Vadim Fomin
Tracing cultural diachronic semantic shifts in Russian using word embeddings: test sets and baselines
May 16, 2019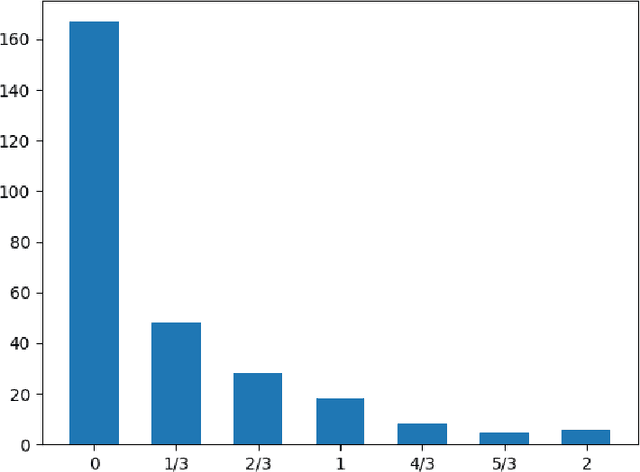

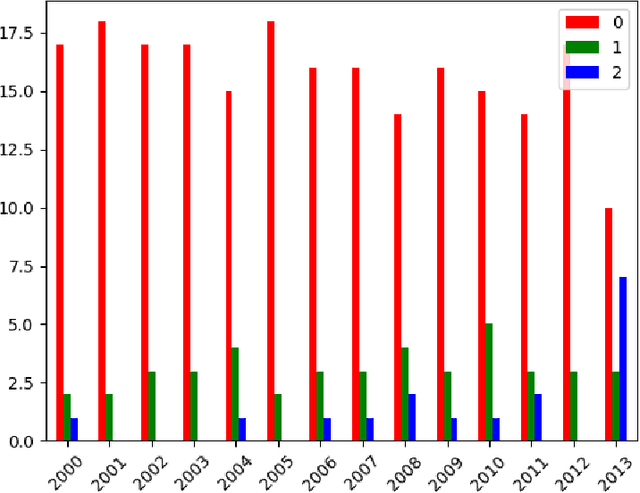
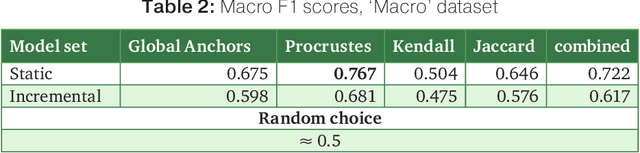
Abstract:The paper introduces manually annotated test sets for the task of tracing diachronic (temporal) semantic shifts in Russian. The two test sets are complementary in that the first one covers comparatively strong semantic changes occurring to nouns and adjectives from pre-Soviet to Soviet times, while the second one covers comparatively subtle socially and culturally determined shifts occurring in years from 2000 to 2014. Additionally, the second test set offers more granular classification of shifts degree, but is limited to only adjectives. The introduction of the test sets allowed us to evaluate several well-established algorithms of semantic shifts detection (posing this as a classification problem), most of which have never been tested on Russian material. All of these algorithms use distributional word embedding models trained on the corresponding in-domain corpora. The resulting scores provide solid comparison baselines for future studies tackling similar tasks. We publish the datasets, code and the trained models in order to facilitate further research in automatically detecting temporal semantic shifts for Russian words, with time periods of different granularities.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge