Taylor Hearn
ZipIt! Merging Models from Different Tasks without Training
May 04, 2023Abstract:Typical deep visual recognition models are capable of performing the one task they were trained on. In this paper, we tackle the extremely difficult problem of combining completely distinct models with different initializations, each solving a separate task, into one multi-task model without any additional training. Prior work in model merging permutes one model to the space of the other then adds them together. While this works for models trained on the same task, we find that this fails to account for the differences in models trained on disjoint tasks. Thus, we introduce "ZipIt!", a general method for merging two arbitrary models of the same architecture that incorporates two simple strategies. First, in order to account for features that aren't shared between models, we expand the model merging problem to additionally allow for merging features within each model by defining a general "zip" operation. Second, we add support for partially zipping the models up until a specified layer, naturally creating a multi-head model. We find that these two changes combined account for a staggering 20-60% improvement over prior work, making the merging of models trained on disjoint tasks feasible.
Unified State Representation Learning under Data Augmentation
Sep 12, 2022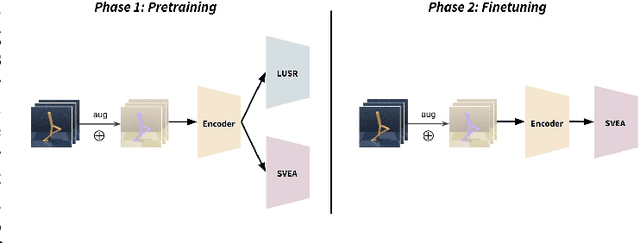

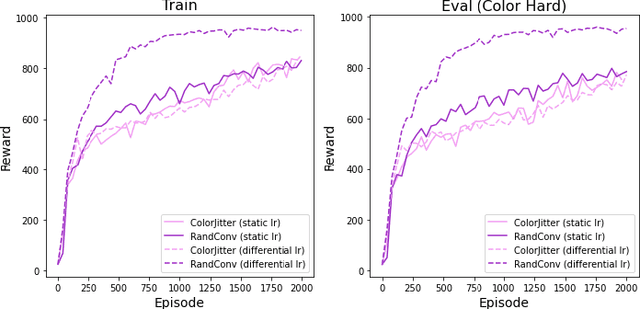

Abstract:The capacity for rapid domain adaptation is important to increasing the applicability of reinforcement learning (RL) to real world problems. Generalization of RL agents is critical to success in the real world, yet zero-shot policy transfer is a challenging problem since even minor visual changes could make the trained agent completely fail in the new task. We propose USRA: Unified State Representation Learning under Data Augmentation, a representation learning framework that learns a latent unified state representation by performing data augmentations on its observations to improve its ability to generalize to unseen target domains. We showcase the success of our approach on the DeepMind Control Generalization Benchmark for the Walker environment and find that USRA achieves higher sample efficiency and 14.3% better domain adaptation performance compared to the best baseline results.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge