Vishal Shah
Exploring Diseases and Syndromes in Neurology Case Reports from 1955 to 2017 with Text Mining
May 23, 2019
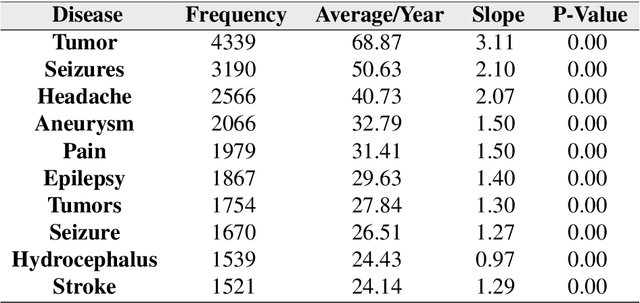
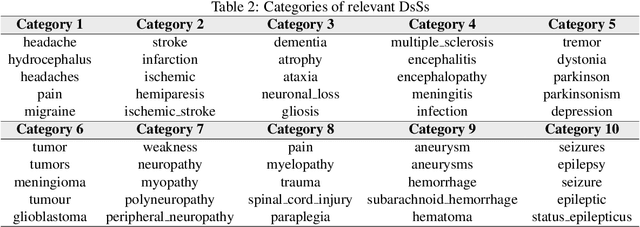
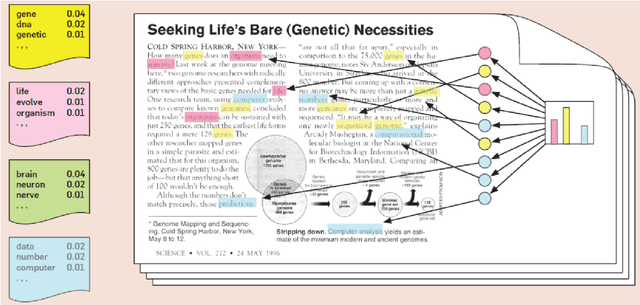
Abstract:Background: A large number of neurology case reports have been published, but it is a challenging task for human medical experts to explore all of these publications. Text mining offers a computational approach to investigate neurology literature and capture meaningful patterns. The overarching goal of this study is to provide a new perspective on case reports of neurological disease and syndrome analysis over the last six decades using text mining. Methods: We extracted diseases and syndromes (DsSs) from more than 65,000 neurology case reports from 66 journals in PubMed over the last six decades from 1955 to 2017. Text mining was applied to reports on the detected DsSs to investigate high-frequency DsSs, categorize them, and explore the linear trends over the 63-year time frame. Results: The text mining methods explored high-frequency neurologic DsSs and their trends and the relationships between them from 1955 to 2017. We detected more than 18,000 unique DsSs and found 10 categories of neurologic DsSs. While the trend analysis showed the increasing trends in the case reports for top-10 high-frequency DsSs, the categories had mixed trends. Conclusion: Our study provided new insights into the application of text mining methods to investigate DsSs in a large number of medical case reports that occur over several decades. The proposed approach can be used to provide a macro level analysis of medical literature by discovering interesting patterns and tracking them over several years to help physicians explore these case reports more efficiently.
Twitter Speaks: A Case of National Disaster Situational Awareness
Mar 07, 2019

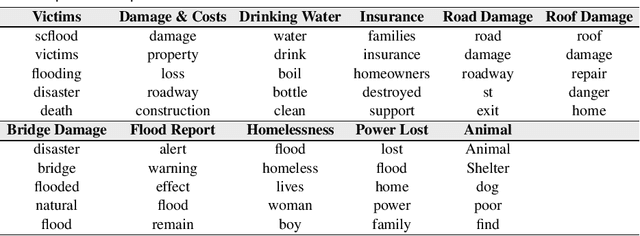
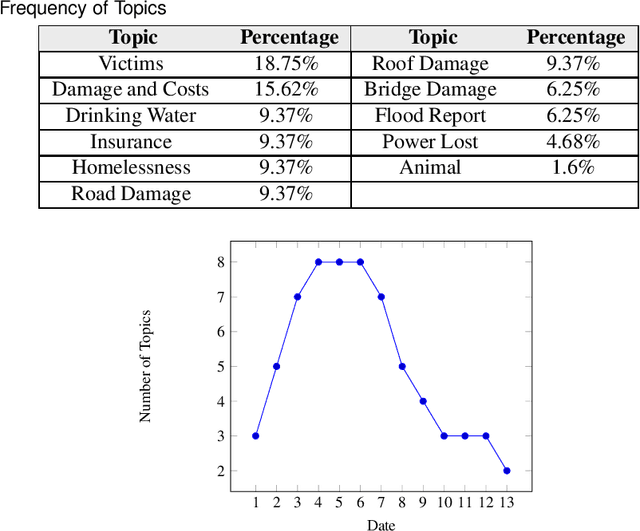
Abstract:In recent years, we have been faced with a series of natural disasters causing a tremendous amount of financial, environmental, and human losses. The unpredictable nature of natural disasters' behavior makes it hard to have a comprehensive situational awareness (SA) to support disaster management. Using opinion surveys is a traditional approach to analyze public concerns during natural disasters; however, this approach is limited, expensive, and time-consuming. Luckily the advent of social media has provided scholars with an alternative means of analyzing public concerns. Social media enable users (people) to freely communicate their opinions and disperse information regarding current events including natural disasters. This research emphasizes the value of social media analysis and proposes an analytical framework: Twitter Situational Awareness (TwiSA). This framework uses text mining methods including sentiment analysis and topic modeling to create a better SA for disaster preparedness, response, and recovery. TwiSA has also effectively deployed on a large number of tweets and tracks the negative concerns of people during the 2015 South Carolina flood.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge