Vladimir Lazarev
Unleashing the power of novel conditional generative approaches for new materials discovery
Nov 05, 2024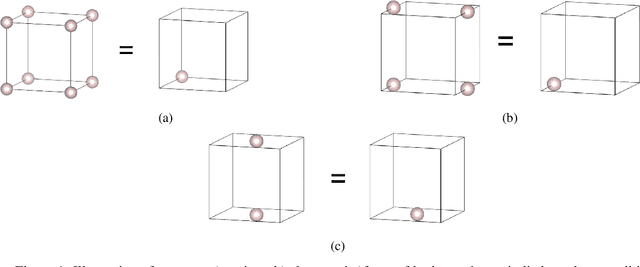
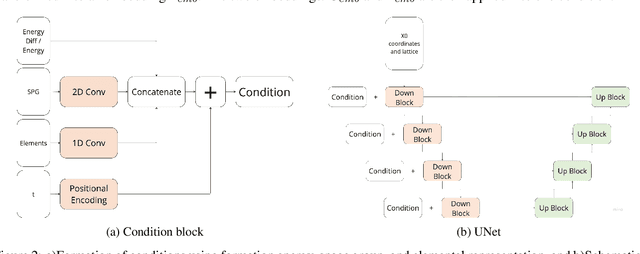
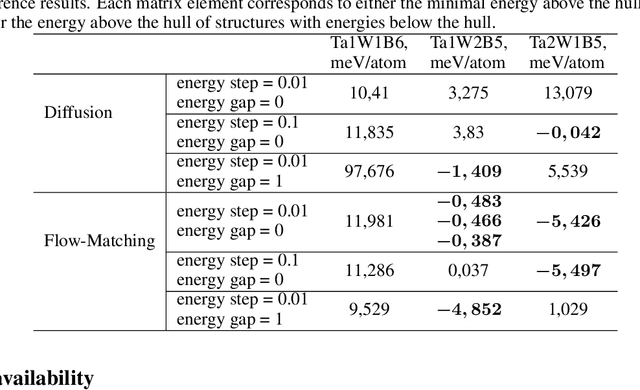
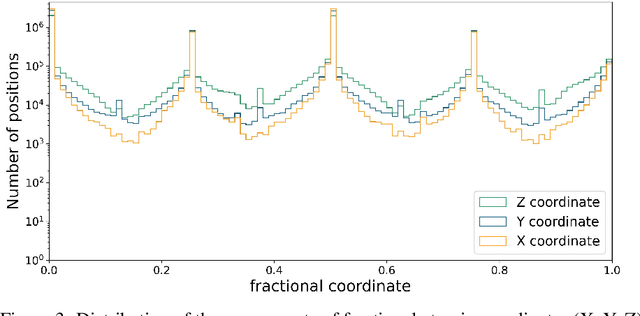
Abstract:For a very long time, computational approaches to the design of new materials have relied on an iterative process of finding a candidate material and modeling its properties. AI has played a crucial role in this regard, helping to accelerate the discovery and optimization of crystal properties and structures through advanced computational methodologies and data-driven approaches. To address the problem of new materials design and fasten the process of new materials search, we have applied latest generative approaches to the problem of crystal structure design, trying to solve the inverse problem: by given properties generate a structure that satisfies them without utilizing supercomputer powers. In our work we propose two approaches: 1) conditional structure modification: optimization of the stability of an arbitrary atomic configuration, using the energy difference between the most energetically favorable structure and all its less stable polymorphs and 2) conditional structure generation. We used a representation for materials that includes the following information: lattice, atom coordinates, atom types, chemical features, space group and formation energy of the structure. The loss function was optimized to take into account the periodic boundary conditions of crystal structures. We have applied Diffusion models approach, Flow matching, usual Autoencoder (AE) and compared the results of the models and approaches. As a metric for the study, physical PyMatGen matcher was employed: we compare target structure with generated one using default tolerances. So far, our modifier and generator produce structures with needed properties with accuracy 41% and 82% respectively. To prove the offered methodology efficiency, inference have been carried out, resulting in several potentially new structures with formation energy below the AFLOW-derived convex hulls.
Eco2AI: carbon emissions tracking of machine learning models as the first step towards sustainable AI
Aug 03, 2022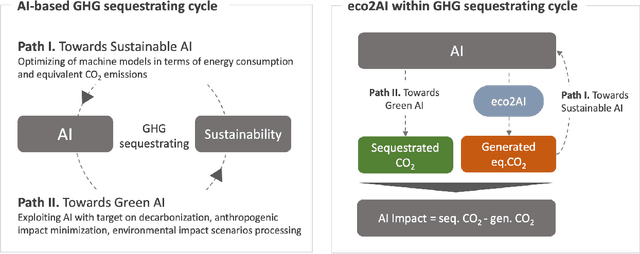
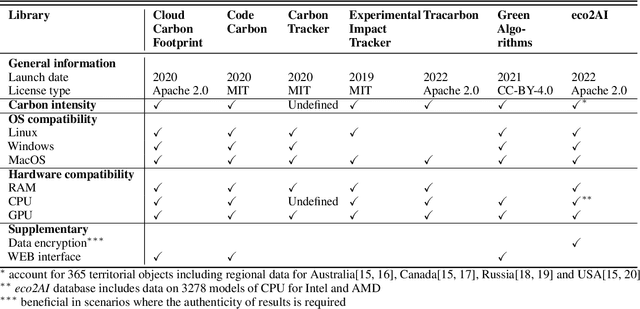

Abstract:The size and complexity of deep neural networks continue to grow exponentially, significantly increasing energy consumption for training and inference by these models. We introduce an open-source package eco2AI to help data scientists and researchers to track energy consumption and equivalent CO2 emissions of their models in a straightforward way. In eco2AI we put emphasis on accuracy of energy consumption tracking and correct regional CO2 emissions accounting. We encourage research community to search for new optimal Artificial Intelligence (AI) architectures with a lower computational cost. The motivation also comes from the concept of AI-based green house gases sequestrating cycle with both Sustainable AI and Green AI pathways.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge