Tim Koglin
When the goal is to generate a series of activities: A self-organized simulated robot arm
May 17, 2019



Abstract:Behavior is characterized by sequences of goal-oriented conducts, such as food uptake, socializing and resting. Classically, one would define for each task a corresponding satisfaction level, with the agent engaging, at a given time, in the activity having the lowest satisfaction level. Alternatively, one may consider that the agent follows the overarching objective to generate sequences of distinct activities. To achieve a balanced distribution of activities would then be the primary goal, and not to master a specific task. In this setting, the agent would show two types of behaviors, task-oriented, and task-searching phases, with the latter interseeding the former. We study the emergence of autonomous task switching for the case of a simulated robot arm. Grasping one of several moving objects corresponds in this setting to a specific activity. Overall, the arm should follow a given object temporarily and then move away, in order to search for a new target and reengage. We show that this behavior can be generated robustly when modeling the arm as an adaptive dynamical system. The dissipation function is in this approach time dependent. The arm is in a dissipative state when searching for a nearby object, dissipating energy on approach. Once close, the dissipation function starts to increase, with the eventual sign change implying that the arm will take up energy and wander off. The resulting explorative state ends when the dissipation function becomes again negative and the arm selects a new target. We believe that our approach may be generalized to generate self-organized sequences of activities in general.
Kick control: using the attracting states arising within the sensorimotor loop of self-organized robots as motor primitives
Jun 25, 2018


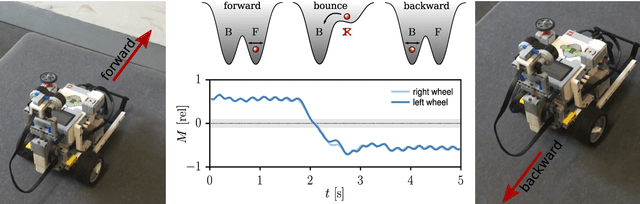
Abstract:Self-organized robots may develop attracting states within the sensorimotor loop, that is within the phase space of neural activity, body, and environmental variables. Fixpoints, limit cycles, and chaotic attractors correspond in this setting to a non-moving robot, to directed, and to irregular locomotion respectively. Short higher-order control commands may hence be used to kick the system from one self-organized attractor robustly into the basin of attraction of a different attractor, a concept termed here as kick control. The individual sensorimotor states serve in this context as highly compliant motor primitives. We study different implementations of kick control for the case of simulated and real-world wheeled robots, for which the dynamics of the distinct wheels is generated independently by local feedback loops. The feedback loops are mediated by rate-encoding neurons disposing exclusively of propriosensoric inputs in terms of projections of the actual rotational angle of the wheel. The changes of the neural activity are then transmitted into a rotational motion by a simulated transmission rod akin to the transmission rods used for steam locomotives. We find that the self-organized attractor landscape may be morphed both by higher-level control signals, in the spirit of kick control, and by interacting with the environment. Bumping against a wall destroys the limit cycle corresponding to forward motion, with the consequence that the dynamical variables are then attracted in phase space by the limit cycle corresponding to backward moving. The robot, which does not dispose of any distance or contact sensors, hence reverses direction autonomously.
* 17 pages, 9 figures
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge