Vinod Chandran
ECG-Based Driver Stress Levels Detection System Using Hyperparameter Optimization
Jan 01, 2021
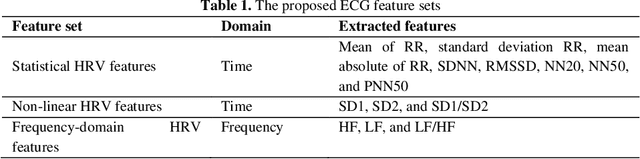
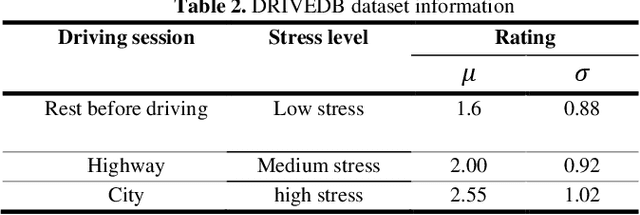

Abstract:Stress and driving are a dangerous combination which can lead to crashes, as evidenced by the large number of road traffic crashes that involve stress. Motivated by the need to address the significant costs of driver stress, it is essential to build a practical system that can classify driver stress level with high accuracy. However, the performance of an accurate driving stress levels classification system depends on hyperparameter optimization choices such as data segmentation (windowing hyperparameters). The configuration setting of hyperparameters, which has an enormous impact on the system performance, are typically hand-tuned while evaluating the algorithm. This tuning process is time consuming and often depends on personal experience. There are also no generic optimal values for hyperparameters values. In this work, we propose a meta-heuristic approach to support automated hyperparameter optimization and provide a real-time driver stress detection system. This is the first systematic study of optimizing windowing hyperparameters based on Electrocardiogram (ECG) signal in the domain of driving safety. Our approach is to propose a framework based on Particle Swarm Optimization algorithm (PSO) to select an optimal/near optimal windowing hyperparameters values. The performance of the proposed framework is evaluated on two datasets: a public dataset (DRIVEDB dataset) and our collected dataset using an advanced simulator. DRIVEDB dataset was collected in a real time driving scenario, and our dataset was collected using an advanced driving simulator in the control environment. We demonstrate that optimising the windowing hyperparameters yields significant improvement in terms of accuracy. The most accurate built model applied to the public dataset and our dataset, based on the selected windowing hyperparameters, achieved 92.12% and 77.78% accuracy, respectively.
Facial Expression Analysis under Partial Occlusion: A Survey
Feb 24, 2018



Abstract:Automatic machine-based Facial Expression Analysis (FEA) has made substantial progress in the past few decades driven by its importance for applications in psychology, security, health, entertainment and human computer interaction. The vast majority of completed FEA studies are based on non-occluded faces collected in a controlled laboratory environment. Automatic expression recognition tolerant to partial occlusion remains less understood, particularly in real-world scenarios. In recent years, efforts investigating techniques to handle partial occlusion for FEA have seen an increase. The context is right for a comprehensive perspective of these developments and the state of the art from this perspective. This survey provides such a comprehensive review of recent advances in dataset creation, algorithm development, and investigations of the effects of occlusion critical for robust performance in FEA systems. It outlines existing challenges in overcoming partial occlusion and discusses possible opportunities in advancing the technology. To the best of our knowledge, it is the first FEA survey dedicated to occlusion and aimed at promoting better informed and benchmarked future work.
* Authors pre-print of the article accepted for publication in ACM Computing Surveys (accepted on 02-Nov-2017)
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge