Tuomo Lehtonen
Instantiations and Computational Aspects of Non-Flat Assumption-based Argumentation
Apr 17, 2024



Abstract:Most existing computational tools for assumption-based argumentation (ABA) focus on so-called flat frameworks, disregarding the more general case. In this paper, we study an instantiation-based approach for reasoning in possibly non-flat ABA. We make use of a semantics-preserving translation between ABA and bipolar argumentation frameworks (BAFs). By utilizing compilability theory, we establish that the constructed BAFs will in general be of exponential size. In order to keep the number of arguments and computational cost low, we present three ways of identifying redundant arguments. Moreover, we identify fragments of ABA which admit a poly-sized instantiation. We propose two algorithmic approaches for reasoning in possibly non-flat ABA. The first approach utilizes the BAF instantiation while the second works directly without constructing arguments. An empirical evaluation shows that the former outperforms the latter on many instances, reflecting the lower complexity of BAF reasoning. This result is in contrast to flat ABA, where direct approaches dominate instantiation-based approaches.
Harnessing Incremental Answer Set Solving for Reasoning in Assumption-Based Argumentation
Aug 09, 2021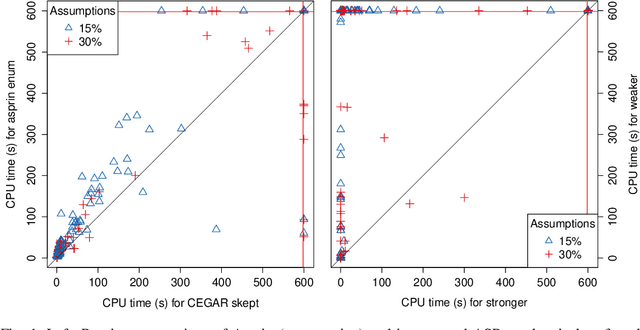
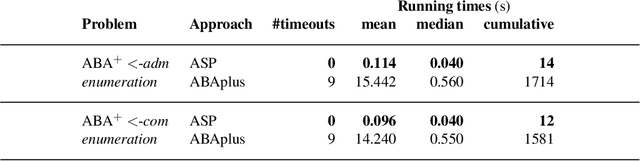
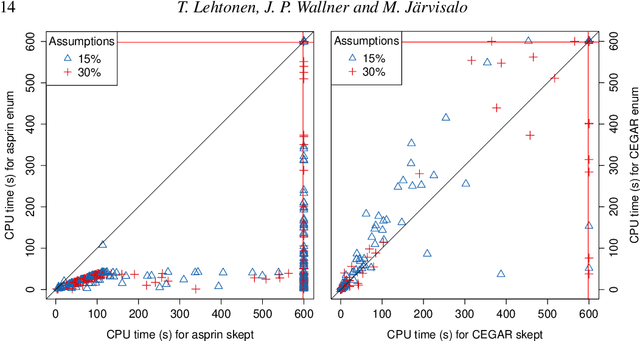
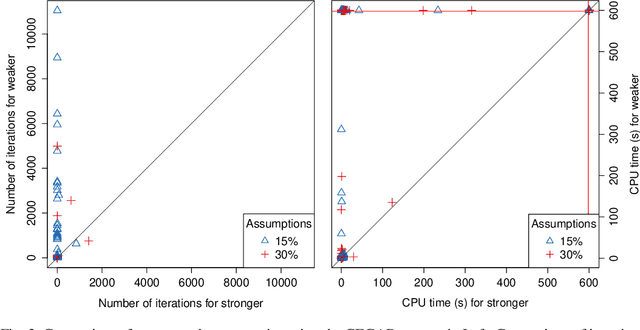
Abstract:Assumption-based argumentation (ABA) is a central structured argumentation formalism. As shown recently, answer set programming (ASP) enables efficiently solving NP-hard reasoning tasks of ABA in practice, in particular in the commonly studied logic programming fragment of ABA. In this work, we harness recent advances in incremental ASP solving for developing effective algorithms for reasoning tasks in the logic programming fragment of ABA that are presumably hard for the second level of the polynomial hierarchy, including skeptical reasoning under preferred semantics as well as preferential reasoning. In particular, we develop non-trivial counterexample-guided abstraction refinement procedures based on incremental ASP solving for these tasks. We also show empirically that the procedures are significantly more effective than previously proposed algorithms for the tasks. This paper is under consideration for acceptance in TPLP.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge