Wangkai Jin
Feint in Multi-Player Games
Mar 04, 2024Abstract:This paper introduces the first formalization, implementation and quantitative evaluation of Feint in Multi-Player Games. Our work first formalizes Feint from the perspective of Multi-Player Games, in terms of the temporal, spatial, and their collective impacts. The formalization is built upon Non-transitive Active Markov Game Model, where Feint can have a considerable amount of impacts. Then, our work considers practical implementation details of Feint in Multi-Player Games, under the state-of-the-art progress of multi-agent modeling to date (namely Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning). Finally, our work quantitatively examines the effectiveness of our design, and the results show that our design of Feint can (1) greatly improve the reward gains from the game; (2) significantly improve the diversity of Multi-Player Games; and (3) only incur negligible overheads in terms of time consumption. We conclude that our design of Feint is effective and practical, to make Multi-Player Games more interesting.
Polyphonic Sound Event Detection Using Capsule Neural Network on Multi-Type-Multi-Scale Time-Frequency Representation
Nov 25, 2021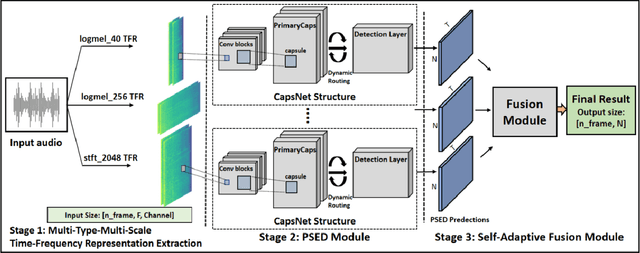
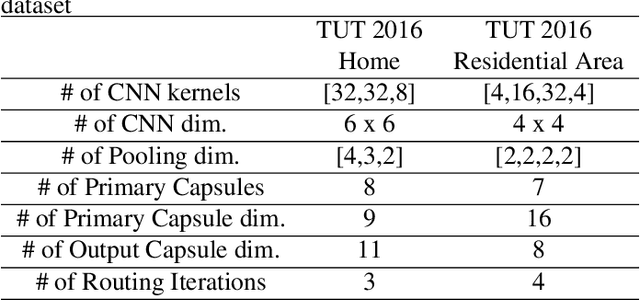
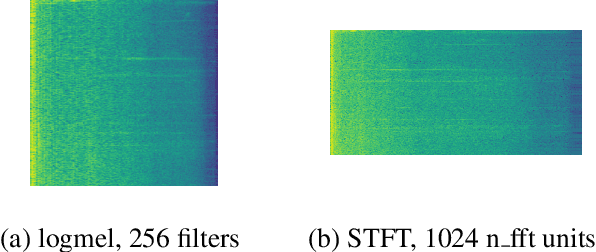
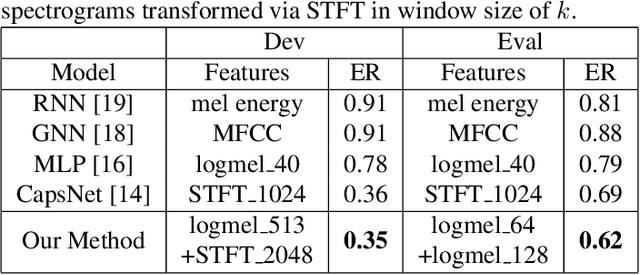
Abstract:The challenges of polyphonic sound event detection (PSED) stem from the detection of multiple overlapping events in a time series. Recent efforts exploit Deep Neural Networks (DNNs) on Time-Frequency Representations (TFRs) of audio clips as model inputs to mitigate such issues. However, existing solutions often rely on a single type of TFR, which causes under-utilization of input features. To this end, we propose a novel PSED framework, which incorporates Multi-Type-Multi-Scale TFRs. Our key insight is that: TFRs, which are of different types or in different scales, can reveal acoustics patterns in a complementary manner, so that the overlapped events can be best extracted by combining different TFRs. Moreover, our framework design applies a novel approach, to adaptively fuse different models and TFRs symbiotically. Hence, the overall performance can be significantly improved. We quantitatively examine the benefits of our framework by using Capsule Neural Networks, a state-of-the-art approach for PSED. The experimental results show that our method achieves a reduction of 7\% in error rate compared with the state-of-the-art solutions on the TUT-SED 2016 dataset.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge