Teresa M. A. Basile
GRASP and path-relinking for Coalition Structure Generation
Mar 09, 2011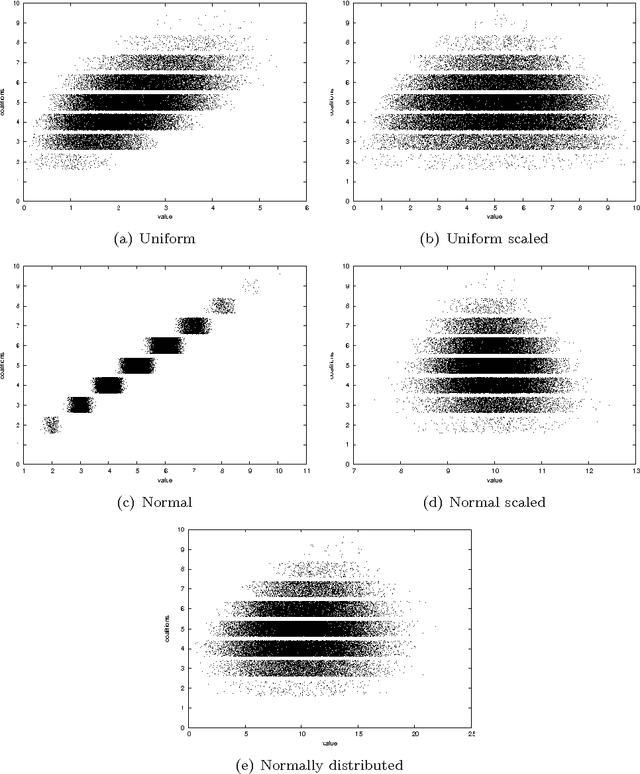
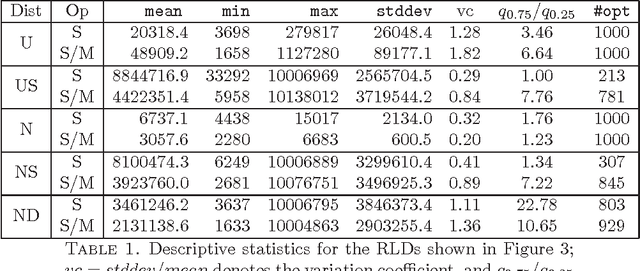
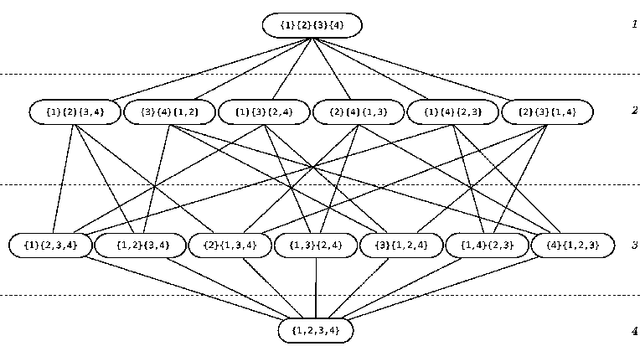

Abstract:In Artificial Intelligence with Coalition Structure Generation (CSG) one refers to those cooperative complex problems that require to find an optimal partition, maximising a social welfare, of a set of entities involved in a system into exhaustive and disjoint coalitions. The solution of the CSG problem finds applications in many fields such as Machine Learning (covering machines, clustering), Data Mining (decision tree, discretization), Graph Theory, Natural Language Processing (aggregation), Semantic Web (service composition), and Bioinformatics. The problem of finding the optimal coalition structure is NP-complete. In this paper we present a greedy adaptive search procedure (GRASP) with path-relinking to efficiently search the space of coalition structures. Experiments and comparisons to other algorithms prove the validity of the proposed method in solving this hard combinatorial problem.
Feature Construction for Relational Sequence Learning
Jun 27, 2010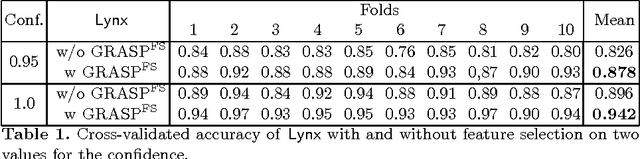
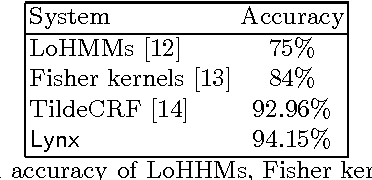
Abstract:We tackle the problem of multi-class relational sequence learning using relevant patterns discovered from a set of labelled sequences. To deal with this problem, firstly each relational sequence is mapped into a feature vector using the result of a feature construction method. Since, the efficacy of sequence learning algorithms strongly depends on the features used to represent the sequences, the second step is to find an optimal subset of the constructed features leading to high classification accuracy. This feature selection task has been solved adopting a wrapper approach that uses a stochastic local search algorithm embedding a naive Bayes classifier. The performance of the proposed method applied to a real-world dataset shows an improvement when compared to other established methods, such as hidden Markov models, Fisher kernels and conditional random fields for relational sequences.
GRASP for the Coalition Structure Formation Problem
Apr 16, 2010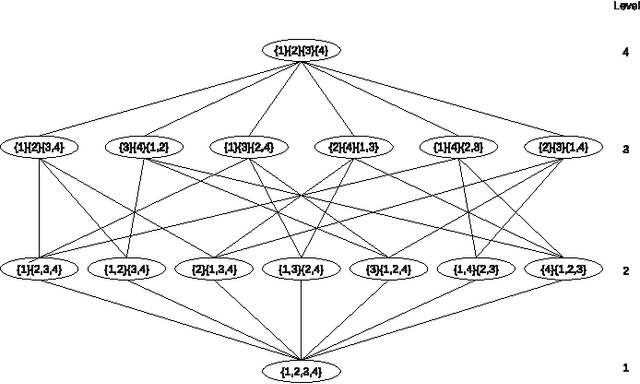
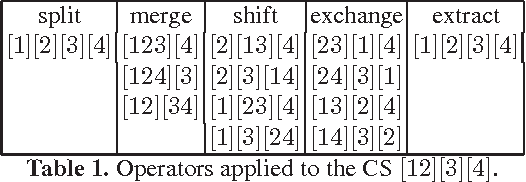
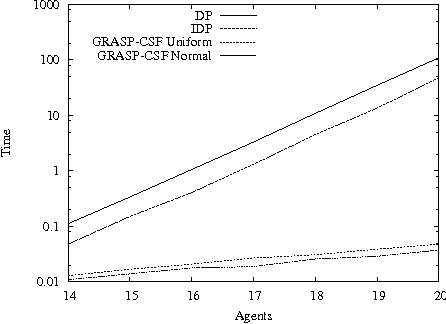
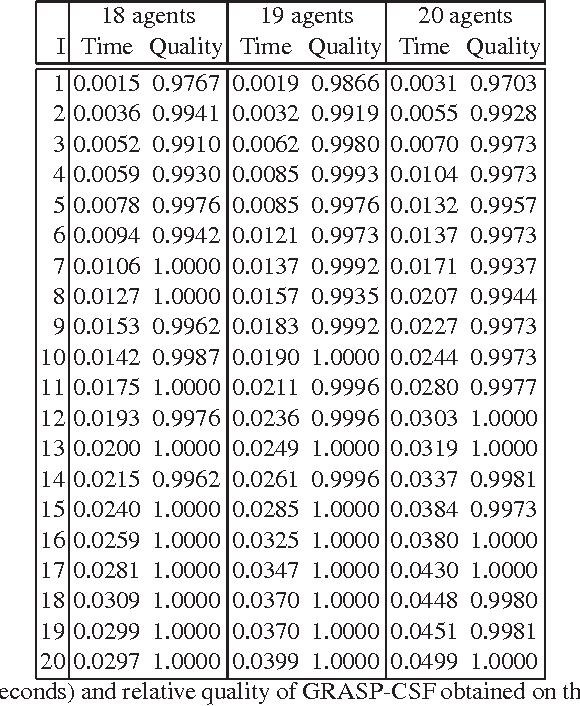
Abstract:The coalition structure formation problem represents an active research area in multi-agent systems. A coalition structure is defined as a partition of the agents involved in a system into disjoint coalitions. The problem of finding the optimal coalition structure is NP-complete. In order to find the optimal solution in a combinatorial optimization problem it is theoretically possible to enumerate the solutions and evaluate each. But this approach is infeasible since the number of solutions often grows exponentially with the size of the problem. In this paper we present a greedy adaptive search procedure (GRASP) to efficiently search the space of coalition structures in order to find an optimal one. Experiments and comparisons to other algorithms prove the validity of the proposed method in solving this hard combinatorial problem.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge