Ton Weijters
Dept. of Information Technology, Eindhoven University of Technology
Modularity in inductively-learned word pronunciation systems
Jan 26, 1998Abstract:In leading morpho-phonological theories and state-of-the-art text-to-speech systems it is assumed that word pronunciation cannot be learned or performed without in-between analyses at several abstraction levels (e.g., morphological, graphemic, phonemic, syllabic, and stress levels). We challenge this assumption for the case of English word pronunciation. Using IGTree, an inductive-learning decision-tree algorithms, we train and test three word-pronunciation systems in which the number of abstraction levels (implemented as sequenced modules) is reduced from five, via three, to one. The latter system, classifying letter strings directly as mapping to phonemes with stress markers, yields significantly better generalisation accuracies than the two multi-module systems. Analyses of empirical results indicate that positive utility effects of sequencing modules are outweighed by cascading errors passed on between modules.
* 10 pages, uses nemlap3.sty and epsf and ipamacs (WSU IPA) macros
Morphological Analysis as Classification: an Inductive-Learning Approach
Jul 16, 1996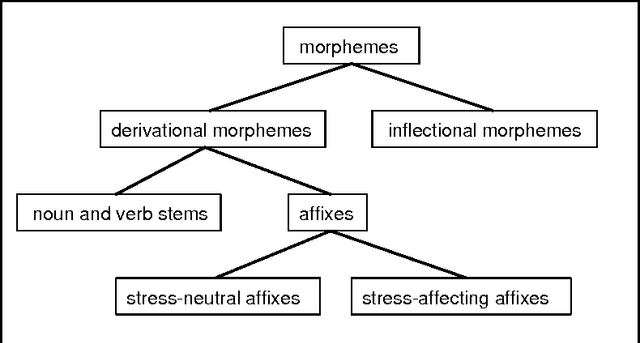
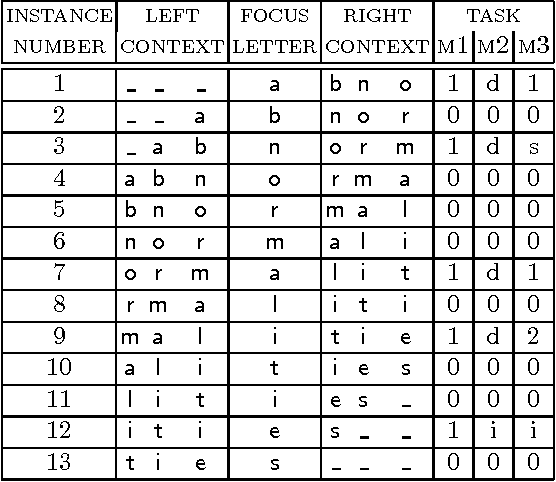
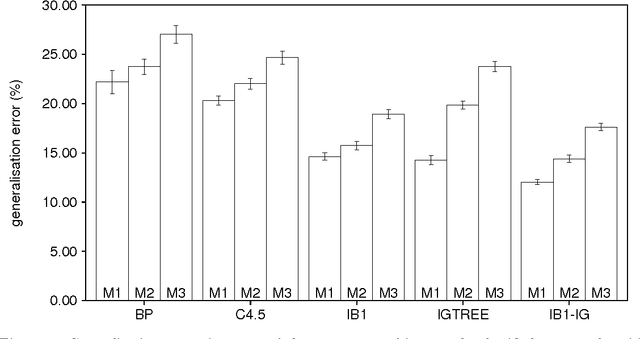
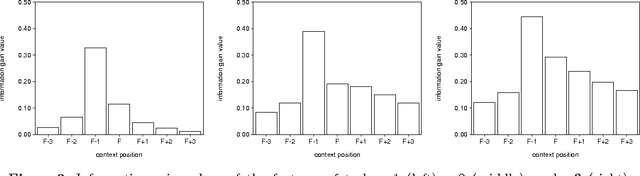
Abstract:Morphological analysis is an important subtask in text-to-speech conversion, hyphenation, and other language engineering tasks. The traditional approach to performing morphological analysis is to combine a morpheme lexicon, sets of (linguistic) rules, and heuristics to find a most probable analysis. In contrast we present an inductive learning approach in which morphological analysis is reformulated as a segmentation task. We report on a number of experiments in which five inductive learning algorithms are applied to three variations of the task of morphological analysis. Results show (i) that the generalisation performance of the algorithms is good, and (ii) that the lazy learning algorithm IB1-IG performs best on all three tasks. We conclude that lazy learning of morphological analysis as a classification task is indeed a viable approach; moreover, it has the strong advantages over the traditional approach of avoiding the knowledge-acquisition bottleneck, being fast and deterministic in learning and processing, and being language-independent.
* 11 pages, 5 encapsulated postscript figures, uses non-standard NeMLaP proceedings style nemlap.sty; inputs ipamacs (international phonetic alphabet) and epsf macros
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge