Tobias Fehenberger
On the Benefits of Rate-Adaptive Transceivers: A Network Planning Study
Dec 18, 2023



Abstract:Flexible-grid Elastic Optical Networks (EONs) have been widely deployed in recent years to support the growing demand for bandwidth-intensive applications. To address this cost-efficiently, optimized utilization of EONs is required. Next-generation bandwidth-variable transceivers (BVTs) will offer increased adaptivity in symbol rate as well as modulation through probabilistic constellation shaping. In this work, we therefore investigate the impact of increased configuration granularity on various aspects of optical networks. We account for practical implementation considerations of BVT configurations for the estimation of the required signal-to-noise ratio. Additionally, an optimization algorithm is presented that selects the most efficient configuration for each considered data rate and bandwidth combination. Based on the advanced transceiver configurations, we conduct a network planning study using a physical-layer-aware algorithm for flexible-grid EONs, and present results for a national and a continental optical backbone network topology. Our research demonstrates that a rise in modulation rate adaptivity results in substantial savings in resources, decreasing the number of necessary lightpaths by as much as 20% in EONs. In contrast, increased symbol rate granularity only results in minor savings.
Experimental Demonstration of ML-Based DWDM System Margin Estimation
Feb 16, 2023


Abstract:SNR margins between partially and fully loaded DWDM systems are estimated without detailed knowledge of the network. The ML model, trained on simulation data, achieves accurate predictions on experimental data with an RMSE of 0.16 dB.
Discrete-Time Accuracy Analysis of the Time-Domain Regular Perturbation Model for Unamplified Links
Jun 09, 2021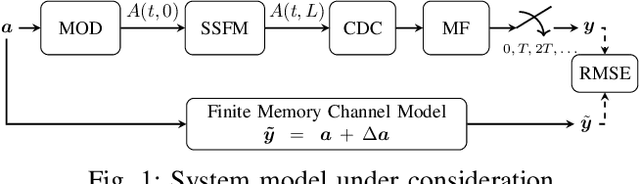
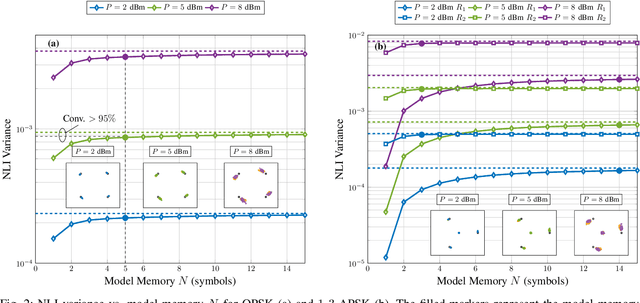
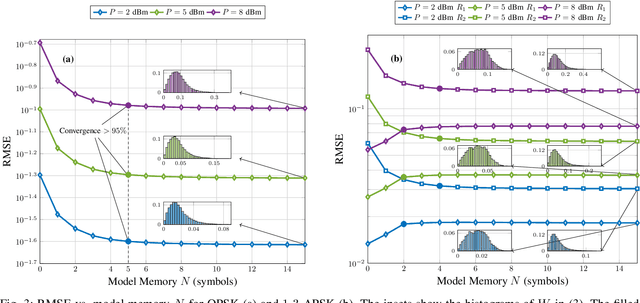

Abstract:The accuracy of a discrete-time channel model based on regular perturbation is numerically studied for unamplified links. We analyse the distance between discrete nonlinear interference points and show that such distance can be used to estimate the effective channel memory.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge