Vikas Mehta
Novel Clinical-Grade Prostate Cancer Detection and Grading Model: Development and Prospective Validation Using Real World Data, with Performance Assessment on IHC Requested Cases
Oct 31, 2024



Abstract:Artificial intelligence may assist healthcare systems in meeting increasing demand for pathology services while maintaining diagnostic quality and reducing turnaround time and costs. We aimed to investigate the performance of an institutionally developed system for prostate cancer detection, grading, and workflow optimization and to contrast this with commercial alternatives. From August 2021 to March 2023, we scanned 21,396 slides from 1,147 patients with positive biopsies. We developed models for cancer detection, grading, and screening of equivocal cases for IHC ordering. We compared a task-specific model trained using the PANDA dataset of prostate cancer biopsies with one built using features extracted by the general-purpose histology foundation model, UNI and compare their performance in an unfiltered prospectively collected dataset that reflects our patient population (1737 slides,95 patients). We evaluated the contributions of a bespoke model designed to improve sensitivity in detecting small cancer foci and scoring of broader patterns observed at lower resolution. We found high concordance between the developed systems and pathologist reference in detection (AUC 98.5, sensitivity 95.0, and specificity 97.8), ISUP grading (quadratic Cohen's kappa 0.869), grade group 3 or higher (AUC 97.5, sensitivity 94.9, specificity 96.6) and comparable to published data from commercial systems. Screening could reduce IHC ordering for equivocal cases by 44.5% with an overall error rate of 1.8% (1.4% false positive, 0.4% false negative rates). Institutions like academic medical centers that have high scanning volumes and report abstraction capabilities can develop accurate computational pathology models for internal use. These models have the potential to aid in quality control role and to improve workflow in the pathology lab to help meet future challenges in prostate cancer diagnosis.
Learning-Based Image Compression for Machines
Sep 27, 2024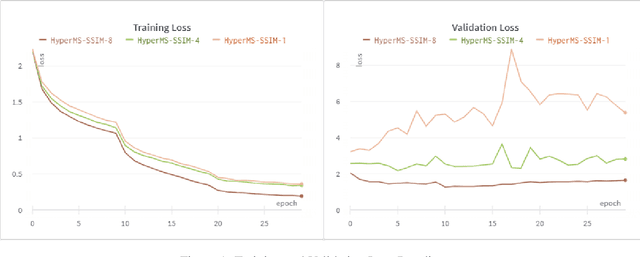
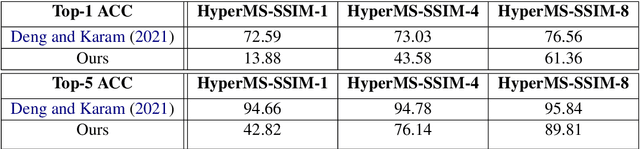
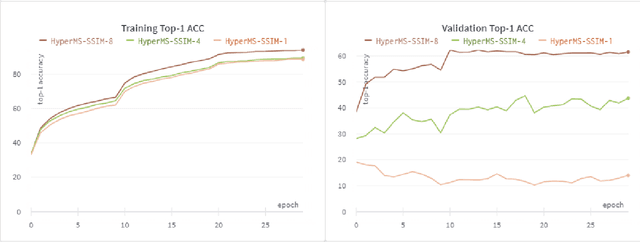
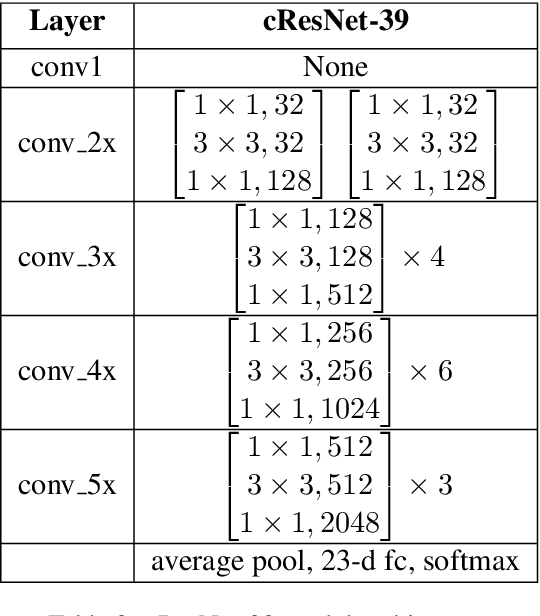
Abstract:While learning based compression techniques for images have outperformed traditional methods, they have not been widely adopted in machine learning pipelines. This is largely due to lack of standardization and lack of retention of salient features needed for such tasks. Decompression of images have taken a back seat in recent years while the focus has shifted to an image's utility in performing machine learning based analysis on top of them. Thus the demand for compression pipelines that incorporate such features from images has become ever present. The methods outlined in the report build on the recent work done on learning based image compression techniques to incorporate downstream tasks in them. We propose various methods of finetuning and enhancing different parts of pretrained compression encoding pipeline and present the results of our investigation regarding the performance of vision tasks using compression based pipelines.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge