Tanuj Kumar
ChatGPT-4 with Code Interpreter can be used to solve introductory college-level vector calculus and electromagnetism problems
Sep 16, 2023Abstract:We evaluated ChatGPT 3.5, 4, and 4 with Code Interpreter on a set of college-level engineering-math and electromagnetism problems, such as those often given to sophomore electrical engineering majors. We selected a set of 13 problems, and had ChatGPT solve them multiple times, using a fresh instance (chat) each time. We found that ChatGPT-4 with Code Interpreter was able to satisfactorily solve most problems we tested most of the time -- a major improvement over the performance of ChatGPT-4 (or 3.5) without Code Interpreter. The performance of ChatGPT was observed to be somewhat stochastic, and we found that solving the same problem N times in new ChatGPT instances and taking the most-common answer was an effective strategy. Based on our findings and observations, we provide some recommendations for instructors and students of classes at this level.
NFDLM: A Lightweight Network Flow based Deep Learning Model for DDoS Attack Detection in IoT Domains
Jul 15, 2022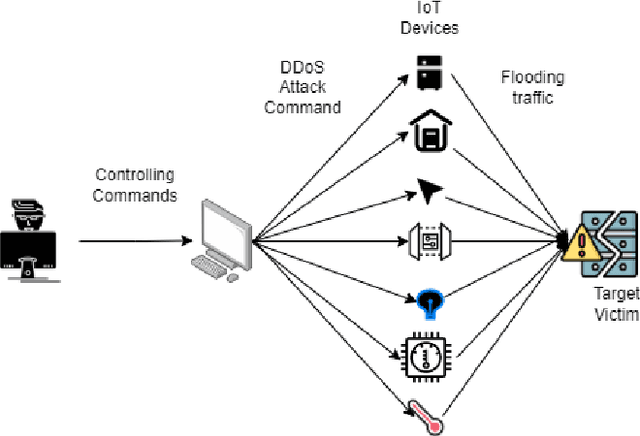
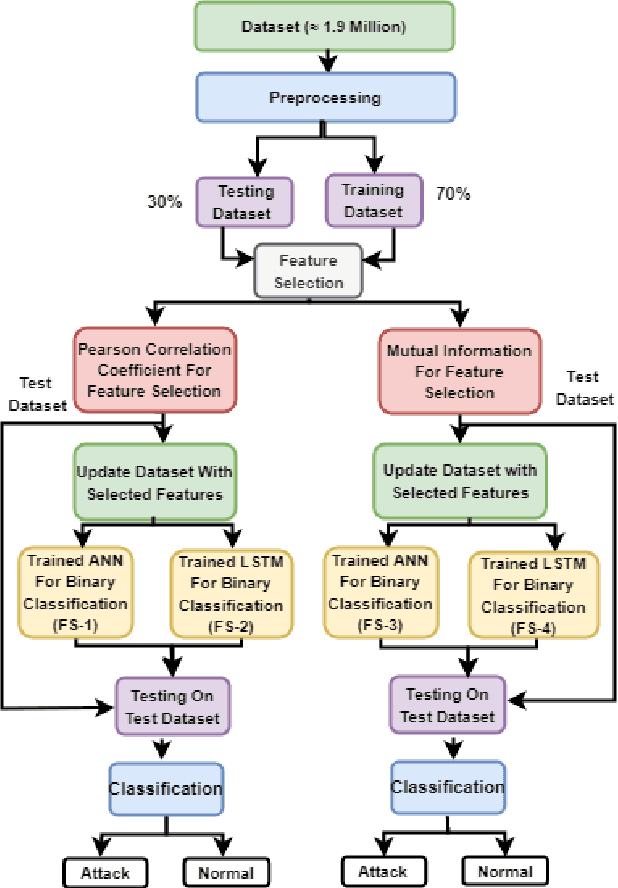
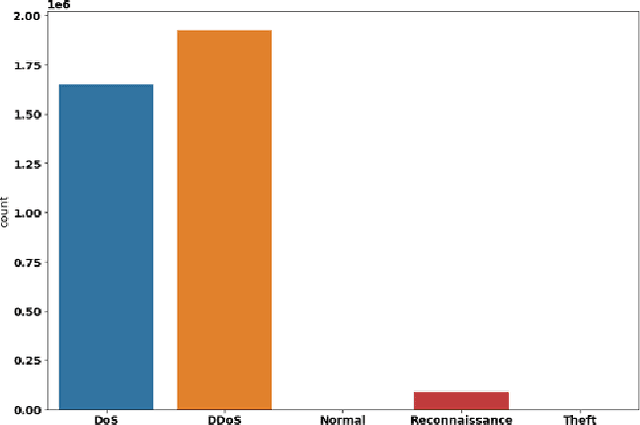
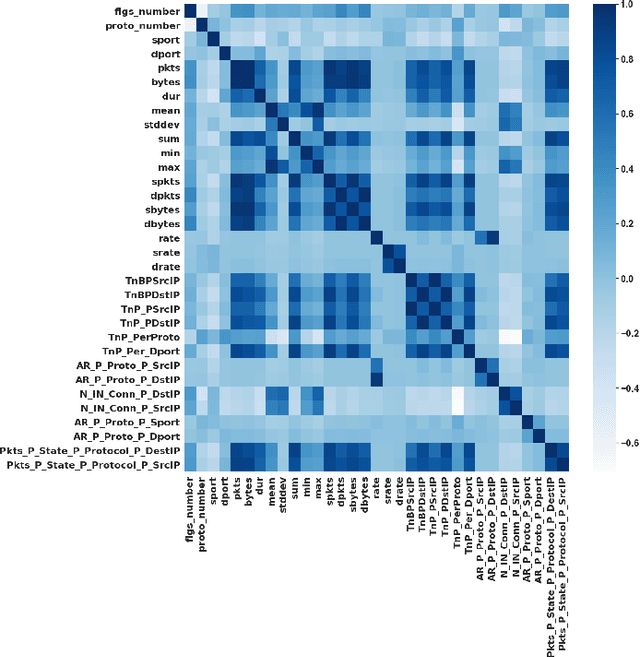
Abstract:In the recent years, Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks on Internet of Things (IoT) devices have become one of the prime concerns to Internet users around the world. One of the sources of the attacks on IoT ecosystems are botnets. Intruders force IoT devices to become unavailable for its legitimate users by sending large number of messages within a short interval. This study proposes NFDLM, a lightweight and optimised Artificial Neural Network (ANN) based Distributed Denial of Services (DDoS) attack detection framework with mutual correlation as feature selection method which produces a superior result when compared with Long Short Term Memory (LSTM) and simple ANN. Overall, the detection performance achieves approximately 99\% accuracy for the detection of attacks from botnets. In this work, we have designed and compared four different models where two are based on ANN and the other two are based on LSTM to detect the attack types of DDoS.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge