Unathi Mahola
HMM Speaker Identification Using Linear and Non-linear Merging Techniques
May 11, 2007



Abstract:Speaker identification is a powerful, non-invasive and in-expensive biometric technique. The recognition accuracy, however, deteriorates when noise levels affect a specific band of frequency. In this paper, we present a sub-band based speaker identification that intends to improve the live testing performance. Each frequency sub-band is processed and classified independently. We also compare the linear and non-linear merging techniques for the sub-bands recognizer. Support vector machines and Gaussian Mixture models are the non-linear merging techniques that are investigated. Results showed that the sub-band based method used with linear merging techniques enormously improved the performance of the speaker identification over the performance of wide-band recognizers when tested live. A live testing improvement of 9.78% was achieved
Fault Classification in Cylinders Using Multilayer Perceptrons, Support Vector Machines and Guassian Mixture Models
May 02, 2007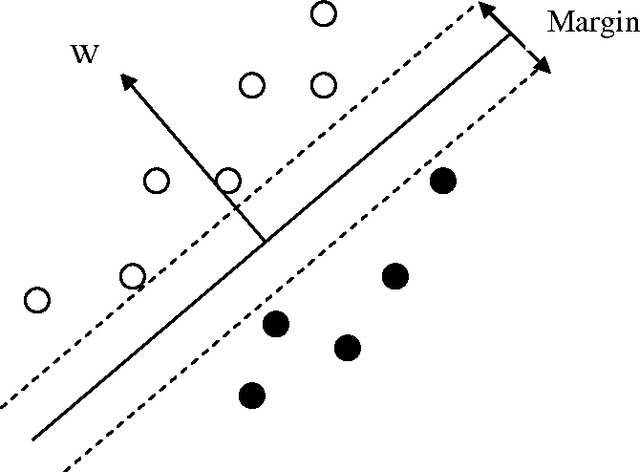
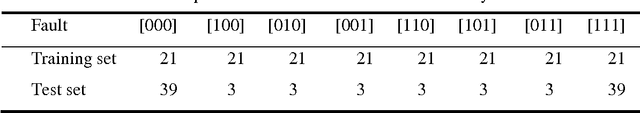
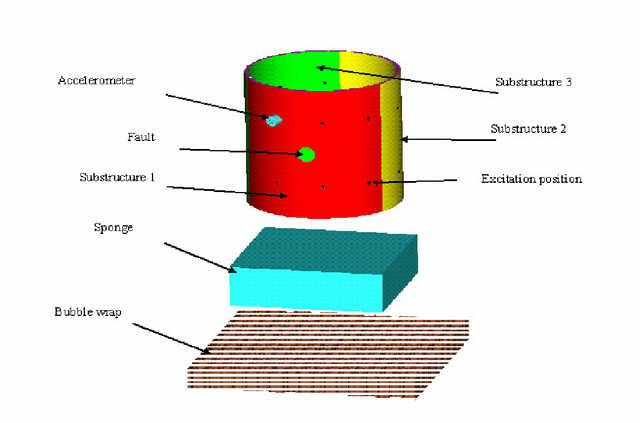
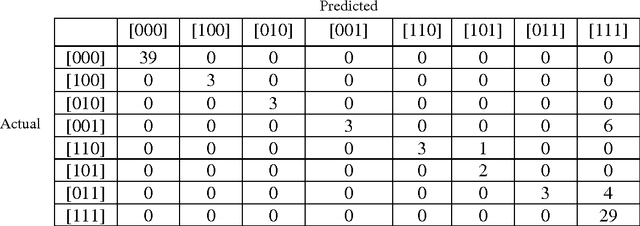
Abstract:Gaussian mixture models (GMM) and support vector machines (SVM) are introduced to classify faults in a population of cylindrical shells. The proposed procedures are tested on a population of 20 cylindrical shells and their performance is compared to the procedure, which uses multi-layer perceptrons (MLP). The modal properties extracted from vibration data are used to train the GMM, SVM and MLP. It is observed that the GMM produces 98%, SVM produces 94% classification accuracy while the MLP produces 88% classification rates.
* 10 pages, 2 figures, 4 tables
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge