Vivian Y. Nastl
Limits to scalable evaluation at the frontier: LLM as Judge won't beat twice the data
Oct 17, 2024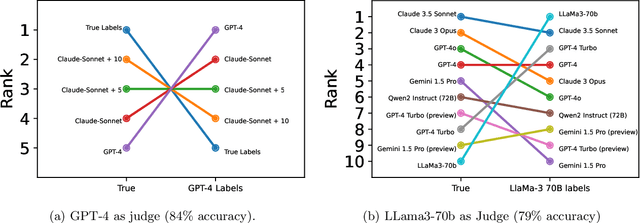
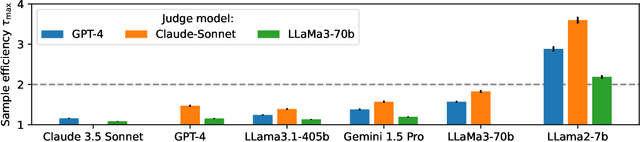
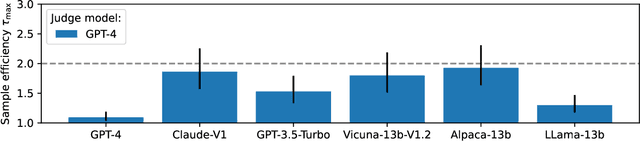
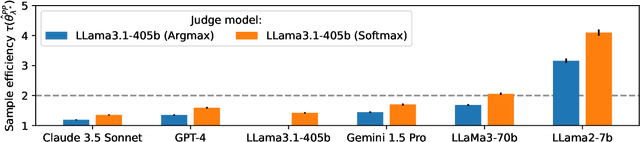
Abstract:High quality annotations are increasingly a bottleneck in the explosively growing machine learning ecosystem. Scalable evaluation methods that avoid costly annotation have therefore become an important research ambition. Many hope to use strong existing models in lieu of costly labels to provide cheap model evaluations. Unfortunately, this method of using models as judges introduces biases, such as self-preferencing, that can distort model comparisons. An emerging family of debiasing tools promises to fix these issues by using a few high quality labels to debias a large number of model judgments. In this paper, we study how far such debiasing methods, in principle, can go. Our main result shows that when the judge is no more accurate than the evaluated model, no debiasing method can decrease the required amount of ground truth labels by more than half. Our result speaks to the severe limitations of the LLM-as-a-judge paradigm at the evaluation frontier where the goal is to assess newly released models that are possibly better than the judge. Through an empirical evaluation, we demonstrate that the sample size savings achievable in practice are even more modest than what our theoretical limit suggests. Along the way, our work provides new observations about debiasing methods for model evaluation, and points out promising avenues for future work.
Predictors from causal features do not generalize better to new domains
Feb 15, 2024



Abstract:We study how well machine learning models trained on causal features generalize across domains. We consider 16 prediction tasks on tabular datasets covering applications in health, employment, education, social benefits, and politics. Each dataset comes with multiple domains, allowing us to test how well a model trained in one domain performs in another. For each prediction task, we select features that have a causal influence on the target of prediction. Our goal is to test the hypothesis that models trained on causal features generalize better across domains. Without exception, we find that predictors using all available features, regardless of causality, have better in-domain and out-of-domain accuracy than predictors using causal features. Moreover, even the absolute drop in accuracy from one domain to the other is no better for causal predictors than for models that use all features. If the goal is to generalize to new domains, practitioners might as well train the best possible model on all available features.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge