Vrijendra Singh
Multimodal Data-Driven Classification of Mental Disorders: A Comprehensive Approach to Diagnosing Depression, Anxiety, and Schizophrenia
Feb 06, 2025



Abstract:This study investigates the potential of multimodal data integration, which combines electroencephalogram (EEG) data with sociodemographic characteristics like age, sex, education, and intelligence quotient (IQ), to diagnose mental diseases like schizophrenia, depression, and anxiety. Using Apache Spark and convolutional neural networks (CNNs), a data-driven classification pipeline has been developed for big data environment to effectively analyze massive datasets. In order to evaluate brain activity and connection patterns associated with mental disorders, EEG parameters such as power spectral density (PSD) and coherence are examined. The importance of coherence features is highlighted by comparative analysis, which shows significant improvement in classification accuracy and robustness. This study emphasizes the significance of holistic approaches for efficient diagnostic tools by integrating a variety of data sources. The findings open the door for creative, data-driven approaches to treating psychiatric diseases by demonstrating the potential of utilizing big data, sophisticated deep learning methods, and multimodal datasets to enhance the precision, usability, and comprehension of mental health diagnostics.
Innovative Framework for Early Estimation of Mental Disorder Scores to Enable Timely Interventions
Feb 06, 2025



Abstract:Individual's general well-being is greatly impacted by mental health conditions including depression and Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD), underscoring the importance of early detection and precise diagnosis in order to facilitate prompt clinical intervention. An advanced multimodal deep learning system for the automated classification of PTSD and depression is presented in this paper. Utilizing textual and audio data from clinical interview datasets, the method combines features taken from both modalities by combining the architectures of LSTM (Long Short Term Memory) and BiLSTM (Bidirectional Long Short-Term Memory).Although text features focus on speech's semantic and grammatical components; audio features capture vocal traits including rhythm, tone, and pitch. This combination of modalities enhances the model's capacity to identify minute patterns connected to mental health conditions. Using test datasets, the proposed method achieves classification accuracies of 92% for depression and 93% for PTSD, outperforming traditional unimodal approaches and demonstrating its accuracy and robustness.
Advanced Gesture Recognition in Autism: Integrating YOLOv7, Video Augmentation and VideoMAE for Video Analysis
Oct 12, 2024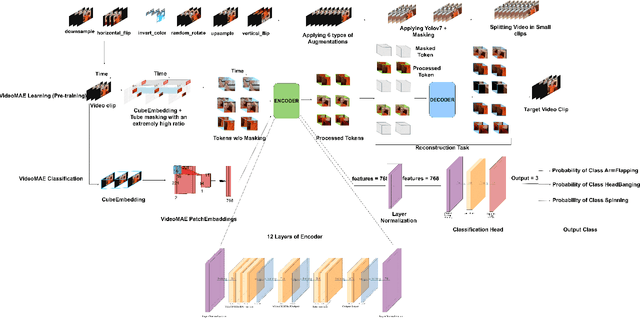



Abstract:Deep learning and advancements in contactless sensors have significantly enhanced our ability to understand complex human activities in healthcare settings. In particular, deep learning models utilizing computer vision have been developed to enable detailed analysis of human gesture recognition, especially repetitive gestures which are commonly observed behaviors in children with autism. This research work aims to identify repetitive behaviors indicative of autism by analyzing videos captured in natural settings as children engage in daily activities. The focus is on accurately categorizing real-time repetitive gestures such as spinning, head banging, and arm flapping. To this end, we utilize the publicly accessible Self-Stimulatory Behavior Dataset (SSBD) to classify these stereotypical movements. A key component of the proposed methodology is the use of \textbf{VideoMAE}, a model designed to improve both spatial and temporal analysis of video data through a masking and reconstruction mechanism. This model significantly outperformed traditional methods, achieving an accuracy of 97.7\%, a 14.7\% improvement over the previous state-of-the-art.
Leveraging Machine Learning for Early Autism Detection via INDT-ASD Indian Database
Apr 02, 2024



Abstract:Machine learning (ML) has advanced quickly, particularly throughout the area of health care. The diagnosis of neurodevelopment problems using ML is a very important area of healthcare. Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) is one of the developmental disorders that is growing the fastest globally. The clinical screening tests used to identify autistic symptoms are expensive and time-consuming. But now that ML has been advanced, it's feasible to identify autism early on. Previously, many different techniques have been used in investigations. Still, none of them have produced the anticipated outcomes when it comes to the capacity to predict autistic features utilizing a clinically validated Indian ASD database. Therefore, this study aimed to develop a simple, quick, and inexpensive technique for identifying ASD by using ML. Various machine learning classifiers, including Adaboost (AB), Gradient Boost (GB), Decision Tree (DT), Logistic Regression (LR), Random Forest (RF), Gaussian Naive Bayes (GNB), Linear Discriminant Analysis (LDA), Quadratic Discriminant Analysis (QDA), K-Nearest Neighbors (KNN), and Support Vector Machine (SVM), were used to develop the autism prediction model. The proposed method was tested with records from the AIIMS Modified INDT-ASD (AMI) database, which were collected through an application developed by AIIMS in Delhi, India. Feature engineering has been applied to make the proposed solution easier than already available solutions. Using the proposed model, we succeeded in predicting ASD using a minimized set of 20 questions rather than the 28 questions presented in AMI with promising accuracy. In a comparative evaluation, SVM emerged as the superior model among others, with 100 $\pm$ 0.05\% accuracy, higher recall by 5.34\%, and improved accuracy by 2.22\%-6.67\% over RF. We have also introduced a web-based solution supporting both Hindi and English.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge