Vedant Dharnidharka
Named Entity Linking on Namesakes
May 21, 2022
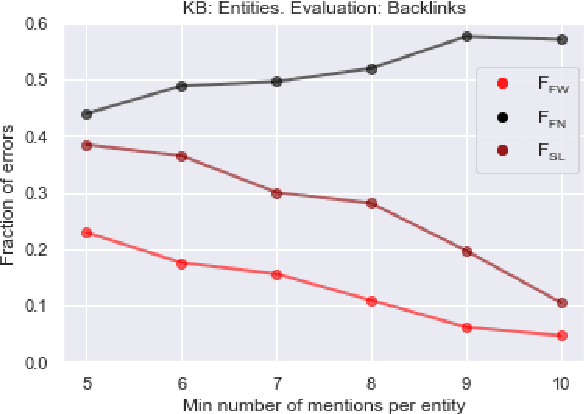

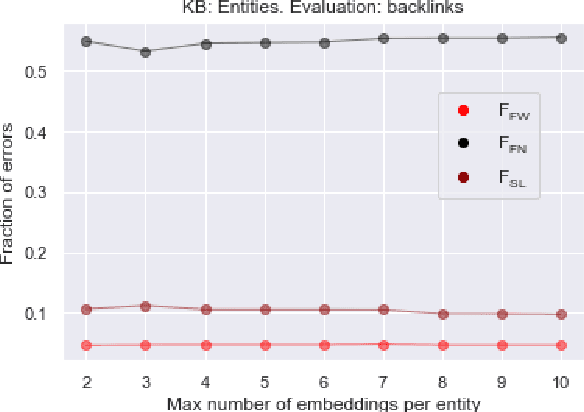
Abstract:We propose a simple and practical method of named entity linking (NEL), and explore its features and performance on a dataset of ambiguous named entities - Namesakes. We represent knowledge base (KB) entity by a set of embeddings. Our observations suggest that it is reasonable to keep a limited number of such embeddings, and that the number of mentions required to create a KB entity is important. We show that representations of entities in the knowledge base (KB) can be adjusted using only KB data, and the adjustment improves NEL performance.
Namesakes: Ambiguously Named Entities from Wikipedia and News
Nov 22, 2021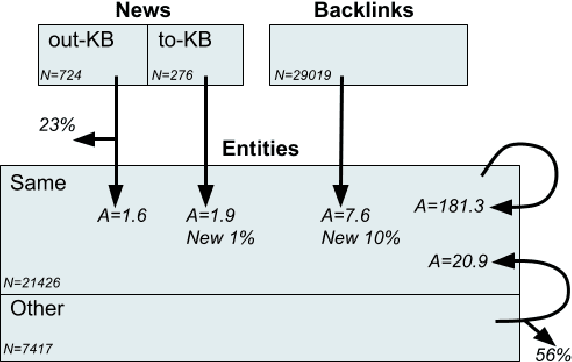



Abstract:We present Namesakes, a dataset of ambiguously named entities obtained from English-language Wikipedia and news articles. It consists of 58862 mentions of 4148 unique entities and their namesakes: 1000 mentions from news, 28843 from Wikipedia articles about the entity, and 29019 Wikipedia backlink mentions. Namesakes should be helpful in establishing challenging benchmarks for the task of named entity linking (NEL).
Sensitivity of BLANC to human-scored qualities of text summaries
Oct 13, 2020



Abstract:We explore the sensitivity of a document summary quality estimator, BLANC, to human assessment of qualities for the same summaries. In our human evaluations, we distinguish five summary qualities, defined by how fluent, understandable, informative, compact, and factually correct the summary is. We make the case for optimal BLANC parameters, at which the BLANC sensitivity to almost all of summary qualities is about as good as the sensitivity of a human annotator.
Fill in the BLANC: Human-free quality estimation of document summaries
Feb 23, 2020



Abstract:We present BLANC, a new approach to the automatic estimation of document summary quality. Our goal is to measure the functional performance of a summary with an objective, reproducible, and fully automated method. Our approach achieves this by measuring the performance boost gained by a pre-trained language model with access to a document summary while carrying out its language understanding task on the document's text. We present evidence that BLANC scores have at least as good correlation with human evaluations as do the ROUGE family of summary quality measurements. And unlike ROUGE, the BLANC method does not require human-written reference summaries, allowing for fully human-free summary quality estimation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge