Twyla Hill
PatchBMI-Net: Lightweight Facial Patch-based Ensemble for BMI Prediction
Nov 29, 2023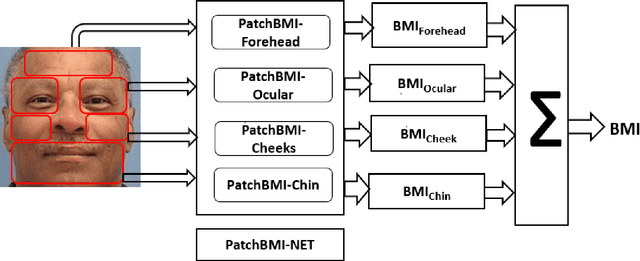

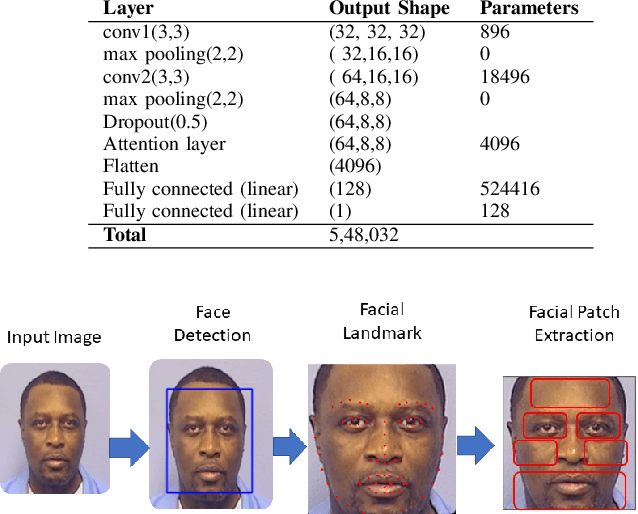
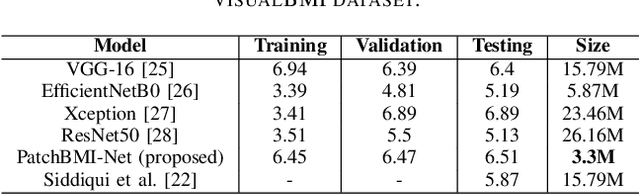
Abstract:Due to an alarming trend related to obesity affecting 93.3 million adults in the United States alone, body mass index (BMI) and body weight have drawn significant interest in various health monitoring applications. Consequently, several studies have proposed self-diagnostic facial image-based BMI prediction methods for healthy weight monitoring. These methods have mostly used convolutional neural network (CNN) based regression baselines, such as VGG19, ResNet50, and Efficient-NetB0, for BMI prediction from facial images. However, the high computational requirement of these heavy-weight CNN models limits their deployment to resource-constrained mobile devices, thus deterring weight monitoring using smartphones. This paper aims to develop a lightweight facial patch-based ensemble (PatchBMI-Net) for BMI prediction to facilitate the deployment and weight monitoring using smartphones. Extensive experiments on BMI-annotated facial image datasets suggest that our proposed PatchBMI-Net model can obtain Mean Absolute Error (MAE) in the range [3.58, 6.51] with a size of about 3.3 million parameters. On cross-comparison with heavyweight models, such as ResNet-50 and Xception, trained for BMI prediction from facial images, our proposed PatchBMI-Net obtains equivalent MAE along with the model size reduction of about 5.4x and the average inference time reduction of about 3x when deployed on Apple-14 smartphone. Thus, demonstrating performance efficiency as well as low latency for on-device deployment and weight monitoring using smartphone applications.
An Examination of Bias of Facial Analysis based BMI Prediction Models
Apr 21, 2022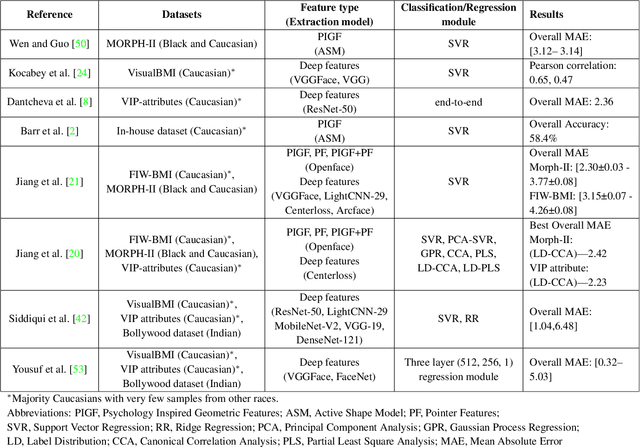
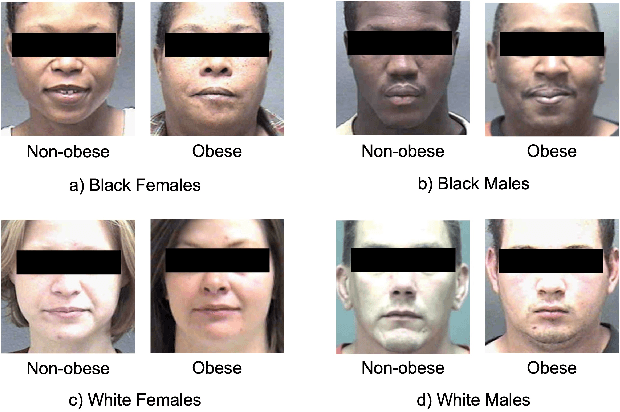

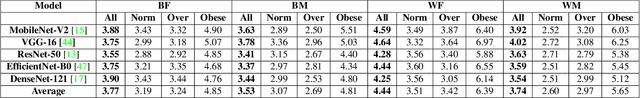
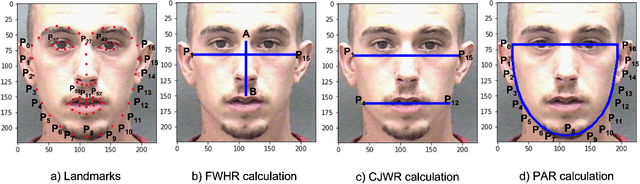
Abstract:Obesity is one of the most important public health problems that the world is facing today. A recent trend is in the development of intervention tools that predict BMI using facial images for weight monitoring and management to combat obesity. Most of these studies used BMI annotated facial image datasets that mainly consisted of Caucasian subjects. Research on bias evaluation of face-based gender-, age-classification, and face recognition systems suggest that these technologies perform poorly for women, dark-skinned people, and older adults. The bias of facial analysis-based BMI prediction tools has not been studied until now. This paper evaluates the bias of facial-analysis-based BMI prediction models across Caucasian and African-American Males and Females. Experimental investigations on the gender, race, and BMI balanced version of the modified MORPH-II dataset suggested that the error rate in BMI prediction was least for Black Males and highest for White Females. Further, the psychology-related facial features correlated with weight suggested that as the BMI increases, the changes in the facial region are more prominent for Black Males and the least for White Females. This is the reason for the least error rate of the facial analysis-based BMI prediction tool for Black Males and highest for White Females.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge