. Current research often assumes a one-shot interaction paradigm, where the users' preferences are estimated based on past observed behavior and where the presentation of a ranked list of suggestions is the main, one-directional form of user interaction. Conversational recommender systems (CRS) take a different approach and support a richer set of interactions. These interactions can, for example, help to improve the preference elicitation process or allow the user to ask questions about the recommendations and to give feedback. The interest in CRS has significantly increased in the past few years. This development is mainly due to the significant progress in the area of natural language processing, the emergence of new voice-controlled home assistants, and the increased use of chatbot technology. With this paper, we provide a detailed survey of existing approaches to conversational recommendation. We categorize these approaches in various dimensions, e.g., in terms of the supported user intents or the knowledge they use in the background. Moreover, we discuss technological approaches, review how CRS are evaluated, and finally identify a number of gaps that deserve more research in the future.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge