Vali Tawosi
Software Vulnerability and Functionality Assessment using LLMs
Mar 13, 2024
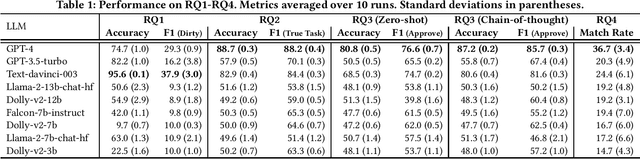


Abstract:While code review is central to the software development process, it can be tedious and expensive to carry out. In this paper, we investigate whether and how Large Language Models (LLMs) can aid with code reviews. Our investigation focuses on two tasks that we argue are fundamental to good reviews: (i) flagging code with security vulnerabilities and (ii) performing software functionality validation, i.e., ensuring that code meets its intended functionality. To test performance on both tasks, we use zero-shot and chain-of-thought prompting to obtain final ``approve or reject'' recommendations. As data, we employ seminal code generation datasets (HumanEval and MBPP) along with expert-written code snippets with security vulnerabilities from the Common Weakness Enumeration (CWE). Our experiments consider a mixture of three proprietary models from OpenAI and smaller open-source LLMs. We find that the former outperforms the latter by a large margin. Motivated by promising results, we finally ask our models to provide detailed descriptions of security vulnerabilities. Results show that 36.7% of LLM-generated descriptions can be associated with true CWE vulnerabilities.
Search-based Optimisation of LLM Learning Shots for Story Point Estimation
Mar 13, 2024Abstract:One of the ways Large Language Models (LLMs) are used to perform machine learning tasks is to provide them with a few examples before asking them to produce a prediction. This is a meta-learning process known as few-shot learning. In this paper, we use available Search-Based methods to optimise the number and combination of examples that can improve an LLM's estimation performance, when it is used to estimate story points for new agile tasks. Our preliminary results show that our SBSE technique improves the estimation performance of the LLM by 59.34% on average (in terms of mean absolute error of the estimation) over three datasets against a zero-shot setting.
* 6 pages, Accepted at SSBSE'23 NIER Track
Deep Learning for Agile Effort Estimation Have We Solved the Problem Yet?
Jan 14, 2022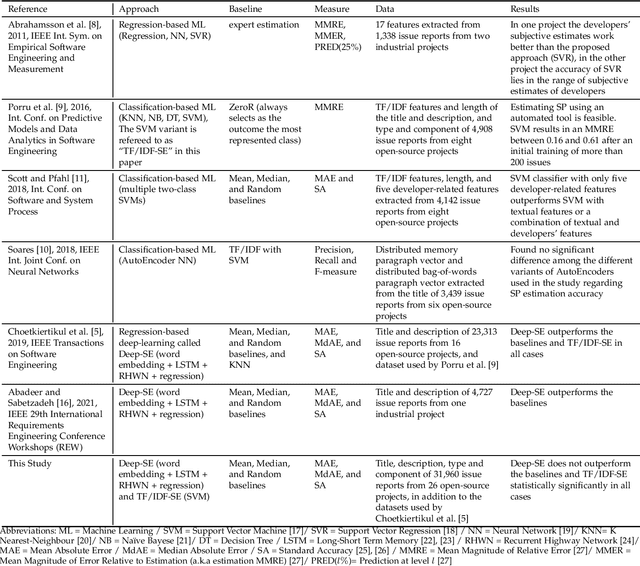
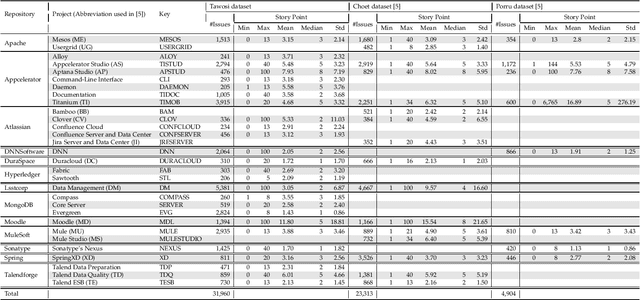
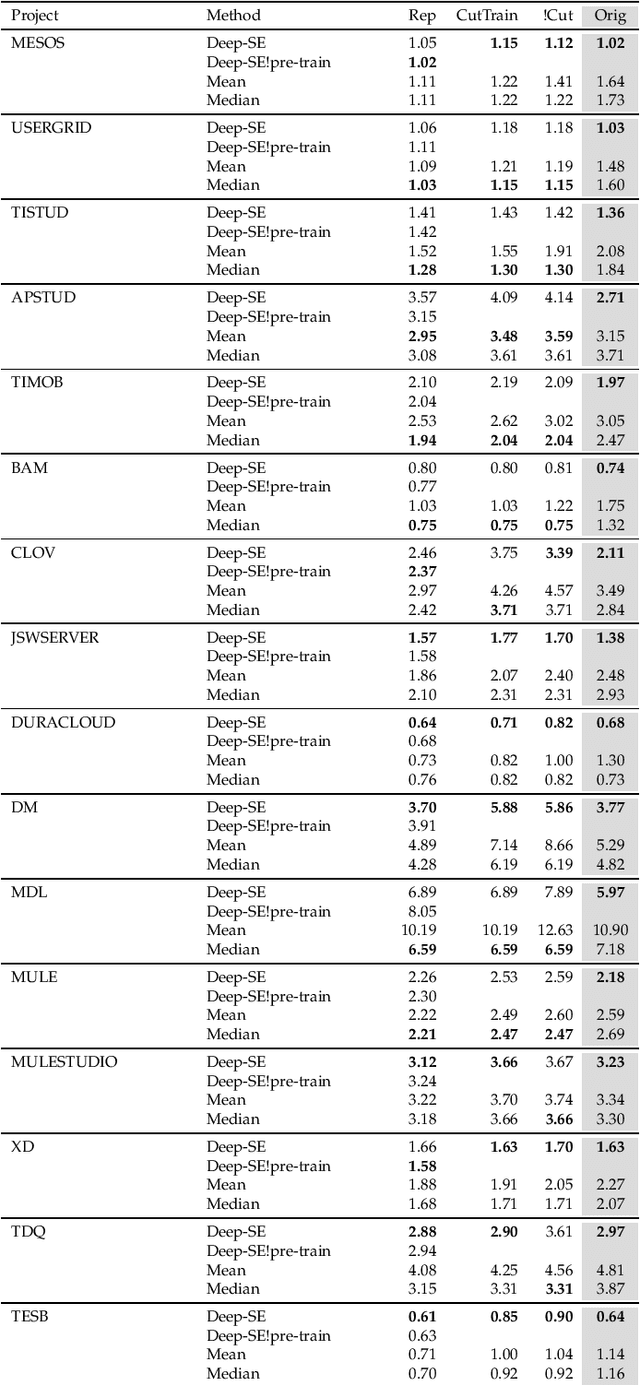
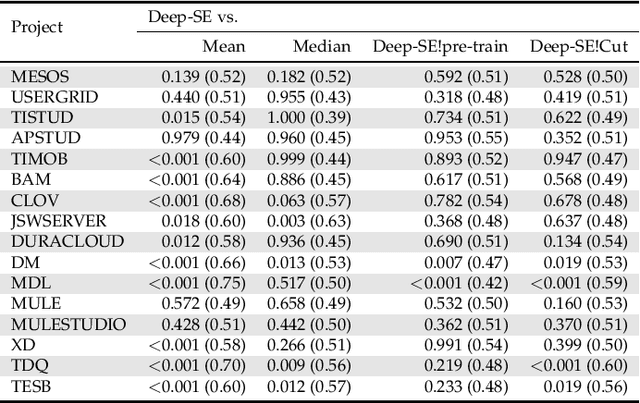
Abstract:In the last decade, several studies have proposed the use of automated techniques to estimate the effort of agile software development. In this paper we perform a close replication and extension of a seminal work proposing the use of Deep Learning for agile effort estimation (namely Deep-SE), which has set the state-of-the-art since. Specifically, we replicate three of the original research questions aiming at investigating the effectiveness of Deep-SE for both within-project and cross-project effort estimation. We benchmark Deep-SE against three baseline techniques (i.e., Random, Mean and Median effort prediction) and a previously proposed method to estimate agile software project development effort (dubbed TF/IDF-SE), as done in the original study. To this end, we use both the data from the original study and a new larger dataset of 31,960 issues, which we mined from 29 open-source projects. Using more data allows us to strengthen our confidence in the results and further mitigate the threat to the external validity of the study. We also extend the original study by investigating two additional research questions. One evaluates the accuracy of Deep-SE when the training set is augmented with issues from all other projects available in the repository at the time of estimation, and the other examines whether an expensive pre-training step used by the original Deep-SE, has any beneficial effect on its accuracy and convergence speed. The results of our replication show that Deep-SE outperforms the Median baseline estimator and TF/IDF-SE in only very few cases with statistical significance (8/42 and 9/32 cases, respectively), thus confounding previous findings on the efficacy of Deep-SE. The two additional RQs revealed that neither augmenting the training set nor pre-training Deep-SE play a role in improving its accuracy and convergence speed. ...
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge