Uwe Nagel
Graph Based Relational Features for Collective Classification
Feb 09, 2017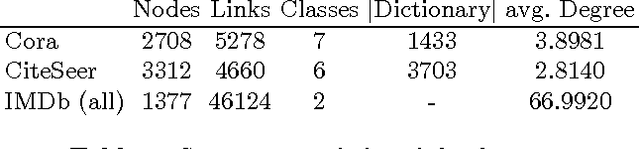
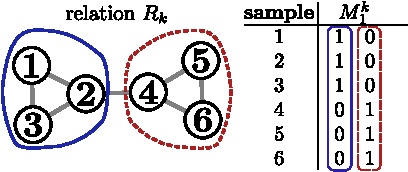
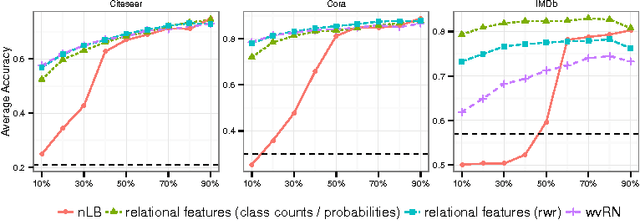
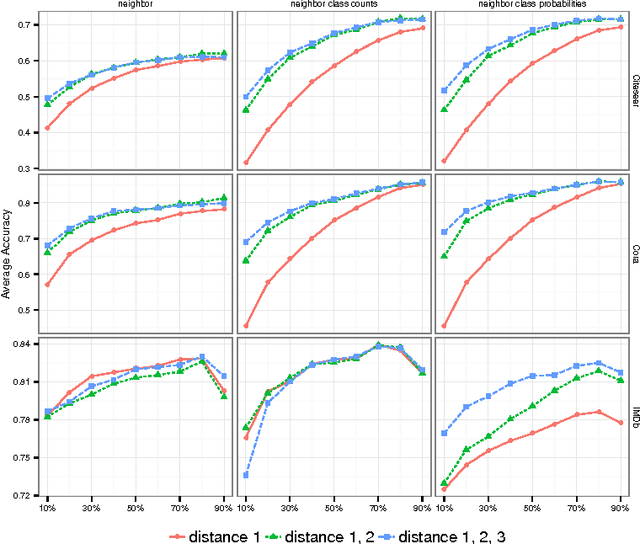
Abstract:Statistical Relational Learning (SRL) methods have shown that classification accuracy can be improved by integrating relations between samples. Techniques such as iterative classification or relaxation labeling achieve this by propagating information between related samples during the inference process. When only a few samples are labeled and connections between samples are sparse, collective inference methods have shown large improvements over standard feature-based ML methods. However, in contrast to feature based ML, collective inference methods require complex inference procedures and often depend on the strong assumption of label consistency among related samples. In this paper, we introduce new relational features for standard ML methods by extracting information from direct and indirect relations. We show empirically on three standard benchmark datasets that our relational features yield results comparable to collective inference methods. Finally we show that our proposal outperforms these methods when additional information is available.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge