Tanveer Ahmed
MCFFA-Net: Multi-Contextual Feature Fusion and Attention Guided Network for Apple Foliar Disease Classification
Nov 25, 2022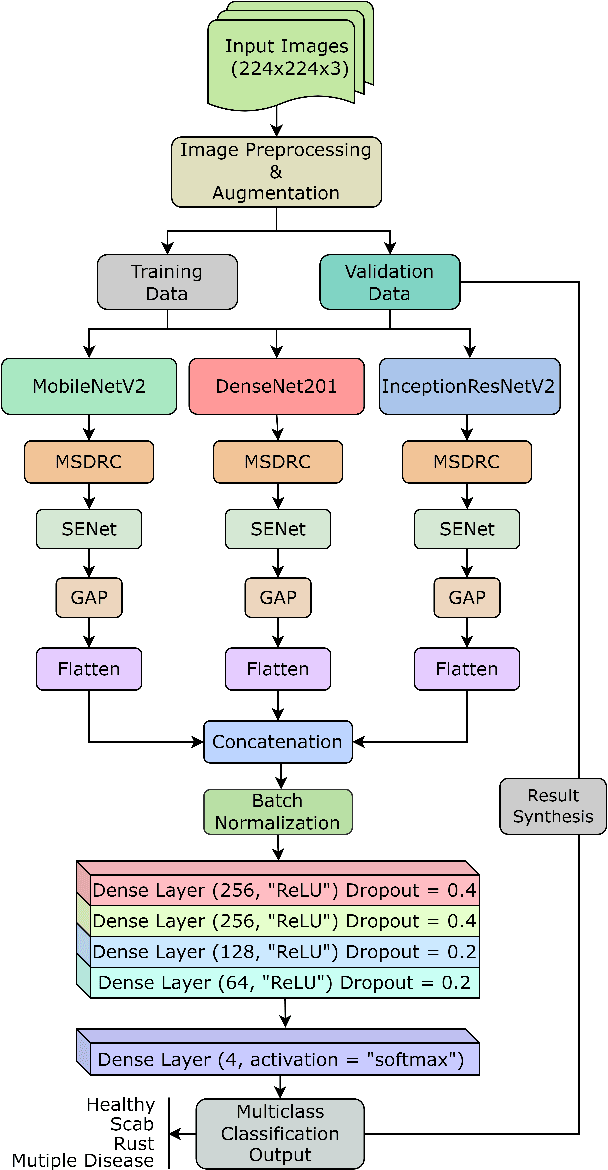
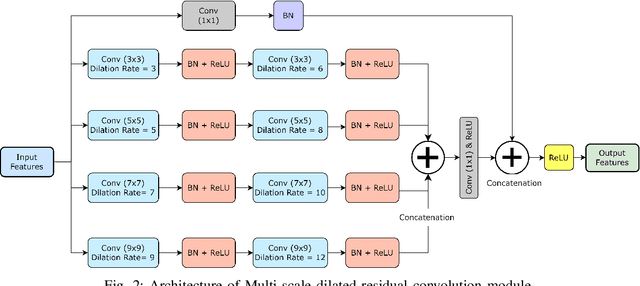
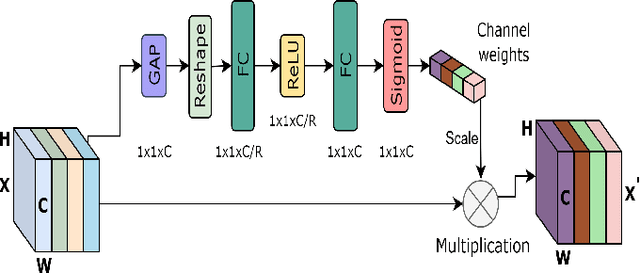
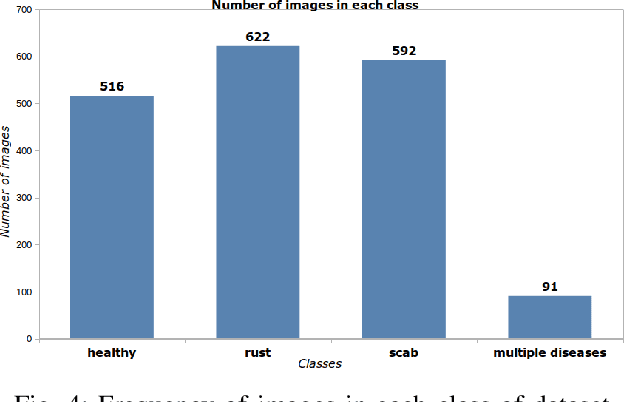
Abstract:Numerous diseases cause severe economic loss in the apple production-based industry. Early disease identification in apple leaves can help to stop the spread of infections and provide better productivity. Therefore, it is crucial to study the identification and classification of different apple foliar diseases. Various traditional machine learning and deep learning methods have addressed and investigated this issue. However, it is still challenging to classify these diseases because of their complex background, variation in the diseased spot in the images, and the presence of several symptoms of multiple diseases on the same leaf. This paper proposes a novel transfer learning-based stacked ensemble architecture named MCFFA-Net, which is composed of three pre-trained architectures named MobileNetV2, DenseNet201, and InceptionResNetV2 as backbone networks. We also propose a novel multi-scale dilated residual convolution module to capture multi-scale contextual information with several dilated receptive fields from the extracted features. Channel-based attention mechanism is provided through squeeze and excitation networks to make the MCFFA-Net focused on the relevant information in the multi-receptive fields. The proposed MCFFA-Net achieves a classification accuracy of 90.86%.
Machine Learning Towards Enabling Spectrum-as-a-Service Dynamic Sharing
Sep 04, 2020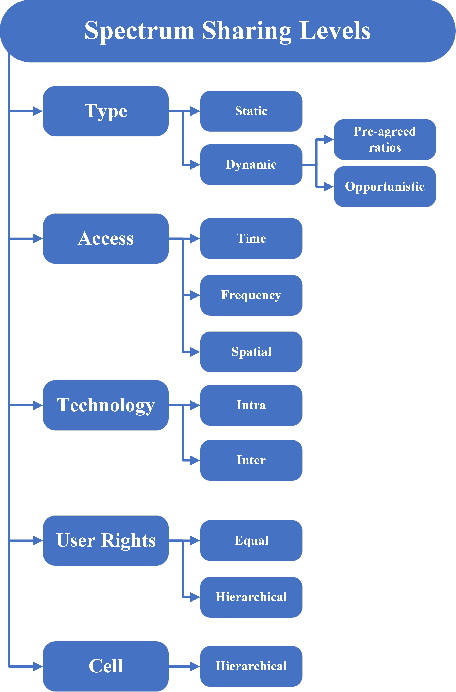
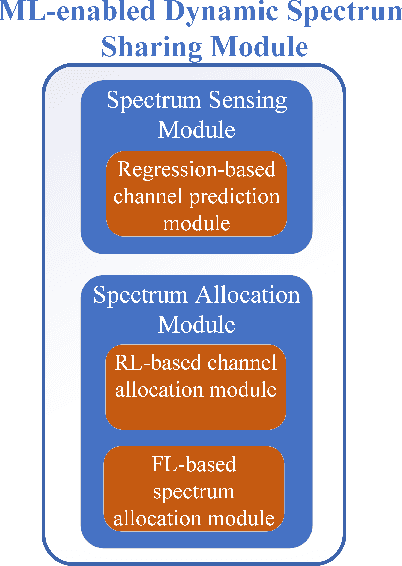
Abstract:The growth in wireless broadband users, devices, and novel applications has led to a significant increase in the demand for new radio frequency spectrum. This is expected to grow even further given the projection that the global traffic per year will reach 4.8 zettabytes by 2022. Moreover, it is projected that the number of Internet users will reach 4.8 billion and the number of connected devices will be close 28.5 billion devices. However, due to the spectrum being mostly allocated and divided, providing more spectrum to expand existing services or offer new ones has become more challenging. To address this, spectrum sharing has been proposed as a potential solution to improve spectrum utilization efficiency. Adopting effective and efficient spectrum sharing mechanisms is in itself a challenging task given the multitude of levels and techniques that can be integrated to enable it. To that end, this paper provides an overview of the different spectrum sharing levels and techniques that have been proposed in the literature. Moreover, it discusses the potential of adopting dynamic sharing mechanisms by offering Spectrum-as-a-Service architecture. Furthermore, it describes the potential role of machine learning models in facilitating the automated and efficient dynamic sharing of the spectrum and offering Spectrum-as-a-Service.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge