Tiago A. Almeida
Vulnerable Road User Detection and Safety Enhancement: A Comprehensive Survey
May 29, 2024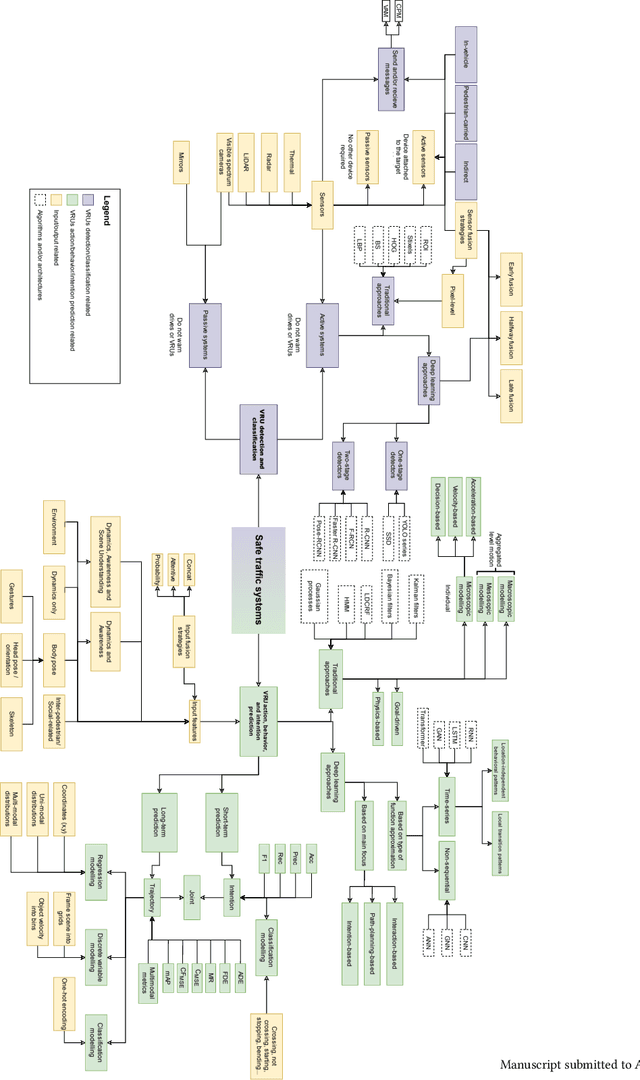
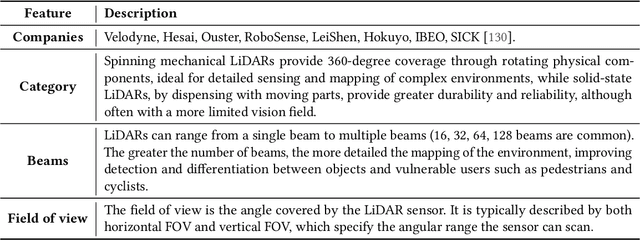
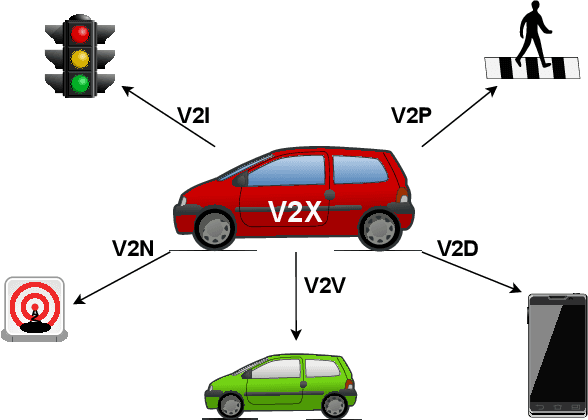

Abstract:Traffic incidents involving vulnerable road users (VRUs) constitute a significant proportion of global road accidents. Advances in traffic communication ecosystems, coupled with sophisticated signal processing and machine learning techniques, have facilitated the utilization of data from diverse sensors. Despite these advancements and the availability of extensive datasets, substantial progress is required to mitigate traffic casualties. This paper provides a comprehensive survey of state-of-the-art technologies and methodologies to enhance the safety of VRUs. The study delves into the communication networks between vehicles and VRUs, emphasizing the integration of advanced sensors and the availability of relevant datasets. It explores preprocessing techniques and data fusion methods to enhance sensor data quality. Furthermore, our study assesses critical simulation environments essential for developing and testing VRU safety systems. Our research also highlights recent advances in VRU detection and classification algorithms, addressing challenges such as variable environmental conditions. Additionally, we cover cutting-edge research in predicting VRU intentions and behaviors, which is crucial for proactive collision avoidance strategies. Through this survey, we aim to provide a comprehensive understanding of the current landscape of VRU safety technologies, identifying areas of progress and areas needing further research and development.
An explainable model to support the decision about the therapy protocol for AML
Jul 15, 2023

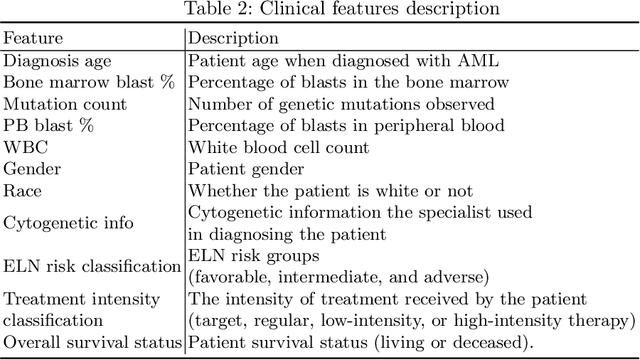

Abstract:Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML) is one of the most aggressive types of hematological neoplasm. To support the specialists' decision about the appropriate therapy, patients with AML receive a prognostic of outcomes according to their cytogenetic and molecular characteristics, often divided into three risk categories: favorable, intermediate, and adverse. However, the current risk classification has known problems, such as the heterogeneity between patients of the same risk group and no clear definition of the intermediate risk category. Moreover, as most patients with AML receive an intermediate-risk classification, specialists often demand other tests and analyses, leading to delayed treatment and worsening of the patient's clinical condition. This paper presents the data analysis and an explainable machine-learning model to support the decision about the most appropriate therapy protocol according to the patient's survival prediction. In addition to the prediction model being explainable, the results obtained are promising and indicate that it is possible to use it to support the specialists' decisions safely. Most importantly, the findings offered in this study have the potential to open new avenues of research toward better treatments and prognostic markers.
Deep learning models for representing out-of-vocabulary words
Jul 28, 2020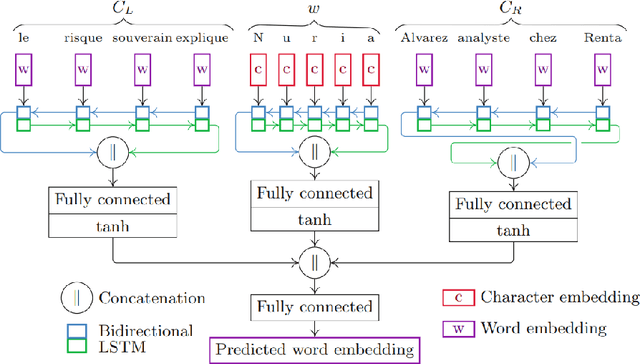
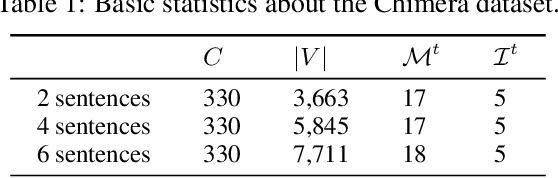
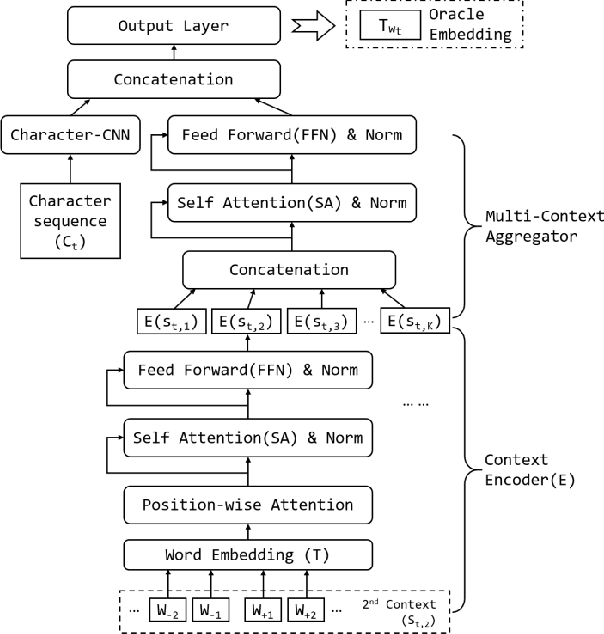
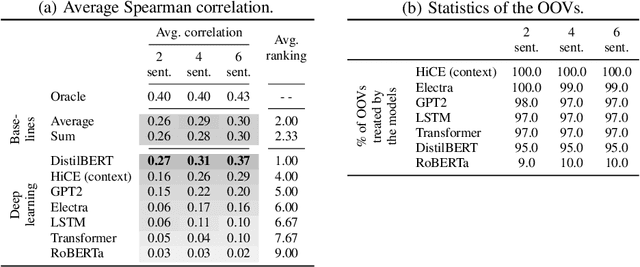
Abstract:Communication has become increasingly dynamic with the popularization of social networks and applications that allow people to express themselves and communicate instantly. In this scenario, distributed representation models have their quality impacted by new words that appear frequently or that are derived from spelling errors. These words that are unknown by the models, known as out-of-vocabulary (OOV) words, need to be properly handled to not degrade the quality of the natural language processing (NLP) applications, which depend on the appropriate vector representation of the texts. To better understand this problem and finding the best techniques to handle OOV words, in this study, we present a comprehensive performance evaluation of deep learning models for representing OOV words. We performed an intrinsic evaluation using a benchmark dataset and an extrinsic evaluation using different NLP tasks: text categorization, named entity recognition, and part-of-speech tagging. Although the results indicated that the best technique for handling OOV words is different for each task, Comick, a deep learning method that infers the embedding based on the context and the morphological structure of the OOV word, obtained promising results.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge