Vid Hanžel
RAG Enabled Conversations about Household Electricity Monitoring
Jun 03, 2024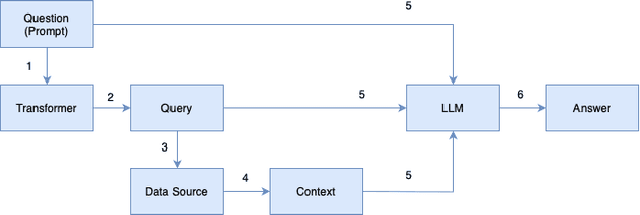
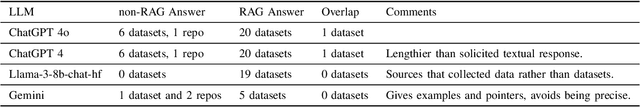
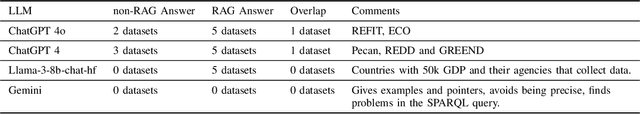
Abstract:In this paper, we investigate the integration of Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) with large language models (LLMs) such as ChatGPT, Gemini, and Llama to enhance the accuracy and specificity of responses to complex questions about electricity datasets. Recognizing the limitations of LLMs in generating precise and contextually relevant answers due to their dependency on the patterns in training data rather than factual understanding, we propose a solution that leverages a specialized electricity knowledge graph. This approach facilitates the retrieval of accurate, real-time data which is then synthesized with the generative capabilities of LLMs. Our findings illustrate that the RAG approach not only reduces the incidence of incorrect information typically generated by LLMs but also significantly improves the quality of the output by grounding responses in verifiable data. This paper details our methodology, presents a comparative analysis of responses with and without RAG, and discusses the implications of our findings for future applications of AI in specialized sectors like energy data analysis.
Towards Data-Driven Electricity Management: Multi-Region Harmonized Data and Knowledge Graph
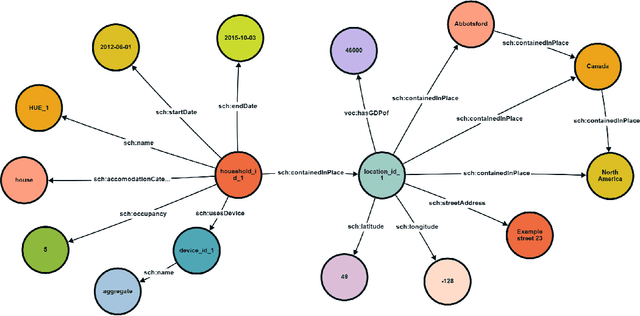
May 29, 2024Abstract:Due to growing population and technological advances, global electricity consumption, and consequently also CO2 emissions are increasing. The residential sector makes up 25% of global electricity consumption and has great potential to increase efficiency and reduce CO2 footprint without sacrificing comfort. However, a lack of uniform consumption data at the household level spanning multiple regions hinders large-scale studies and robust multi-region model development. This paper introduces a multi-region dataset compiled from publicly available sources and presented in a uniform format. This data enables machine learning tasks such as disaggregation, demand forecasting, appliance ON/OFF classification, etc. Furthermore, we develop an RDF knowledge graph that characterizes the electricity consumption of the households and contextualizes it with household related properties enabling semantic queries and interoperability with other open knowledge bases like Wikidata and DBpedia. This structured data can be utilized to inform various stakeholders towards data-driven policy and business development.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge