Tanja Amerstorfer
Beacon2Science: Enhancing STEREO/HI beacon data1 with machine learning for efficient CME tracking
Mar 19, 2025Abstract:Observing and forecasting coronal mass ejections (CME) in real-time is crucial due to the strong geomagnetic storms they can generate that can have a potentially damaging effect, for example, on satellites and electrical devices. With its near-real-time availability, STEREO/HI beacon data is the perfect candidate for early forecasting of CMEs. However, previous work concluded that CME arrival prediction based on beacon data could not achieve the same accuracy as with high-resolution science data due to data gaps and lower quality. We present our novel pipeline entitled ''Beacon2Science'', bridging the gap between beacon and science data to improve CME tracking. Through this pipeline, we first enhance the quality (signal-to-noise ratio and spatial resolution) of beacon data. We then increase the time resolution of enhanced beacon images through learned interpolation to match science data's 40-minute resolution. We maximize information coherence between consecutive frames with adapted model architecture and loss functions through the different steps. The improved beacon images are comparable to science data, showing better CME visibility than the original beacon data. Furthermore, we compare CMEs tracked in beacon, enhanced beacon, and science images. The tracks extracted from enhanced beacon data are closer to those from science images, with a mean average error of $\sim 0.5 ^\circ$ of elongation compared to $1^\circ$ with original beacon data. The work presented in this paper paves the way for its application to forthcoming missions such as Vigil and PUNCH.
Automatic Detection of Interplanetary Coronal Mass Ejections in Solar Wind In Situ Data
May 07, 2022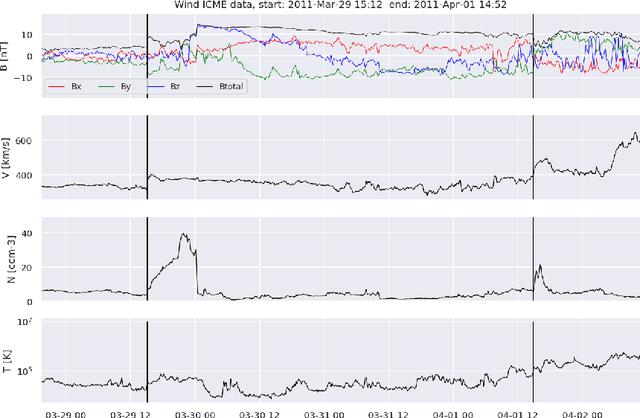
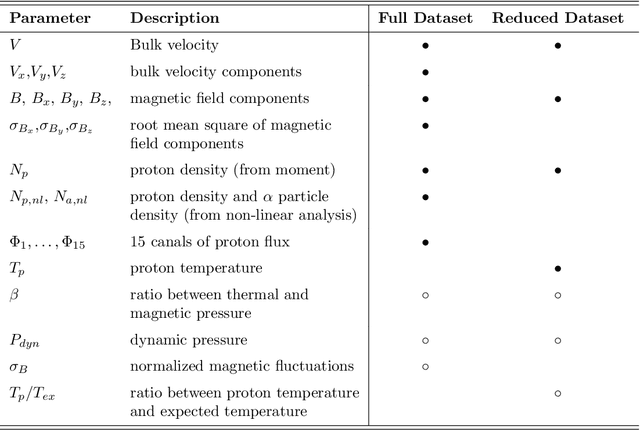

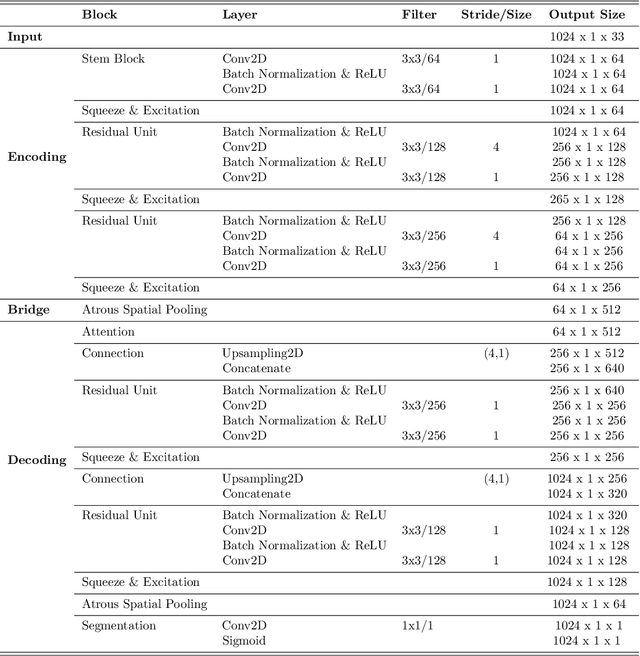
Abstract:Interplanetary coronal mass ejections (ICMEs) are one of the main drivers for space weather disturbances. In the past, different approaches have been used to automatically detect events in existing time series resulting from solar wind in situ observations. However, accurate and fast detection still remains a challenge when facing the large amount of data from different instruments. For the automatic detection of ICMEs we propose a pipeline using a method that has recently proven successful in medical image segmentation. Comparing it to an existing method, we find that while achieving similar results, our model outperforms the baseline regarding training time by a factor of approximately 20, thus making it more applicable for other datasets. The method has been tested on in situ data from the Wind spacecraft between 1997 and 2015 with a True Skill Statistic (TSS) of 0.64. Out of the 640 ICMEs, 466 were detected correctly by our algorithm, producing a total of 254 False Positives. Additionally, it produced reasonable results on datasets with fewer features and smaller training sets from Wind, STEREO-A and STEREO-B with True Skill Statistics of 0.56, 0.57 and 0.53, respectively. Our pipeline manages to find the start of an ICME with a mean absolute error (MAE) of around 2 hours and 56 minutes, and the end time with a MAE of 3 hours and 20 minutes. The relatively fast training allows straightforward tuning of hyperparameters and could therefore easily be used to detect other structures and phenomena in solar wind data, such as corotating interaction regions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge