Vittoria Cozza
A study on text-score disagreement in online reviews
Jul 21, 2017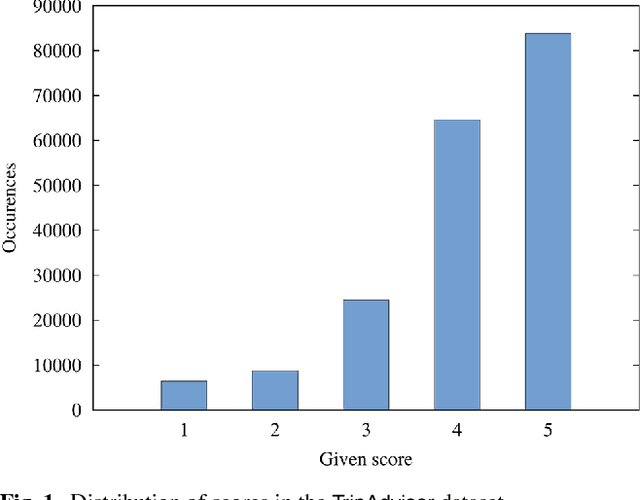


Abstract:In this paper, we focus on online reviews and employ artificial intelligence tools, taken from the cognitive computing field, to help understanding the relationships between the textual part of the review and the assigned numerical score. We move from the intuitions that 1) a set of textual reviews expressing different sentiments may feature the same score (and vice-versa); and 2) detecting and analyzing the mismatches between the review content and the actual score may benefit both service providers and consumers, by highlighting specific factors of satisfaction (and dissatisfaction) in texts. To prove the intuitions, we adopt sentiment analysis techniques and we concentrate on hotel reviews, to find polarity mismatches therein. In particular, we first train a text classifier with a set of annotated hotel reviews, taken from the Booking website. Then, we analyze a large dataset, with around 160k hotel reviews collected from Tripadvisor, with the aim of detecting a polarity mismatch, indicating if the textual content of the review is in line, or not, with the associated score. Using well established artificial intelligence techniques and analyzing in depth the reviews featuring a mismatch between the text polarity and the score, we find that -on a scale of five stars- those reviews ranked with middle scores include a mixture of positive and negative aspects. The approach proposed here, beside acting as a polarity detector, provides an effective selection of reviews -on an initial very large dataset- that may allow both consumers and providers to focus directly on the review subset featuring a text/score disagreement, which conveniently convey to the user a summary of positive and negative features of the review target.
A matter of words: NLP for quality evaluation of Wikipedia medical articles
Mar 07, 2016
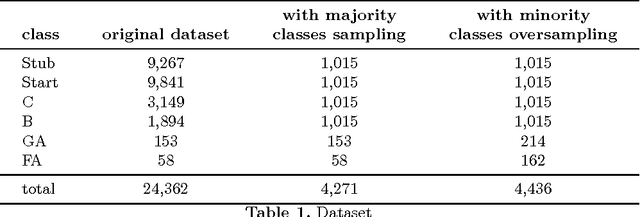

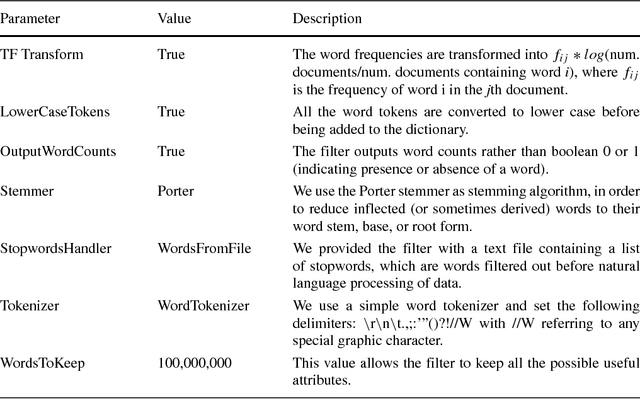
Abstract:Automatic quality evaluation of Web information is a task with many fields of applications and of great relevance, especially in critical domains like the medical one. We move from the intuition that the quality of content of medical Web documents is affected by features related with the specific domain. First, the usage of a specific vocabulary (Domain Informativeness); then, the adoption of specific codes (like those used in the infoboxes of Wikipedia articles) and the type of document (e.g., historical and technical ones). In this paper, we propose to leverage specific domain features to improve the results of the evaluation of Wikipedia medical articles. In particular, we evaluate the articles adopting an "actionable" model, whose features are related to the content of the articles, so that the model can also directly suggest strategies for improving a given article quality. We rely on Natural Language Processing (NLP) and dictionaries-based techniques in order to extract the bio-medical concepts in a text. We prove the effectiveness of our approach by classifying the medical articles of the Wikipedia Medicine Portal, which have been previously manually labeled by the Wiki Project team. The results of our experiments confirm that, by considering domain-oriented features, it is possible to obtain sensible improvements with respect to existing solutions, mainly for those articles that other approaches have less correctly classified. Other than being interesting by their own, the results call for further research in the area of domain specific features suitable for Web data quality assessment.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge