Vignesh Kannan
Seeing Beyond Cancer: Multi-Institutional Validation of Object Localization and 3D Semantic Segmentation using Deep Learning for Breast MRI
Nov 27, 2023Abstract:The clinical management of breast cancer depends on an accurate understanding of the tumor and its anatomical context to adjacent tissues and landmark structures. This context may be provided by semantic segmentation methods; however, previous works have been largely limited to a singular focus on the tumor alone and rarely other tissue types. In contrast, we present a method that exploits tissue-tissue interactions to accurately segment every major tissue type in the breast including: chest wall, skin, adipose tissue, fibroglandular tissue, vasculature and tumor via standard-of-care Dynamic Contrast Enhanced MRI. Comparing our method to prior state-of-the-art, we achieved a superior Dice score on tumor segmentation while maintaining competitive performance on other studied tissues across multiple institutions. Briefly, our method proceeds by localizing the tumor using 2D object detectors, then segmenting the tumor and surrounding tissues independently using two 3D U-nets, and finally integrating these results while mitigating false positives by checking for anatomically plausible tissue-tissue contacts. The object detection models were pre-trained on ImageNet and COCO, and operated on MIP (maximum intensity projection) images in the axial and sagittal planes, establishing a 3D tumor bounding box. By integrating multiple relevant peri-tumoral tissues, our work enables clinical applications in breast cancer staging, prognosis and surgical planning.
Quality Assessment of Low Light Restored Images: A Subjective Study and an Unsupervised Model
Feb 04, 2022
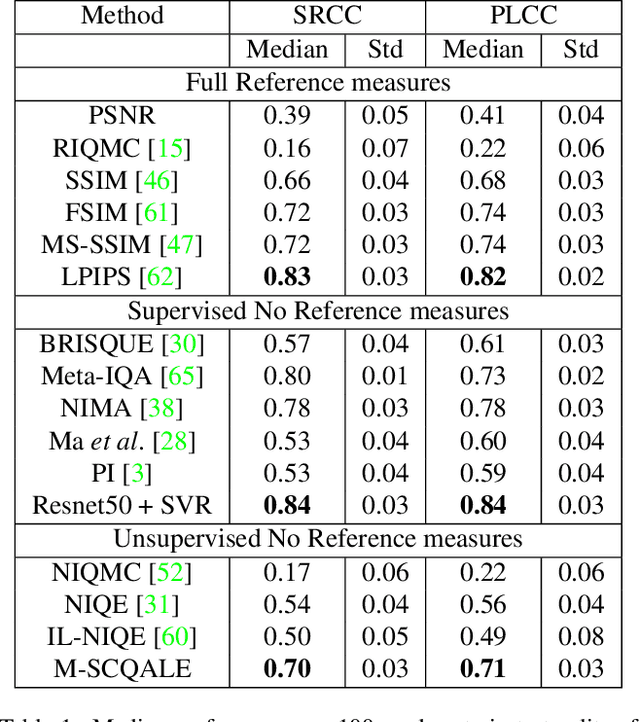
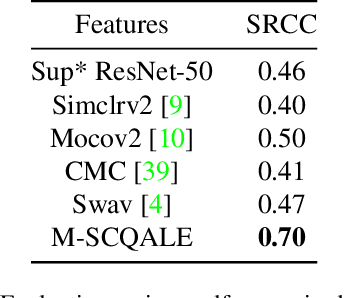
Abstract:The quality assessment (QA) of restored low light images is an important tool for benchmarking and improving low light restoration (LLR) algorithms. While several LLR algorithms exist, the subjective perception of the restored images has been much less studied. Challenges in capturing aligned low light and well-lit image pairs and collecting a large number of human opinion scores of quality for training, warrant the design of unsupervised (or opinion unaware) no-reference (NR) QA methods. This work studies the subjective perception of low light restored images and their unsupervised NR QA. Our contributions are two-fold. We first create a dataset of restored low light images using various LLR methods, conduct a subjective QA study and benchmark the performance of existing QA methods. We then present a self-supervised contrastive learning technique to extract distortion aware features from the restored low light images. We show that these features can be effectively used to build an opinion unaware image quality analyzer. Detailed experiments reveal that our unsupervised NR QA model achieves state-of-the-art performance among all such quality measures for low light restored images.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge