Tianle Zeng
NeeCo: Image Synthesis of Novel Instrument States Based on Dynamic and Deformable 3D Gaussian Reconstruction
Aug 11, 2025
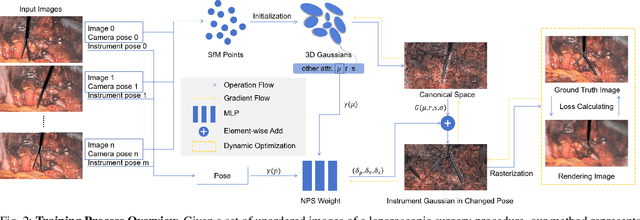

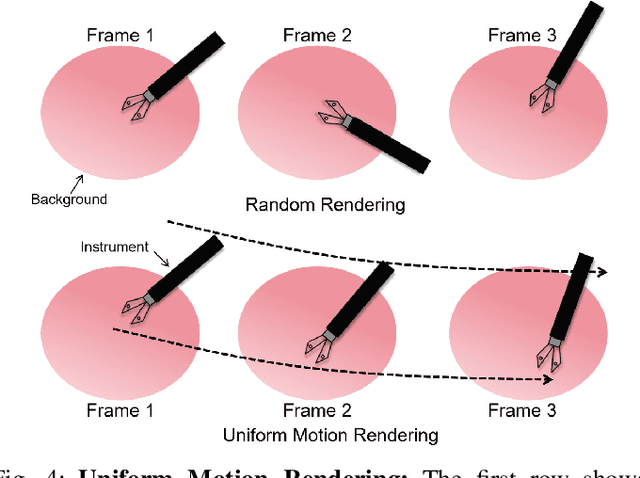
Abstract:Computer vision-based technologies significantly enhance surgical automation by advancing tool tracking, detection, and localization. However, Current data-driven approaches are data-voracious, requiring large, high-quality labeled image datasets, which limits their application in surgical data science. Our Work introduces a novel dynamic Gaussian Splatting technique to address the data scarcity in surgical image datasets. We propose a dynamic Gaussian model to represent dynamic surgical scenes, enabling the rendering of surgical instruments from unseen viewpoints and deformations with real tissue backgrounds. We utilize a dynamic training adjustment strategy to address challenges posed by poorly calibrated camera poses from real-world scenarios. Additionally, we propose a method based on dynamic Gaussians for automatically generating annotations for our synthetic data. For evaluation, we constructed a new dataset featuring seven scenes with 14,000 frames of tool and camera motion and tool jaw articulation, with a background of an ex-vivo porcine model. Using this dataset, we synthetically replicate the scene deformation from the ground truth data, allowing direct comparisons of synthetic image quality. Experimental results illustrate that our method generates photo-realistic labeled image datasets with the highest values in Peak-Signal-to-Noise Ratio (29.87). We further evaluate the performance of medical-specific neural networks trained on real and synthetic images using an unseen real-world image dataset. Our results show that the performance of models trained on synthetic images generated by the proposed method outperforms those trained with state-of-the-art standard data augmentation by 10%, leading to an overall improvement in model performances by nearly 15%.
Implementing blind navigation through multi-modal sensing and gait guidance
Jun 24, 2025Abstract:By the year 2023, the global population of individuals with impaired vision has surpassed 220 million. People with impaired vision will find it difficult while finding path or avoiding obstacles, and must ask for auxiliary tools for help. Although traditional aids such as guide canes and guide dogs exist, they still have some shortcomings. In this paper, we present our wearable blind guiding device, what perform navigation guidance through our proposed Gait-based Guiding System. Our device innovatively integrates gait phase analysis for walking guide, and in terms of environmental perception, we use multimodal sensing to acquire diverse environment information. During the experiment, we conducted both indoor and outdoor experiments, and compared with the standard guide cane. The result shows superior performance of our device in blind guidance.
YOCO: You Only Calibrate Once for Accurate Extrinsic Parameter in LiDAR-Camera Systems
Jul 25, 2024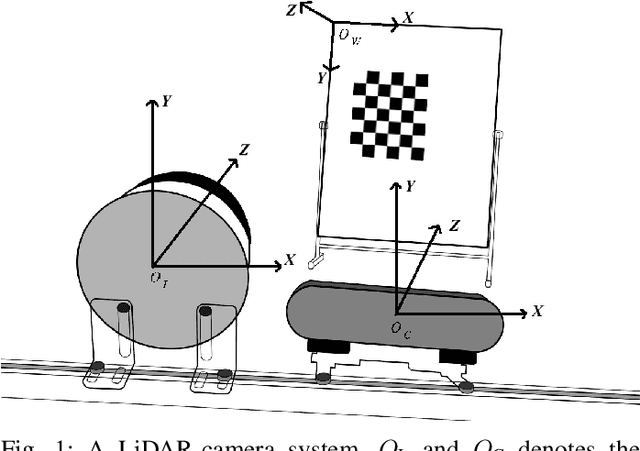

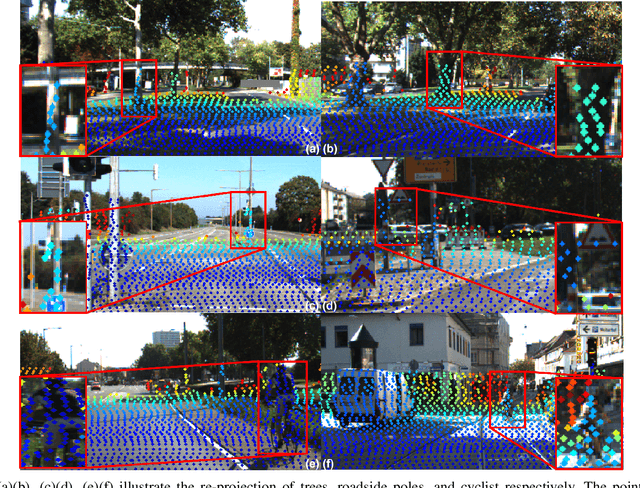
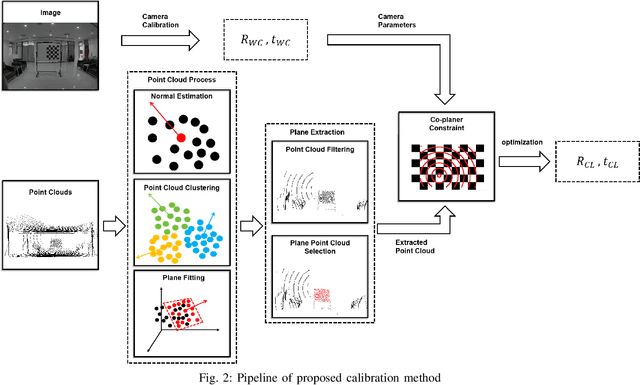
Abstract:In a multi-sensor fusion system composed of cameras and LiDAR, precise extrinsic calibration contributes to the system's long-term stability and accurate perception of the environment. However, methods based on extracting and registering corresponding points still face challenges in terms of automation and precision. This paper proposes a novel fully automatic extrinsic calibration method for LiDAR-camera systems that circumvents the need for corresponding point registration. In our approach, a novel algorithm to extract required LiDAR correspondence point is proposed. This method can effectively filter out irrelevant points by computing the orientation of plane point clouds and extracting points by applying distance- and density-based thresholds. We avoid the need for corresponding point registration by introducing extrinsic parameters between the LiDAR and camera into the projection of extracted points and constructing co-planar constraints. These parameters are then optimized to solve for the extrinsic. We validated our method across multiple sets of LiDAR-camera systems. In synthetic experiments, our method demonstrates superior performance compared to current calibration techniques. Real-world data experiments further confirm the precision and robustness of the proposed algorithm, with average rotation and translation calibration errors between LiDAR and camera of less than 0.05 degree and 0.015m, respectively. This method enables automatic and accurate extrinsic calibration in a single one step, emphasizing the potential of calibration algorithms beyond using corresponding point registration to enhance the automation and precision of LiDAR-camera system calibration.
* IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON INSTRUMENTATION AND MEASUREMENT
Realistic Surgical Image Dataset Generation Based On 3D Gaussian Splatting
Jul 20, 2024



Abstract:Computer vision technologies markedly enhance the automation capabilities of robotic-assisted minimally invasive surgery (RAMIS) through advanced tool tracking, detection, and localization. However, the limited availability of comprehensive surgical datasets for training represents a significant challenge in this field. This research introduces a novel method that employs 3D Gaussian Splatting to generate synthetic surgical datasets. We propose a method for extracting and combining 3D Gaussian representations of surgical instruments and background operating environments, transforming and combining them to generate high-fidelity synthetic surgical scenarios. We developed a data recording system capable of acquiring images alongside tool and camera poses in a surgical scene. Using this pose data, we synthetically replicate the scene, thereby enabling direct comparisons of the synthetic image quality (29.592 PSNR). As a further validation, we compared two YOLOv5 models trained on the synthetic and real data, respectively, and assessed their performance in an unseen real-world test dataset. Comparing the performances, we observe an improvement in neural network performance, with the synthetic-trained model outperforming the real-world trained model by 12%, testing both on real-world data.
* This paper has already been accepted by INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON MEDICAL IMAGE COMPUTING AND COMPUTER ASSISTED INTERVENTION (MICCAI 2024)
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge