Vignesh Babu Manjunath Gandudi
Applications of Robots for COVID-19 Response
Aug 16, 2020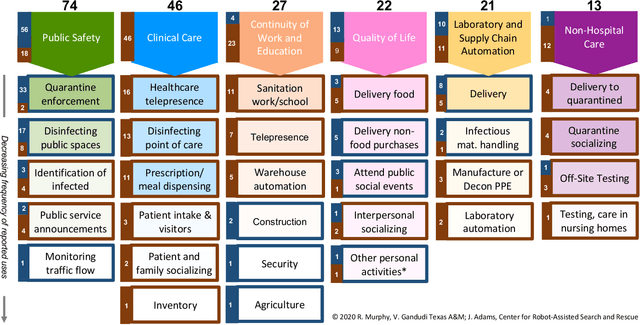

Abstract:This paper reviews 262 reports appearing between March 27 and July 4, 2020, in the press, social media, and scientific literature describing 203 instances of actual use of 104 different models of ground and aerial robots for the COVID19 response. The reports are organized by stakeholders and work domain into a novel taxonomy of six application categories, reflecting major differences in work envelope, adoption strategy, and human-robot interaction constraints. Each application category is further divided into a total of 30 subcategories based on differences in mission. The largest number of reported instances were for public safety (74 out of 203) and clinical care (46), though robots for quality of life (27), continuity of work and education (22), laboratory and supply chain automation (21), and non-clinical care (13) were notable. Ground robots were used more frequently (119) than aerial systems (84), but unlike ground robots, aerial applications appeared to take advantage of existing general purpose platforms that were used for multiple applications and missions. Of the 104 models of robots, 82 were determined to be commercially available or already existed as a prototype, 11 were modifications to existing robots, 11 were built from scratch. Teleoperation dominated the control style (105 instances), with the majority of those applications intentionally providing remote presence and thus not amenable to full autonomy in the future. Automation accounted for 74 instances and taskable agency forms of autonomy, 24. The data suggests areas for further research in autonomy, human-robot interaction, and adaptability.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge