Tzu-Hsuan Lin
FROAV: A Framework for RAG Observation and Agent Verification -- Lowering the Barrier to LLM Agent Research
Jan 12, 2026Abstract:The rapid advancement of Large Language Models (LLMs) and their integration into autonomous agent systems has created unprecedented opportunities for document analysis, decision support, and knowledge retrieval. However, the complexity of developing, evaluating, and iterating on LLM-based agent workflows presents significant barriers to researchers, particularly those without extensive software engineering expertise. We present FROAV (Framework for RAG Observation and Agent Verification), an open-source research platform that democratizes LLM agent research by providing a plug-and-play architecture combining visual workflow orchestration, a comprehensive evaluation framework, and extensible Python integration. FROAV implements a multi-stage Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) pipeline coupled with a rigorous "LLM-as-a-Judge" evaluation system, all accessible through intuitive graphical interfaces. Our framework integrates n8n for no-code workflow design, PostgreSQL for granular data management, FastAPI for flexible backend logic, and Streamlit for human-in-the-loop interaction. Through this integrated ecosystem, researchers can rapidly prototype RAG strategies, conduct prompt engineering experiments, validate agent performance against human judgments, and collect structured feedback-all without writing infrastructure code. We demonstrate the framework's utility through its application to financial document analysis, while emphasizing its material-agnostic architecture that adapts to any domain requiring semantic analysis. FROAV represents a significant step toward making LLM agent research accessible to a broader scientific community, enabling researchers to focus on hypothesis testing and algorithmic innovation rather than system integration challenges.
Quantum Information-Empowered Graph Neural Network for Hyperspectral Change Detection
Nov 12, 2024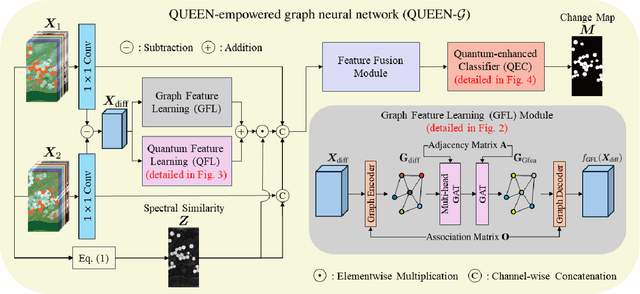
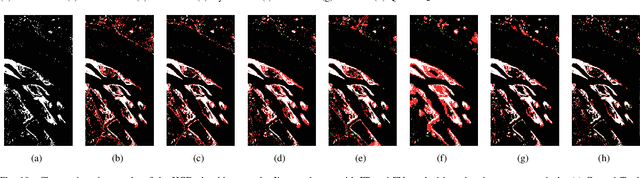
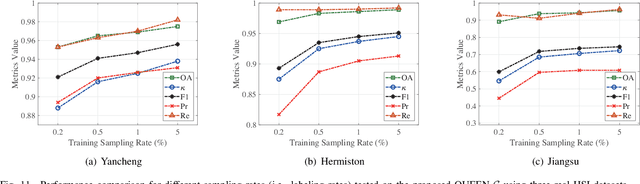
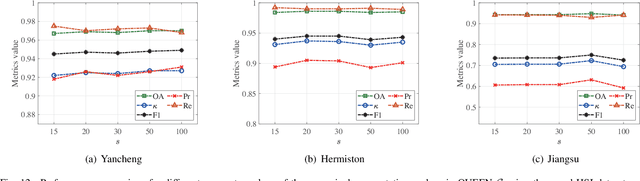
Abstract:Change detection (CD) is a critical remote sensing technique for identifying changes in the Earth's surface over time. The outstanding substance identifiability of hyperspectral images (HSIs) has significantly enhanced the detection accuracy, making hyperspectral change detection (HCD) an essential technology. The detection accuracy can be further upgraded by leveraging the graph structure of HSIs, motivating us to adopt the graph neural networks (GNNs) in solving HCD. For the first time, this work introduces quantum deep network (QUEEN) into HCD. Unlike GNN and CNN, both extracting the affine-computing features, QUEEN provides fundamentally different unitary-computing features. We demonstrate that through the unitary feature extraction procedure, QUEEN provides radically new information for deciding whether there is a change or not. Hierarchically, a graph feature learning (GFL) module exploits the graph structure of the bitemporal HSIs at the superpixel level, while a quantum feature learning (QFL) module learns the quantum features at the pixel level, as a complementary to GFL by preserving pixel-level detailed spatial information not retained in the superpixels. In the final classification stage, a quantum classifier is designed to cooperate with a traditional fully connected classifier. The superior HCD performance of the proposed QUEEN-empowered GNN (i.e., QUEEN-G) will be experimentally demonstrated on real hyperspectral datasets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge