Vineet Jagadeesan Nair
Improving accuracy and convergence of federated learning edge computing methods for generalized DER forecasting applications in power grid
Oct 13, 2024
Abstract:This proposal aims to develop more accurate federated learning (FL) methods with faster convergence properties and lower communication requirements, specifically for forecasting distributed energy resources (DER) such as renewables, energy storage, and loads in modern, low-carbon power grids. This will be achieved by (i) leveraging recently developed extensions of FL such as hierarchical and iterative clustering to improve performance with non-IID data, (ii) experimenting with different types of FL global models well-suited to time-series data, and (iii) incorporating domain-specific knowledge from power systems to build more general FL frameworks and architectures that can be applied to diverse types of DERs beyond just load forecasting, and with heterogeneous clients.
Enhanced physics-informed neural networks (PINNs) for high-order power grid dynamics
Oct 10, 2024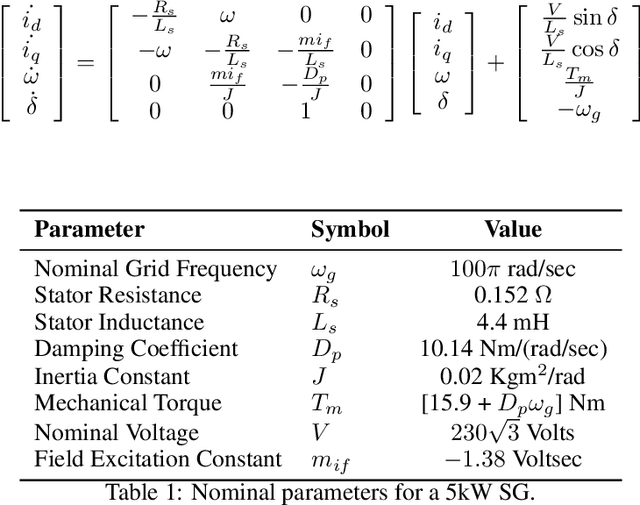
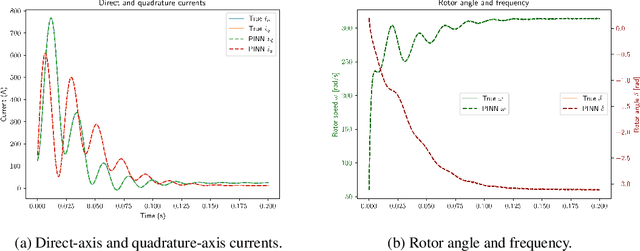
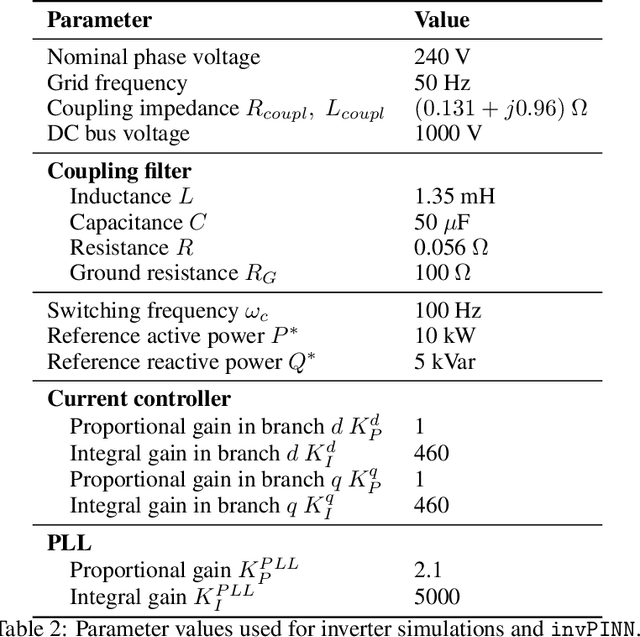
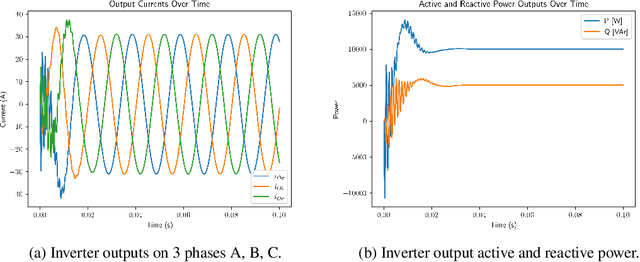
Abstract:We develop improved physics-informed neural networks (PINNs) for high-order and high-dimensional power system models described by nonlinear ordinary differential equations. We propose some novel enhancements to improve PINN training and accuracy and also implement several other recently proposed ideas from the literature. We successfully apply these to study the transient dynamics of synchronous generators. We also make progress towards applying PINNs to advanced inverter models. Such enhanced PINNs can allow us to accelerate high-fidelity simulations needed to ensure a stable and reliable renewables-rich future grid.
Federated Learning Forecasting for Strengthening Grid Reliability and Enabling Markets for Resilience
Jul 16, 2024



Abstract:We propose a comprehensive approach to increase the reliability and resilience of future power grids rich in distributed energy resources. Our distributed scheme combines federated learning-based attack detection with a local electricity market-based attack mitigation method. We validate the scheme by applying it to a real-world distribution grid rich in solar PV. Simulation results demonstrate that the approach is feasible and can successfully mitigate the grid impacts of cyber-physical attacks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge