Rahamatullah Khondoker
NFDLM: A Lightweight Network Flow based Deep Learning Model for DDoS Attack Detection in IoT Domains
Jul 15, 2022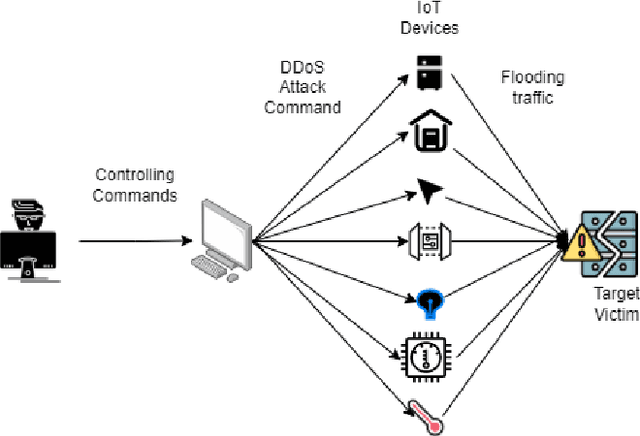
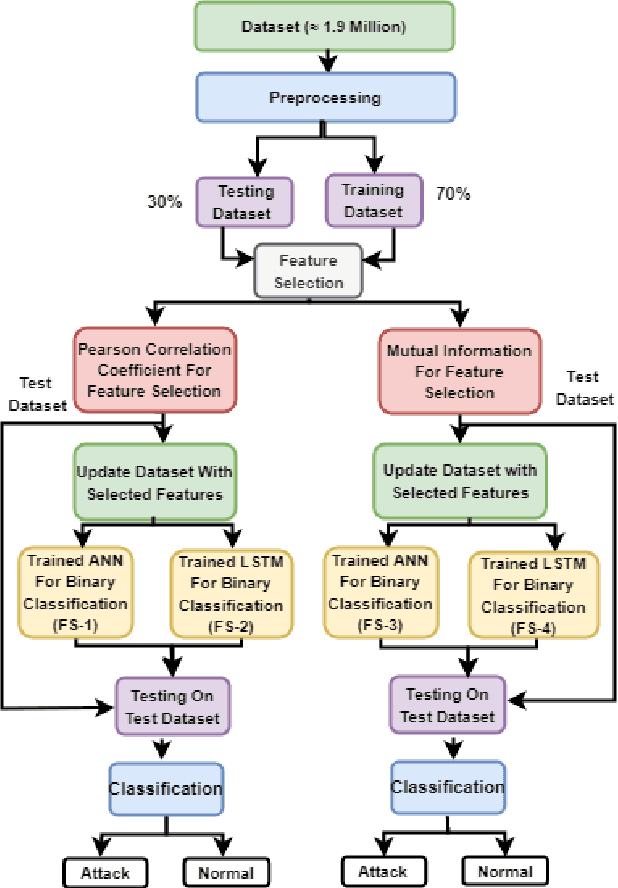
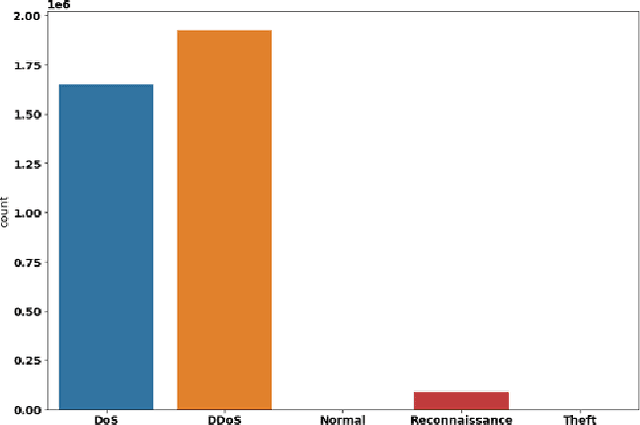
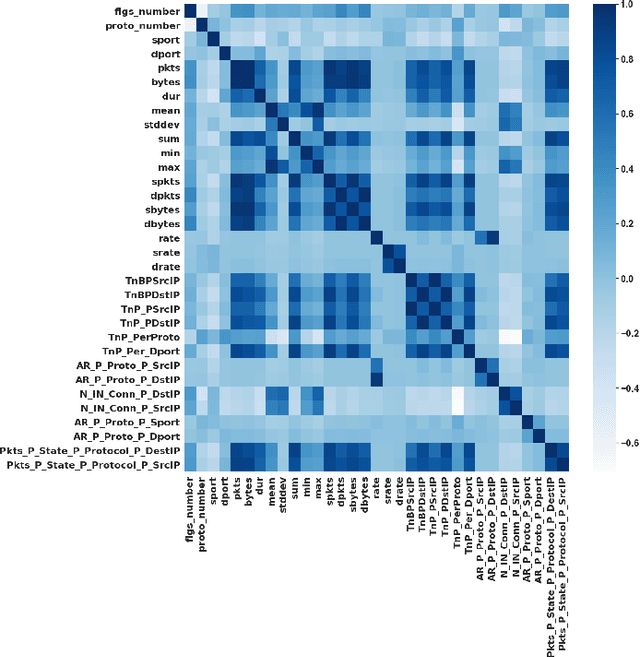
Abstract:In the recent years, Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks on Internet of Things (IoT) devices have become one of the prime concerns to Internet users around the world. One of the sources of the attacks on IoT ecosystems are botnets. Intruders force IoT devices to become unavailable for its legitimate users by sending large number of messages within a short interval. This study proposes NFDLM, a lightweight and optimised Artificial Neural Network (ANN) based Distributed Denial of Services (DDoS) attack detection framework with mutual correlation as feature selection method which produces a superior result when compared with Long Short Term Memory (LSTM) and simple ANN. Overall, the detection performance achieves approximately 99\% accuracy for the detection of attacks from botnets. In this work, we have designed and compared four different models where two are based on ANN and the other two are based on LSTM to detect the attack types of DDoS.
LBDMIDS: LSTM Based Deep Learning Model for Intrusion Detection Systems for IoT Networks
Jun 23, 2022



Abstract:In the recent years, we have witnessed a huge growth in the number of Internet of Things (IoT) and edge devices being used in our everyday activities. This demands the security of these devices from cyber attacks to be improved to protect its users. For years, Machine Learning (ML) techniques have been used to develop Network Intrusion Detection Systems (NIDS) with the aim of increasing their reliability/robustness. Among the earlier ML techniques DT performed well. In the recent years, Deep Learning (DL) techniques have been used in an attempt to build more reliable systems. In this paper, a Deep Learning enabled Long Short Term Memory (LSTM) Autoencoder and a 13-feature Deep Neural Network (DNN) models were developed which performed a lot better in terms of accuracy on UNSW-NB15 and Bot-IoT datsets. Hence we proposed LBDMIDS, where we developed NIDS models based on variants of LSTMs namely, stacked LSTM and bidirectional LSTM and validated their performance on the UNSW\_NB15 and BoT\-IoT datasets. This paper concludes that these variants in LBDMIDS outperform classic ML techniques and perform similarly to the DNN models that have been suggested in the past.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge